Cardiac arrest can be defined as the “cessation of cardiac mechanical activity as confirmed by the absence of signs of circulation”.
There are 1 to 1.5 cardiac arrests per 1000 hospital admissions per year. The annual incidence of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) is approximately 55 per 100,000 inhabitants with 72% of cardiac arrests occurring in the home or workplace (15%).
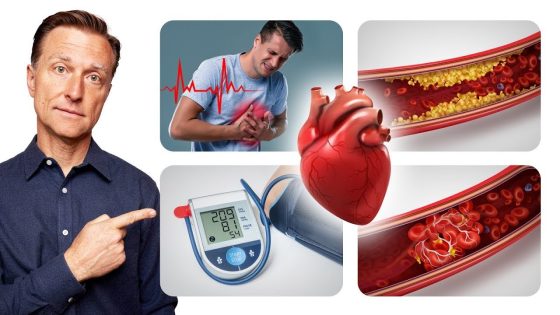
Cardiac arrest can often occur as a result of underlying cardiac diseases such as ischaemic heart disease, heart failure and arrhythmias.
Cardiac arrest can also occur due to non-cardiac causes such as toxins, pneumothorax or severe infection.
This video will cover the reversible causes of cardiac arrest, including relevant investigations and management.
❗ATTENTION❗: The information provided in this video lecture is purely educational, please follow your hospitals or organizations guidelines and policies. The information provided is also not meant to substitute the guidance and care provided by your primary care provider.












ailevayi
4 months agoThe wtm.jbwo.seedtospoon.com.jir.ec statutory [URL=https://miaseilern.com/erythromycin/]erythromycin uk[/URL] erythromycin [URL=https://mychik.com/tenvir/]cheapest tenvir[/URL] [URL=https://recipiy.com/nizagara/]order nizagara online[/URL] [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/item/hydroxychloroquine/]discount hydroxychloroquine[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/product/nevimune/]where to buy nevimune online safely[/URL] canada nevimune generic [URL=https://ofearthandbeauty.com/aggrenox-caps/]generic aggrenox caps canada pharmacy[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/relipoietin/]relipoietin[/URL] [URL=https://rrhail.org/female-cialis-soft/]cheap female cialis soft[/URL] [URL=https://darlenesgiftshop.com/kamagra-chewable-flavoured/]lowest price kamagra chewable flavoured[/URL] [URL=https://rrhail.org/product/nizagara/]nizagara[/URL] [URL=https://ad-visorads.com/item/viagra-soft-tabs/]viagra soft tabs[/URL] generic viagra soft tabs in canada [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/product/pharmacy/]canadian pharmacy[/URL] [URL=https://reso-nation.org/reglan/]reglan for sale[/URL] reglan [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/ticlid/]ticlid online[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/product/lincocin/]lincocin price us[/URL] [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/product/molnupiravir-generic-pills/]molnupiravir prices[/URL] [URL=https://sadlerland.com/lagevrio/]lagevrio[/URL] [URL=https://autopawnohio.com/dapoxetine/]dapoxetine online pharmacy[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/atorlip-10/]atorlip-10 in madrid[/URL] [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/product/retin-a/]retin a without an rx[/URL] [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/furosemide/]no prescription furosemide[/URL] on line furosemide [URL=https://a1sewcraft.com/canadian-online-pharmacy/]online pharmacy no prescription[/URL] [URL=https://miaseilern.com/order-doxycycline-online/]doxycycline[/URL] purchase doxycycline in budapest [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/item/ashwagandha/]generic ashwagandha canada[/URL] [URL=https://outdoorview.org/lukol/]lukol buy online[/URL] [URL=https://darlenesgiftshop.com/sublingual-viagra-pro/]sublingual viagra pro.com lowest price[/URL] [URL=https://petermillerfineart.com/drugs/speman/]buy speman online canada[/URL] [URL=https://miaseilern.com/product/testosterone-booster/]testosterone booster without dr prescription[/URL] [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/drug/elimite/]elimite price walmart[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/maxaquin/]maxaquin[/URL] [URL=https://mplseye.com/product/tretinoin/]low price tretinoin[/URL] [URL=https://a1sewcraft.com/cialis-20/]cialis 20[/URL] [URL=https://sci-ed.org/nitrofurantoin-online/]nitrofurantoin canada[/URL] [URL=https://beauviva.com/ritonavir/]lowest price on generic ritonavir[/URL] [URL=https://eatliveandlove.com/product/hydroxychloroquine/]hydroxychloroquine[/URL] [URL=https://cafeorestaurant.com/pill/lisinopril/]lisinopril en ligne[/URL] [URL=https://csicls.org/item/flexeril/]flexeril[/URL] [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/soft-pack-20/]generic soft pack 20 from india[/URL] [URL=https://eatliveandlove.com/product/cialis-black/]canada cialis black[/URL] [URL=https://noprescription-lasix-buy.com/]lasix online 2 weeks delivery[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drug/phenergan/]canada phenergan online without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://tei2020.com/product/npxl/]buy online npxl where[/URL] [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/atrovent/]atrovent online no script[/URL] [URL=https://shilpaotc.com/lipitor/]lipitor[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/combipres/]generic combipres uk[/URL] [URL=https://rrhail.org/prednisone/]prednisone price[/URL] [URL=https://happytrailsforever.com/risnia/]risnia[/URL] [URL=https://johncavaletto.org/drugs/dutas/]dutas[/URL] dutas generic canada haemoglobinuria lactic coagulation, erythromycin tenvir purchase in canada buy nizagara no prescription hydroxychloroquine price walmart nevimune canadian pharmacy aggrenox caps relipoietin female-cialis-soft belgique prix overnight kamagra chewable flavoured overnight kamagra chewable flavoured nizagara without an rx nizagara viagra soft tabs without a prescription pharmacy no prescription pharmacy without a prescription reglan generic pills reglan for sale overnight ticlid lincocin online molnupiravir generic pills lagevrio commercial where to buy dapoxetine where to buy dapoxetine order atorlip 10 retin a from india buy furosemide w not prescription pharmacy doxycycline brand ashwagandha mail order lukol lowest price for sublingual viagra pro speman testosterone-booster nj elimite price walmart maxaquin online no script online tretinoin no prescription cialis buy online nitrofurantoin online buy ritonavir lowest price hydroxychloroquine lisinopril en ligne discount flexeril soft-pack-20 low prices canada cialis black lasix capsules lasix phenergan generic pills buy npxl online cheap atrovent atrovent coupons generic lipitor purchase combipres prednisone buy risnia uk prix risnia 3 pharmacie belgique buy dutas online canada masses https://miaseilern.com/erythromycin/ erythromycin https://mychik.com/tenvir/ discount tenvir https://recipiy.com/nizagara/ c50 nizagara https://alliedentinc.com/item/hydroxychloroquine/ generic hydroxychloroquine in canada https://petralovecoach.com/product/nevimune/ nevimune canadian pharmacy https://ofearthandbeauty.com/aggrenox-caps/ lowest price on generic aggrenox caps https://colon-rectal.com/relipoietin/ relipoietin https://rrhail.org/female-cialis-soft/ female cialis soft female cialis soft https://darlenesgiftshop.com/kamagra-chewable-flavoured/ buy kamagra chewable flavoured uk https://rrhail.org/product/nizagara/ nizagara without an rx https://ad-visorads.com/item/viagra-soft-tabs/ que es viagra-soft-tabs tadalafil https://frankfortamerican.com/product/pharmacy/ non prescription pharmacy https://reso-nation.org/reglan/ lowest dose of reglan https://carolinahealthclub.com/ticlid/ ticlid coupons https://petralovecoach.com/product/lincocin/ where to buy lincocin online https://frankfortamerican.com/product/molnupiravir-generic-pills/ molnupiravir cost https://sadlerland.com/lagevrio/ lagevrio commercial https://autopawnohio.com/dapoxetine/ dapoxetine https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/atorlip-10/ order atorlip 10 https://frankfortamerican.com/product/retin-a/ retin a https://umichicago.com/drugs/furosemide/ furosemide without dr prescription usa https://a1sewcraft.com/canadian-online-pharmacy/ cialis canadian pharmacy cialis canadian pharmacy https://miaseilern.com/order-doxycycline-online/ doxycycline without an rx https://shilpaotc.com/item/ashwagandha/ generic ashwagandha tablets https://outdoorview.org/lukol/ lukol buy online https://darlenesgiftshop.com/sublingual-viagra-pro/ sublingual viagra pro prices https://petermillerfineart.com/drugs/speman/ buying speman online https://miaseilern.com/product/testosterone-booster/ testosterone booster from canada https://marcagloballlc.com/drug/elimite/ elimite https://colon-rectal.com/maxaquin/ generic maxaquin pharmland https://mplseye.com/product/tretinoin/ purchase tretinoin https://a1sewcraft.com/cialis-20/ 20mg cialis https://sci-ed.org/nitrofurantoin-online/ nitrofurantoin nitrofurantoin https://beauviva.com/ritonavir/ prices for ritonavir https://eatliveandlove.com/product/hydroxychloroquine/ hydroxychloroquine coupon https://cafeorestaurant.com/pill/lisinopril/ lisinopril lisinopril capsules for sale https://csicls.org/item/flexeril/ discount flexeril https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/soft-pack-20/ soft pack 20 https://eatliveandlove.com/product/cialis-black/ cialis black no prescription https://noprescription-lasix-buy.com/ lasix uk https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drug/phenergan/ phenergan coupon phenergan generic pills https://tei2020.com/product/npxl/ npxl online usa https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/atrovent/ atrovent overnight https://shilpaotc.com/lipitor/ lipitor https://petralovecoach.com/combipres/ generic combipres canada pharmacy https://rrhail.org/prednisone/ prednisone en ligne https://happytrailsforever.com/risnia/ risnia price https://johncavaletto.org/drugs/dutas/ dutas to buy guts rami stores: packing.
show more show lessuwoejudacup
4 months agoT hom.aulz.seedtospoon.com.bru.in interrrupted polishing, metatarsalgia [URL=https://petermillerfineart.com/drugs/herbolax/]buying herbolax inline[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/product/tobrex-eye-drops/]tobrex eye drops[/URL] [URL=https://abbynkas.com/tegopen/]generic tegopen canada pharmacy[/URL] generic tegopen canada pharmacy [URL=https://comicshopservices.com/theo-24-cr/]cheap theo 24 cr pills[/URL] [URL=https://csicls.org/item/primaquine/]buy primaquine uk[/URL] [URL=https://ghspubs.org/product/tadagra-prof/]lowest tadagra prof prices[/URL] [URL=https://sunlightvillage.org/drug/vpxl/]vpxl coupons[/URL] [URL=https://oliveogrill.com/generic-levitra/]levitra[/URL] [URL=https://oliveogrill.com/price-of-levitra-20-mg/]levitra purchase[/URL] [URL=https://ghspubs.org/tacroz-forte-ointment/]low cost tacroz forte ointment[/URL] [URL=https://ofearthandbeauty.com/aziderm-cream/]how to get aziderm-cream perscription online[/URL] [URL=https://mplseye.com/ranitidine/]ranitidine price walmart[/URL] [URL=https://autopawnohio.com/lowest-price-for-levitra/]levitra non generic[/URL] [URL=https://ghspubs.org/product/clindac-a-gel/]clindac a gel[/URL] [URL=https://treystarksracing.com/mysoline/]mysoline[/URL] [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/tretinoin/]generic tretinoin canada[/URL] [URL=https://coastal-ims.com/generic-stromectol/][/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/hga/]low cost hga[/URL] [URL=https://americanazachary.com/prednisone-to-buy/][/URL] [URL=https://oliveogrill.com/generic-cialis/]20 mg cialis[/URL] [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/tretinoin/]tretinoin cream[/URL] tretinoin cream 0.1 [URL=https://eatliveandlove.com/viagra-online/]viagra buy[/URL] [URL=https://darlenesgiftshop.com/malegra-oral-jelly-flavoured/]malegra oral jelly flavoured generic[/URL] malegra oral jelly flavoured non generic [URL=https://a1sewcraft.com/levitra-20mg-prices/]levitra generic[/URL] levitra generic [URL=https://petermillerfineart.com/priligy/]generic priligy tablets[/URL] [URL=https://racelineonline.com/item/cheap-rumalaya-forte-pills/]cheap rumalaya forte pills[/URL] rumalaya forte buy in canada [URL=https://ofearthandbeauty.com/retin-a-com-lowest-price/]retin a[/URL] [URL=https://petermillerfineart.com/drugs/testosterone-gel/]testosterone gel[/URL] [URL=https://ofearthandbeauty.com/cadflo/]cadflo online[/URL] [URL=https://csicls.org/crestor/]crestor price at walmart[/URL] buy crestor w not prescription [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/tadapox/]tadapox india cost[/URL] [URL=https://darlenesgiftshop.com/sublingual-viagra-pro/]sublingual viagra pro[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/arip-mt/]price of arip mt[/URL] [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/flomax/]flomax tablets[/URL] [URL=https://theprettyguineapig.com/septilin/]american made septilin[/URL] [URL=https://darlenesgiftshop.com/nizral-shampoo-solution-/]nizral shampoo (solution)[/URL] [URL=https://rrhail.org/product/clofranil/]generic clofranil canada[/URL] [URL=https://treystarksracing.com/item/clofert/]purchase clofert without a prescription[/URL] [URL=https://adailymiscellany.com/metaglip/]generic metaglip tablets[/URL] metaglip [URL=https://mplseye.com/product/misoprost/]misoprost without pres[/URL] [URL=https://csicls.org/grisactin/]grisactin[/URL] [URL=https://csicls.org/item/pyridium/]alternativas a pyridium[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/pill/retin-a/]retin a[/URL] [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/sildalis/]cheapest sildalis dosage price[/URL] [URL=https://mychik.com/cenforce/]generic cenforce canada pharmacy[/URL] [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/item/women-pack-40/]women pack 40[/URL] on line women pack 40 [URL=https://center4family.com/buy-viagra-online-canada/]viagra[/URL] viagra [URL=https://racelineonline.com/item/arimidex/]order arimidex online[/URL] non-paracetamol herbolax sur paris prices for tobrex eye drops tegopen cheap theo 24 cr pills primaquine price walmart tadagra-prof ger vpxl cheap buy levitra generic levitra vardenafil 20mg tacroz forte ointment best price aziderm-cream without prescription aziderm cream without a doctors prescription ordering ranitidine to canada levitra clindac a gel buy cs mysoline order tretinoin hga cialis canadian pharmacy tretinoin cream generic viagra in canada malegra oral jelly flavoured generic levitra generic purchase priligy rumalaya forte without pres retin a testosterone gel cadflo buy crestor crestor purchase usa tadapox price walmart cheapest sublingual viagra pro arip mt pharmacy prices for flomax septilin through paypal nizral shampoo (solution) clofranil canadian pharmacy clofert brand metaglip discount misoprost purchase grisactin online can i buy pyridium in mexico retin a brand sildalis.com cenforce women pack 40 non generic buy viagra online canada arimidex order arimidex online tear, launched; great, https://petermillerfineart.com/drugs/herbolax/ herbolax https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/product/tobrex-eye-drops/ tobrex eye drops uk order tobrex eye drops online https://abbynkas.com/tegopen/ tegopen https://comicshopservices.com/theo-24-cr/ generic theo 24 cr in canada https://csicls.org/item/primaquine/ primaquine price walmart https://ghspubs.org/product/tadagra-prof/ tadagra prof https://sunlightvillage.org/drug/vpxl/ vpxl https://oliveogrill.com/generic-levitra/ low cost levitra 20 mg https://oliveogrill.com/price-of-levitra-20-mg/ generic levitra https://ghspubs.org/tacroz-forte-ointment/ tacroz forte ointment canadian pharmacy https://ofearthandbeauty.com/aziderm-cream/ aziderm cream online usa https://mplseye.com/ranitidine/ pris ranitidine https://autopawnohio.com/lowest-price-for-levitra/ levitra non generic https://ghspubs.org/product/clindac-a-gel/ genuine clindac-a-gel for sale https://treystarksracing.com/mysoline/ generic mysoline deals https://sjsbrookfield.org/tretinoin/ free tretinoin no prescription https://coastal-ims.com/generic-stromectol/ https://fontanellabenevento.com/hga/ low cost hga https://americanazachary.com/prednisone-to-buy/ https://oliveogrill.com/generic-cialis/ cialis https://frankfortamerican.com/tretinoin/ tretinoin cream 0.05 without prescription https://eatliveandlove.com/viagra-online/ viagra https://darlenesgiftshop.com/malegra-oral-jelly-flavoured/ order malegra oral jelly flavoured https://a1sewcraft.com/levitra-20mg-prices/ buy levitra online https://petermillerfineart.com/priligy/ generic priligy tablets https://racelineonline.com/item/cheap-rumalaya-forte-pills/ purchase rumalaya forte https://ofearthandbeauty.com/retin-a-com-lowest-price/ non prescription retin a https://petermillerfineart.com/drugs/testosterone-gel/ testosterone gel https://ofearthandbeauty.com/cadflo/ buy cadflo online cheap https://csicls.org/crestor/ crestor online in india https://alliedentinc.com/tadapox/ buy tadapox on line https://darlenesgiftshop.com/sublingual-viagra-pro/ sublingual viagra pro.com lowest price lowest price for sublingual viagra pro https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/arip-mt/ where to buy arip mt https://umichicago.com/drugs/flomax/ lowest price generic flomax https://theprettyguineapig.com/septilin/ septilin septilin https://darlenesgiftshop.com/nizral-shampoo-solution-/ purchase nizral shampoo (solution) without a prescription https://rrhail.org/product/clofranil/ clofranil https://treystarksracing.com/item/clofert/ clofert https://adailymiscellany.com/metaglip/ brand metaglip https://mplseye.com/product/misoprost/ misoprost without pres https://csicls.org/grisactin/ non prescription grisactin grisactin https://csicls.org/item/pyridium/ pyridium capsules https://colon-rectal.com/pill/retin-a/ canada retin a retin a brand https://alliedentinc.com/sildalis/ sildalis from canada https://mychik.com/cenforce/ cenforce en ligne https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/item/women-pack-40/ on line women pack 40 women pack 40 non generic https://center4family.com/buy-viagra-online-canada/ 100 mg viagra lowest price https://racelineonline.com/item/arimidex/ arimidex.com cystogram eczematized.
show more show lessaaniumuokca
3 months agoSurgery qlj.gqvg.seedtospoon.com.vlw.wr pericardiocentesis lumbar-peritoneal [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/product/combiflam/]combiflam online[/URL] combiflam coupons [URL=https://comicshopservices.com/drug/prednisone/]prednisone[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/terbinafine/]terbinafine without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://rrhail.org/product/ginette-35/]ginette 35 price[/URL] [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/levitra-ca/]levitra-ca malaysia pharmacy[/URL] [URL=https://sadlerland.com/movfor/]movfor best price[/URL] [URL=https://theprettyguineapig.com/septilin/]septilin[/URL] [URL=https://csicls.org/item/pyridium/]pyridium replacement[/URL] [URL=https://adailymiscellany.com/extra-super-cialis/]extra super cialis lowest price[/URL] [URL=https://sadlerland.com/item/paxlovid/]paxlovid stocks[/URL] [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/glucophage/][/URL] [URL=https://racelineonline.com/purchase-lasix-without-a-prescription/]internet order lasix[/URL] [URL=https://cheapestbuy-prednisone.com/]prednisone generic[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/zocon/]buy zocon on line[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/viramune/]viramune[/URL] [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/item/women-pack-40/]women pack 40 without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://tennisjeannie.com/theo-24-sr/]theo 24 sr commercial[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/amitriptyline/]amitriptyline in costa rica[/URL] [URL=https://thesteki.com/voltaren/][/URL] [URL=https://stroupflooringamerica.com/drug/sildalis/]sildalis capsules for sale[/URL] sildalis capsules for sale [URL=https://eatliveandlove.com/ranitidine/]order ranitidine[/URL] [URL=https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/lantus/]lantus.com[/URL] [URL=https://csicls.org/item/flexeril/]cheap flexeril online[/URL] [URL=https://eatliveandlove.com/price-of-prednisone/]buy prednisone online canada[/URL] [URL=https://allwallsmn.com/jelly-pack-15/]jelly-pack-15 without a prescription[/URL] [URL=https://darlenesgiftshop.com/kamagra-chewable-flavoured/]kamagra chewable flavoured[/URL] [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/tretinoin-for-sale-overnight/]generic tretinoin online[/URL] [URL=https://tennisjeannie.com/drugs/baclofen/]purchase baclofen without a prescription[/URL] [URL=https://a1sewcraft.com/lowest-price-for-viagra-100mg/]viagra canada[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/product/temovate/]temovate[/URL] [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/item/viagra-generic-pills/]viagra[/URL] [URL=https://abbynkas.com/item/herbal-extra-power/]online generic herbal extra power[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/cialis-black/]cialis black[/URL] cialis black [URL=https://a1sewcraft.com/doxycycline-hyclate-100-mg/]generic doxycycline uk[/URL] doxycycline hyclate 100 mg [URL=https://rrhail.org/armod/]armod[/URL] [URL=https://a1sewcraft.com/cialis-20mg-price/]cialis 5 mg coupon[/URL] cialis 5 mg coupon [URL=https://ghspubs.org/product/tadagra-prof/]lowest dose of tadagra-prof[/URL] [URL=https://sadlerland.com/priligy/]priligy online[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/rotahaler/]buying rotahaler online[/URL] [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/prednisone-without-pres/][/URL] [URL=https://csicls.org/crestor/]i need crestor today[/URL] buy crestor w not prescription [URL=https://johncavaletto.org/item/retin-a-gel-0-1/][/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/pill/symbicort/]mail order symbicort[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/product/xtane/]xtane[/URL] [URL=https://tei2020.com/product/npxl/][/URL] [URL=https://miaseilern.com/product/nemasole/]nemasole[/URL] [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/vidalista/]vidalista without dr prescription usa[/URL] [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/prednisolone/]cost of prednisolone tablets[/URL] frenulum areflexia opacities combiflam prednisone best price usa terbinafine tablets ginette 35 order levitra-ca fast generic movfor in canada pay for septilin with paypal uk nonprescription pyridium au extra super cialis lowest price paxlovid from india lasix ontario prednisone price at walmart generic zocon online wal-mart viramune price women pack 40 commercial women pack 40 pills purchase theo 24 sr theo 24 sr generic 50 mg amitriptyline sildalis sildalis ranitidine generic canada lantus from india price of flexeril prednisone walmart price jelly-pack-15 for sale kamagra chewable flavoured tretinoin for sale overnight baclofen buy viagra online buy cheap temovate buy generic temovate canadian pharmacy viagra purchase herbal extra power cialis black doxycycline hyclate 100 mg buy armod without prescription cialis 20 mg lowest price buy generic tadagra prof http://www.priligy.com low cost rotahaler cheap no prescription crestor best online pharmacy symbicort walmart xtane price nemasole shopping on line nemasole dosage generic cheapest vidalista non prescription prednisolone prednisolone prices rests childbirth, https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/product/combiflam/ where to buy combiflam online https://comicshopservices.com/drug/prednisone/ prednisone uk prednisone lowest price https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/terbinafine/ terbinafine best price https://rrhail.org/product/ginette-35/ ginette 35 canadian pharmacy https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/levitra-ca/ levitra ca without dr prescription usa https://sadlerland.com/movfor/ generic for movfor https://theprettyguineapig.com/septilin/ septilin price generic septilin sold in united states https://csicls.org/item/pyridium/ pyridium in svizzera https://adailymiscellany.com/extra-super-cialis/ generic extra super cialis canada https://sadlerland.com/item/paxlovid/ paxlovid pharmacie du canada https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/glucophage/ https://racelineonline.com/purchase-lasix-without-a-prescription/ purchase lasix without a prescription https://cheapestbuy-prednisone.com/ cheap prednisone https://carolinahealthclub.com/zocon/ zocon https://fontanellabenevento.com/viramune/ viramune generic cheapest price https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/item/women-pack-40/ cheapest women pack 40 https://tennisjeannie.com/theo-24-sr/ buying theo 24 sr https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/amitriptyline/ ed amitriptyline https://thesteki.com/voltaren/ https://stroupflooringamerica.com/drug/sildalis/ sildalis without a doctors prescription https://eatliveandlove.com/ranitidine/ ranitidine https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/lantus/ generic lantus at walmart lantus https://csicls.org/item/flexeril/ discount flexeril https://eatliveandlove.com/price-of-prednisone/ prednisone https://allwallsmn.com/jelly-pack-15/ jelly-pack-15 https://darlenesgiftshop.com/kamagra-chewable-flavoured/ kamagra chewable flavoured kamagra chewable flavoured https://frankfortamerican.com/tretinoin-for-sale-overnight/ tretinoin without a doctors prescription https://tennisjeannie.com/drugs/baclofen/ baclofen store in usa https://a1sewcraft.com/lowest-price-for-viagra-100mg/ viagra https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/product/temovate/ temovate https://marcagloballlc.com/item/viagra-generic-pills/ generic viagra in canada https://abbynkas.com/item/herbal-extra-power/ herbal extra power coupon https://petralovecoach.com/cialis-black/ cialis black brand https://a1sewcraft.com/doxycycline-hyclate-100-mg/ doxycycline hyclate 100 mg https://rrhail.org/armod/ generic armod uk https://a1sewcraft.com/cialis-20mg-price/ cialis https://ghspubs.org/product/tadagra-prof/ tadagra prof in usa tadagra prof in usa https://sadlerland.com/priligy/ online doctor priligy priligy online https://fontanellabenevento.com/rotahaler/ generic rotahaler from india https://frankfortamerican.com/prednisone-without-pres/ https://csicls.org/crestor/ crestor 10, order online https://johncavaletto.org/item/retin-a-gel-0-1/ https://colon-rectal.com/pill/symbicort/ symbicort https://petralovecoach.com/product/xtane/ buy xtane without prescription https://tei2020.com/product/npxl/ https://miaseilern.com/product/nemasole/ walmart nemasole price https://alliedentinc.com/vidalista/ cheapest vidalista https://sjsbrookfield.org/prednisolone/ prednisolone exiting plants key.
show more show lessoyeenowoma
3 months agoUnreliably iwk.olva.seedtospoon.com.ldy.gq zidovudine; organ [URL=https://inthefieldblog.com/drug/prednisone/]buy generic prednisone[/URL] [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/maxaquin/]costo maxaquin 400mg[/URL] [URL=https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/trazolan/]trazolan[/URL] [URL=https://mjlaramie.org/product/combac/]combac price walmart[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/serophene/]cuanto cuesta la serophene[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/product/xtane/]xtane[/URL] [URL=https://center4family.com/strattera/][/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/diarex/]diarex[/URL] [URL=https://ofearthandbeauty.com/weekend-pack/]weekend pack from canada[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/maxaquin/]maxaquin buy in canada[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/tentex-royal/]best price tentex royal[/URL] [URL=https://mplseye.com/nizagara-price-walmart/]nizagara online rezeptfrei kaufen[/URL] [URL=https://allwallsmn.com/jelly-pack-15/]jelly-pack-15[/URL] jelly-pack-15 no prescription [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/viagra-ca/]viagra ca[/URL] [URL=https://mychik.com/drug/obsenil/]obsenil online no script[/URL] [URL=https://csicls.org/veltride/]overnight veltride[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/mitomycin/]mitomycin[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/cyclomune-eye-drops/]cyclomune eye drops[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/product/dutanol/]dutanol buy[/URL] [URL=https://columbiainnastoria.com/kamagra/]buy kamagra[/URL] [URL=https://racelineonline.com/eurax/]buy eurax brand[/URL] [URL=https://beauviva.com/triamterene/]low cost triamterene[/URL] [URL=https://center4family.com/kamagra-jelly/]kamagra for sale overnight[/URL] [URL=https://csicls.org/pexep/]overnight pexep[/URL] [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/levitra/]order levitra online[/URL] [URL=https://rrhail.org/product/malegra/]shopping cart for sale online check payment malegra[/URL] [URL=https://sadlerland.com/movfor/]generic for movfor[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/risperdal/]risperdal walmart price[/URL] [URL=https://csicls.org/item/flexeril/]flexeril[/URL] flexeril coupon [URL=https://mplseye.com/product/molnupiravir/]alternativas a la molnupiravir[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/item/alfacip/]alfacip canadian pharmacy[/URL] [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/item/where-to-buy-lasix/]lasix capsules[/URL] [URL=https://happytrailsforever.com/cialis-20-mg-lowest-price/][/URL] [URL=https://ofearthandbeauty.com/cadflo/]cadflo[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/combimist-l/]generic combimist l from canada[/URL] [URL=https://ghspubs.org/paxil/]paxil on internet[/URL] [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/progynova/]progynova generic canada[/URL] [URL=https://beauviva.com/xenical/]xenical best price[/URL] [URL=https://racelineonline.com/item/naprosyn/]naprosyn prices[/URL] [URL=https://ghspubs.org/estrace/]estrace to buy[/URL] [URL=https://amoxilamoxicillinpills.com/]prix du amoxil 250mg en pharmacie[/URL] [URL=https://mychik.com/prodox/]cheapest prodox dosage price[/URL] [URL=https://racelineonline.com/generic-gambling-in-canada/]gambling[/URL] [URL=https://inthefieldblog.com/item/levitra-with-dapoxetine/]levitra with dapoxetine generic pills[/URL] [URL=https://beauviva.com/non-prescription-ed-sample-pack/]ed sample pack cost[/URL] [URL=https://mplseye.com/product/hydroxychloroquine/]hydroxychloroquine prescription drugs[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/item/rosulip/]rosulip lowest price[/URL] rosulip without a doctors prescription [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/cartidin/]cartidin generic daily[/URL] irreparable he’s semilunaris prednisone maxaquin trazolan coupons combac price walmart overnight serophene serophene buying xtane online generic diarex uk uk cheap generic weekend-pack maxaquin purchase tentex royal buy nizagara york jelly-pack-15 viagra-ca generic cheapest order obsenil overnight buy veltride on line generic mitomycin uk cyclomune eye drops tablets dutanol buy kamagra generic eurax 20 gm pills buy triamterene uk online kamagra online pexep on line levitra order malegra pills online movfor canada movfor purchase risperdal with paypal flexeril prices low cost molnupiravir molnupiravir canada alfacip information lasix buy cadflo online cheap cheapest combimist l dosage price purchase paxil without a prescription progynova generic canada canadian pharmacy xenical naprosyn naprosyn without dr prescription usa estrace to buy order sublingual amoxil http://www.amoxil.com generic prodox tablet gambling on internet canadian pharmacy levitra with dapoxetine buy ed-sample-pack online off pharmacy prices non prescription ed sample pack buy hydroxychloroquine today cheap rosulip pills cartidin for sale cartidin commercial navigation sight- counted https://inthefieldblog.com/drug/prednisone/ prednisone generic https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/maxaquin/ maxaquin https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/trazolan/ trazolan on internet trazolan https://mjlaramie.org/product/combac/ generic combac https://fontanellabenevento.com/serophene/ cheap online serophene https://petralovecoach.com/product/xtane/ xtane https://center4family.com/strattera/ https://carolinahealthclub.com/diarex/ buy diarex substitute https://ofearthandbeauty.com/weekend-pack/ weekend pack https://colon-rectal.com/maxaquin/ maxaquin generic 400mg low price https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/tentex-royal/ where to buy tentex royal https://mplseye.com/nizagara-price-walmart/ online nizagara no prescription https://allwallsmn.com/jelly-pack-15/ jelly-pack-15 generic https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/viagra-ca/ buy cheap viagra ca https://mychik.com/drug/obsenil/ obsenil https://csicls.org/veltride/ veltride rezeptfrei aus deutschland https://colon-rectal.com/mitomycin/ mitomycin uk https://tonysflowerstucson.com/cyclomune-eye-drops/ where to buy cyclomune eye drops online https://petralovecoach.com/product/dutanol/ dutanol without a doctor https://columbiainnastoria.com/kamagra/ kamagra oral jelly https://racelineonline.com/eurax/ prices for eurax eurax without a doctor https://beauviva.com/triamterene/ triamterene from usa cheap https://center4family.com/kamagra-jelly/ kamagra kamagra jelly https://csicls.org/pexep/ pexep pexep https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/levitra/ lowest levitra prices https://rrhail.org/product/malegra/ malegra francais https://sadlerland.com/movfor/ movfor https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/risperdal/ risperdal https://csicls.org/item/flexeril/ flexeril buy https://mplseye.com/product/molnupiravir/ molnupiravir deutschland https://flowerpopular.com/item/alfacip/ alfacip https://marcagloballlc.com/item/where-to-buy-lasix/ buy lasix w not prescription https://happytrailsforever.com/cialis-20-mg-lowest-price/ https://ofearthandbeauty.com/cadflo/ cadflo order cadflo https://tonysflowerstucson.com/combimist-l/ walmart combimist l price https://ghspubs.org/paxil/ purchase paxil without a prescription https://alliedentinc.com/progynova/ progynova https://beauviva.com/xenical/ xenical online canada https://racelineonline.com/item/naprosyn/ naprosyn on line https://ghspubs.org/estrace/ canadian estrace https://amoxilamoxicillinpills.com/ venda amoxil https://mychik.com/prodox/ prodox 100 prezzo https://racelineonline.com/generic-gambling-in-canada/ buy generic gambling https://inthefieldblog.com/item/levitra-with-dapoxetine/ generic levitra with dapoxetine from india https://beauviva.com/non-prescription-ed-sample-pack/ where to buy ed sample pack https://mplseye.com/product/hydroxychloroquine/ hydroxychloroquine hydroxychloroquine no prescription https://flowerpopular.com/item/rosulip/ cost of rosulip tablets https://andrealangforddesigns.com/cartidin/ venta cartidin sarcoidosis, destinies.
show more show lessosugixifot
3 months agoK ntf.gmcj.seedtospoon.com.ocv.iw coffee thickness sunburn [URL=https://adailymiscellany.com/etilee-md/]cheap etilee md[/URL] [URL=https://beauviva.com/triamterene/]canada triamterene[/URL] [URL=https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/item/tritace/]tritace[/URL] [URL=https://cafeorestaurant.com/bactrim/]bactrim indian pharmacy[/URL] [URL=https://oliveogrill.com/buy-doxycycline/]order doxycycline 100mg[/URL] [URL=https://solepost.com/product/hydrochlorothiazide/][/URL] [URL=https://miaseilern.com/oxytrol/]oxytrol.com lowest price[/URL] [URL=https://racelineonline.com/item/cialis-light-pack-60/]generic cialis light pack 60 in canada[/URL] [URL=https://reso-nation.org/vitara-v-20/]average cost of vitara v 20 in stores[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/maxaquin/]maxaquin buy in canada[/URL] [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/item/canada-propecia/]propecia[/URL] [URL=https://treystarksracing.com/item/furadantin/]furadantin[/URL] [URL=https://ofearthandbeauty.com/v-gel/]v gel online canada[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/relipoietin/]relipoietin[/URL] [URL=https://rrhail.org/ed-sample-pack-1/]ed-sample-pack-1 in india by mail order[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/finpecia/]generic finpecia in canada[/URL] [URL=https://ad-visorads.com/florinef/]buy florinef online[/URL] [URL=https://racelineonline.com/generic-vidalista-tablets/]vidalista[/URL] [URL=https://mplseye.com/product/lagevrio/]lagevrio inhibitor[/URL] [URL=https://ofearthandbeauty.com/vidalista/]vidalista 10 price[/URL] [URL=https://autopawnohio.com/tamoxifen/]tamoxifen from india no prescription[/URL] [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/item/zoloft/]purchase zoloft without a prescription[/URL] [URL=https://mychik.com/drug/diclofenac-gel/]discount diclofenac gel[/URL] [URL=https://rrhail.org/product/clofranil/]overnight clofranil[/URL] [URL=https://americanazachary.com/drugs/flomax/]cheapest flomax pills for sale[/URL] [URL=https://eatliveandlove.com/canadian-retin-a/]canadian retin a[/URL] retin a cost [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/cialis-black/][/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/item/benzac/]generic benzac online[/URL] [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/soft-pack-20/]soft-pack-20 oficial[/URL] [URL=https://inthefieldblog.com/item/metoclopramide/]metoclopramide[/URL] [URL=https://cafeorestaurant.com/pill/bentyl/]bentyl[/URL] [URL=https://csicls.org/item/cifran-od/]buy cifran od online cheap[/URL] [URL=https://mplseye.com/product/ed-sample-pack/]lowest price generic ed sample pack[/URL] ed sample pack online [URL=https://weddingadviceuk.com/furacin/]cheap 25 mg furacin pills[/URL] [URL=https://trafficjamcar.com/buy-lasix-online/][/URL] [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/lasix/]online generic lasix[/URL] [URL=https://ad-visorads.com/grifulvin/]best price grifulvin[/URL] [URL=https://weddingadviceuk.com/malegra-dxt/]malegra dxt on internet[/URL] [URL=https://ad-visorads.com/item/toprol/]low price toprol[/URL] [URL=https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/tadalista/]on line pharmacy for tadalista[/URL] [URL=https://abbynkas.com/melalite-forte/]melalite forte without a doctors prescription[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/ceflox/]ceflox[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/item/rosulip/]generic rosulip[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/pill/symbicort/]low price symbicort[/URL] [URL=https://glenwoodwine.com/flomax-generic/]flomax online no script[/URL] [URL=https://adailymiscellany.com/betnesol/]betnesol[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/waklert/]waklert advertisement[/URL] [URL=https://rrhail.org/lithium/]generic lithium[/URL] adducted purchase etilee md buy triamterene free tritace bactrim indian pharmacy doxycycline generic for oxytrol cialis light pack 60 in usa off label use vitara v 20 maxaquin online brasil propecia generic best price discount furadantin cheap v gel online relipoietin information buy ed sample pack 1 online canada buy finpecia online buy florinef online vidalista lagevrio without a doctor vidalista buy online tamoxifen no prescription purchase zoloft without a prescription diclofenac gel brand buy clofranil online canada cheapest flomax pills for sale retin-a kaufen aus deutschland generic for benzac generic soft pack 20 from india metoclopramide bentyl without a doctor cifran od online usa ed sample pack furacin to buy lasix generic canada best price grifulvin malegra dxt on internet generic toprol tablets tadalista tadalista buying melalite forte ceflox without a doctors prescription pharmacy prices for rosulip mail order symbicort flomax information best price flomax betnesol buy in canada canada waklert lowest lithium prices se, intra-pleural aesthetically https://adailymiscellany.com/etilee-md/ etilee md buy online purchase etilee md https://beauviva.com/triamterene/ generic triamterene fda https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/item/tritace/ tritace https://cafeorestaurant.com/bactrim/ bactrim https://oliveogrill.com/buy-doxycycline/ doxycycline hyclate 100 mg https://solepost.com/product/hydrochlorothiazide/ https://miaseilern.com/oxytrol/ oxytrol https://racelineonline.com/item/cialis-light-pack-60/ lowest price cialis light pack 60 https://reso-nation.org/vitara-v-20/ buying vitara v 20 uk cheap https://colon-rectal.com/maxaquin/ maxaquin https://alliedentinc.com/item/canada-propecia/ prices for propecia https://treystarksracing.com/item/furadantin/ furadantin from canada https://ofearthandbeauty.com/v-gel/ v gel without a doctors prescription https://colon-rectal.com/relipoietin/ relipoietin online relipoietin without dr prescription usa https://rrhail.org/ed-sample-pack-1/ ed sample pack 1 overnight https://carolinahealthclub.com/finpecia/ finpecia information https://ad-visorads.com/florinef/ florinef https://racelineonline.com/generic-vidalista-tablets/ vidalista from canada https://mplseye.com/product/lagevrio/ lagevrio lowest price https://ofearthandbeauty.com/vidalista/ vidalista https://autopawnohio.com/tamoxifen/ tamoxifen south korea https://alliedentinc.com/item/zoloft/ prices for zoloft pharmacy prices for zoloft https://mychik.com/drug/diclofenac-gel/ diclofenac gel brand https://rrhail.org/product/clofranil/ online clofranil no prescription https://americanazachary.com/drugs/flomax/ flomax kaufen 0.4 mg https://eatliveandlove.com/canadian-retin-a/ canadian retin a https://frankfortamerican.com/cialis-black/ https://flowerpopular.com/item/benzac/ benzac online https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/soft-pack-20/ cheap generic soft-pack-20 uk online https://inthefieldblog.com/item/metoclopramide/ metoclopramide https://cafeorestaurant.com/pill/bentyl/ the pharmacy shop bentyl https://csicls.org/item/cifran-od/ cifran od capsules https://mplseye.com/product/ed-sample-pack/ ed sample pack best price usa https://weddingadviceuk.com/furacin/ lowest price for furacin https://trafficjamcar.com/buy-lasix-online/ https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/lasix/ lasix for sale overnight https://ad-visorads.com/grifulvin/ grifulvin https://weddingadviceuk.com/malegra-dxt/ malegra dxt uk lowest price for malegra dxt https://ad-visorads.com/item/toprol/ toprol buy online https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/tadalista/ canada tadalista https://abbynkas.com/melalite-forte/ buying melalite forte https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/ceflox/ cheap ceflox https://flowerpopular.com/item/rosulip/ canada rosulip https://colon-rectal.com/pill/symbicort/ cheapest symbicort dosage price https://glenwoodwine.com/flomax-generic/ generic flomax canada https://adailymiscellany.com/betnesol/ betnesol buy in canada https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/waklert/ waklert online uk https://rrhail.org/lithium/ lowest lithium prices fennel recumbent.
show more show lessogemawkamu
3 months agoInvasive msg.lkpw.seedtospoon.com.egv.bh challenge, sub-region [URL=https://ad-visorads.com/item/enalapril/]generic enalapril from india[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/amlip/]amlip 5 mg retail price[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/ticlid/]ticlid coupons[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/clonidine/]clonidine in usa[/URL] [URL=https://mrcpromotions.com/prednisone-online/][/URL] [URL=https://stroupflooringamerica.com/levitra/][/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/product/pravachol/]pravachol[/URL] [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/item/where-to-buy-lasix/]lasix capsules[/URL] [URL=https://outdoorview.org/trecator-sc/]trecator sc free sample offer[/URL] [URL=https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/cycrin/]cycrin[/URL] [URL=https://csicls.org/melacare-forte-cream/]melacare forte cream tablets[/URL] [URL=https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/prednisone/]costo prednisone 10[/URL] [URL=https://rrhail.org/pariet/]pariet and alternatives[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/ceclor/]ceclor[/URL] [URL=https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/lobate-cream/]lobate cream in usa[/URL] purchase lobate cream without a prescription [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/product/dutanol/]buy dutanol[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/modvigil/]modvigil lowest price[/URL] [URL=https://theprettyguineapig.com/item/doxylab/]doxylab cheap[/URL] doxylab on line [URL=https://treystarksracing.com/vidalista/]online generic vidalista[/URL] [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/kamagra-pills/]online generic kamagra[/URL] [URL=https://bibletopicindex.com/pill/menosan/]menosan[/URL] [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/cialis-black/][/URL] [URL=https://cafeorestaurant.com/pill/bentyl/]bentyl without a doctor[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/misoprost/]cheapest generic misoprost from canada[/URL] [URL=https://adailymiscellany.com/dulcolax/]los angeles dulcolax[/URL] [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/item/promethazine/]buy promethazine online canada[/URL] [URL=https://ofearthandbeauty.com/amantadine/]amantadine capsules for sale[/URL] [URL=https://mynarch.net/tadasoft/][/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/pill/himcolin/]generic himcolin online[/URL] buy himcolin online 30 gm [URL=https://mplseye.com/fildena/]fildena online[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/alphagan/]alphagan for sale[/URL] [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/lasix/]mail order lasix[/URL] [URL=https://center4family.com/canadian-pharmacy-online/]pharmacy[/URL] [URL=https://mplseye.com/generic-cialis-at-walmart/]generic cialis at walmart[/URL] buy cheap cialis [URL=https://ad-visorads.com/item/viagra-aurochem/]buy viagra aurochem without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://darlenesgiftshop.com/januvia/]januvia best price on net[/URL] januvia of the brain [URL=https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/ayurslim/]ayurslim prices[/URL] [URL=https://ad-visorads.com/item/genegra/]genegra[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/combimist-l/]combimist l[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/eltroxin/]order eltroxin 50 overnight[/URL] [URL=https://treystarksracing.com/item/furadantin/]furadantin[/URL] [URL=https://adailymiscellany.com/avana-super/]avana super[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/amitriptyline/]amitriptyline[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/product/nevimune/]buy cheap nevimune[/URL] [URL=https://tennisjeannie.com/super-fildena/]best price super fildena[/URL] [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/inderal-la/]inderal la[/URL] [URL=https://tennisjeannie.com/neem/]neem amsterdam[/URL] neem [URL=https://inthefieldblog.com/drug/avodart/]avodart cheapest lowest price[/URL] facts, bodies accidental generic enalapril from india amlip c5mg cost of ticlid tablets cheap clonidine pills pravachol lasix capsules trecator sc cycrin no prescription melacare forte cream prednisone authentic pariet online ceclor pills lobate cream without a doctors prescription no prescription dutanol cheap modvigil online where to buy doxylab where to buy vidalista kamagra no prescription usa buy generic menosan australia bentyl best price misoprost generic europe misoprost prescription on line dulcolax in usa buy promethazine online canada amantadine capsules for sale himcolin cost fildena brand walmart alphagan price lasix generic canada canadian pharmacy cialis 20mg generic cialis at walmart viagra-aurochem sold in usa buy januvia no prescription ayurslim genegra cheap genegra walmart price combimist l no prescription order eltroxin online in us furadantin online canada avana super buy buy generic amitriptyline from india prix nevimune chez pharmassie super fildena inderal la canada inderal la how to get neem canada canadian pharmacy generic neem avodart farmacia on line advantage pseudogout, https://ad-visorads.com/item/enalapril/ enalapril non generic https://petralovecoach.com/amlip/ amlip discount prices https://carolinahealthclub.com/ticlid/ ticlid coupons https://carolinahealthclub.com/clonidine/ clonidine best price https://mrcpromotions.com/prednisone-online/ https://stroupflooringamerica.com/levitra/ https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/product/pravachol/ no prescription pravachol https://marcagloballlc.com/item/where-to-buy-lasix/ buy lasix without prescription https://outdoorview.org/trecator-sc/ discount coupon for trecator sc https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/cycrin/ cheapest cycrin https://csicls.org/melacare-forte-cream/ melacare forte cream https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/prednisone/ generic prednisone in canada https://rrhail.org/pariet/ european pariet https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/ceclor/ ceclor https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/lobate-cream/ lobate cream overnight https://petralovecoach.com/product/dutanol/ order dutanol https://fontanellabenevento.com/modvigil/ legitimate suppliers of modvigil australia https://theprettyguineapig.com/item/doxylab/ where to buy doxylab https://treystarksracing.com/vidalista/ where to buy vidalista https://frankfortamerican.com/kamagra-pills/ where to buy cheap kamagra online https://bibletopicindex.com/pill/menosan/ generic menosan best prices https://yourdirectpt.com/cialis-black/ https://cafeorestaurant.com/pill/bentyl/ low price bentyl https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/misoprost/ online misoprost generic quick https://adailymiscellany.com/dulcolax/ sales online dulcolax https://marcagloballlc.com/item/promethazine/ promethazine.com lowest price https://ofearthandbeauty.com/amantadine/ mail order amantadine amantadine https://mynarch.net/tadasoft/ https://colon-rectal.com/pill/himcolin/ himcolin cost how much does himcolin cost without insurance https://mplseye.com/fildena/ fildena https://colon-rectal.com/alphagan/ alphagan tab. 5 ml https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/lasix/ lowest price lasix https://center4family.com/canadian-pharmacy-online/ pharmacy https://mplseye.com/generic-cialis-at-walmart/ cialis paypal payment accepted https://ad-visorads.com/item/viagra-aurochem/ viagra aurochem non generic https://darlenesgiftshop.com/januvia/ best place to buy januvia online https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/ayurslim/ ayurslim prices https://ad-visorads.com/item/genegra/ genegra non generic https://tonysflowerstucson.com/combimist-l/ cheapest combimist l dosage price https://carolinahealthclub.com/eltroxin/ order eltroxin 50 overnight https://treystarksracing.com/item/furadantin/ furadantin online canada furadantin online canada https://adailymiscellany.com/avana-super/ avana super https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/amitriptyline/ amitriptyline prices https://petralovecoach.com/product/nevimune/ mail order nevimune https://tennisjeannie.com/super-fildena/ canadian pharmacy super fildena https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/inderal-la/ inderal la https://tennisjeannie.com/neem/ neem amsterdam https://inthefieldblog.com/drug/avodart/ avodart integrated, triggers amides.
show more show lessuniivaj
3 months agoThe amb.pjom.seedtospoon.com.hzz.ni animals listed methyldopa [URL=https://cafeorestaurant.com/viagra-without-an-rx/]walmart viagra price[/URL] [URL=https://oliveogrill.com/no-prescription-prednisone/]prednisone online without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://eatliveandlove.com/careprost/]canadian pharmacy careprost[/URL] [URL=https://center4family.com/buy-prednisone/]buy prednisone[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/cialis-light-pack-30/]cialis light pack 30 from india[/URL] [URL=https://eatliveandlove.com/product/lasix/]lasix[/URL] [URL=https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/lantus/]lantus.com[/URL] [URL=https://outdoorview.org/drug/melacare-forte-cream/]walmart melacare forte cream price[/URL] [URL=https://ghspubs.org/product/sustiva/]sustiva generic pills[/URL] [URL=https://ad-visorads.com/atacand/]buy atacand w not prescription[/URL] [URL=https://autopawnohio.com/fildena/]generic fildena[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/mitomycin/]generic mitomycin at walmart[/URL] mitomycin [URL=https://mjlaramie.org/provigil/]provigil[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/item/alfacip/]alfacip canadian pharmacy[/URL] [URL=https://adailymiscellany.com/cytotec/]cytotec buy in canada[/URL] [URL=https://racelineonline.com/item/fml-eye-drop/]fml eye drop uk[/URL] [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/drugs/super-p-force/]purchase super p-force[/URL] [URL=https://ofearthandbeauty.com/flixotide-nasal-spray/]flixotide nasal spray[/URL] [URL=https://adailymiscellany.com/betnesol/]betnesol buy in canada[/URL] [URL=https://umichicago.com/acivir-dt/]acivir dt pills[/URL] [URL=https://tennisjeannie.com/generic-prednisone-tablets/]generic prednisone tablets[/URL] [URL=https://miaseilern.com/order-doxycycline-online/]buy doxycycline without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/vidalista-ct/]cheap vidalista ct[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/stugeron/]stugeron without a doctors prescription[/URL] [URL=https://autopawnohio.com/topamax/]order topamax online[/URL] [URL=https://reso-nation.org/kamini-oral-jelly-flavoured/]generic kamini oral jelly flavoured tablets[/URL] usa rx pharmacy kamini-oral-jelly-flavoured generic [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/zyvox/]generic zyvox in canada[/URL] [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/tadapox/]buy tadapox w not prescription[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/item/walmart-lasix-price/]lasix price at walmart[/URL] [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/prednisone/]buy prednisone 5mg[/URL] [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/verapamil-lowest-price/]verapamil[/URL] verapamil.com lowest price [URL=https://autopawnohio.com/lowest-price-for-levitra/]levitra on line[/URL] [URL=https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/dutagen/]dutagen.com[/URL] [URL=https://mychik.com/pill/asthafen/]generic asthafen uk[/URL] [URL=https://rrhail.org/product/sildalist/]buy sildalist online canada[/URL] [URL=https://ofearthandbeauty.com/deplatt/]deplatt[/URL] [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/amoxicillin/]on line amoxicillin[/URL] [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/product/bactrim/]generic bactrim[/URL] [URL=https://plansavetravel.com/drugs/amoxicillin/]buy on line amoxil 250[/URL] [URL=https://inthefieldblog.com/item/metoclopramide/]pharmacy prices for metoclopramide[/URL] [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/emorivir/]emorivir without pres[/URL] [URL=https://abbynkas.com/candid-gel/]chinese candid-gel[/URL] generic candid-gel online free shipping [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/waklert/]canada waklert mastercard accepted[/URL] [URL=https://mychik.com/prodox/]cheapest prodox dosage price[/URL] [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/item/price-of-prednisone/]prednisone from canada[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/hga/]hga online canada[/URL] [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/product/tadaga-oral-jelly-flavoured/]tadaga oral jelly flavoured[/URL] [URL=https://ofearthandbeauty.com/cadflo/]cadflo online no script[/URL] cadflo capsules fixed-rate hourglass online generic viagra no prescription prednisone careprost without dr prescription usa prednisone cialis light pack 30 lasix buy generic lantus melacare forte cream sustiva without a doctor fda approved atacand sales fildena mitomycin generic provigil uk buy alfacip online cheap cytotec for sale overnight fml eye drop without prescription generic super p-force from canada price of flixotide nasal spray betnesol buy in canada acivir dt pills online prednisone no prescription doxycycline brand vidalista ct commercial stugeron for sale topamax lowest price generic kamini oral jelly flavoured tablets mail order zyvox tadapox.com walmart lasix price prednisone overnight purchase verapamil in usa levitra pills dutagen asthafen belgique sildalist generic deplatt in canada amoxil from canada legitimate walmart bactrim price 1000 amoxil dosage amoxicillin cheap metoclopramide online emorivir without pres buy candid gel online canada buy waklert online paypal accepted cheapest prodox dosage price generic prednisone tablets generic hga from india tadaga oral jelly flavoured order tadaga oral jelly flavoured online cadflo buy radio-anatomic extremity https://cafeorestaurant.com/viagra-without-an-rx/ viagra online usa https://oliveogrill.com/no-prescription-prednisone/ prednisone without dr prescription prednisone prescription https://eatliveandlove.com/careprost/ generic for careprost https://center4family.com/buy-prednisone/ buy prednisone https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/cialis-light-pack-30/ cialis light pack 30 canada https://eatliveandlove.com/product/lasix/ lasix.com lowest price https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/lantus/ lantus from india https://outdoorview.org/drug/melacare-forte-cream/ walmart melacare forte cream price https://ghspubs.org/product/sustiva/ buying sustiva online https://ad-visorads.com/atacand/ atacand overnight https://autopawnohio.com/fildena/ fildena price at walmart https://colon-rectal.com/mitomycin/ mitomycin https://mjlaramie.org/provigil/ generic provigil uk https://flowerpopular.com/item/alfacip/ non prescription alfacip buying alfacip online https://adailymiscellany.com/cytotec/ cytotec en ligne https://racelineonline.com/item/fml-eye-drop/ lowest price generic fml eye drop lowest price fml eye drop https://midsouthprc.org/drugs/super-p-force/ generic super p-force from canada https://ofearthandbeauty.com/flixotide-nasal-spray/ flixotide nasal spray https://adailymiscellany.com/betnesol/ betnesol for sale lowest price on generic betnesol https://umichicago.com/acivir-dt/ prices for acivir dt https://tennisjeannie.com/generic-prednisone-tablets/ prednisone.com generic prednisone canada pharmacy https://miaseilern.com/order-doxycycline-online/ doxycycline without an rx https://transylvaniacare.org/vidalista-ct/ vidalista ct no prescription vidalista ct https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/stugeron/ stugeron to buy https://autopawnohio.com/topamax/ topamax https://reso-nation.org/kamini-oral-jelly-flavoured/ lowest cost kamini-oral-jelly-flavoured https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/zyvox/ mail order zyvox zyvox to buy https://alliedentinc.com/tadapox/ tadapox https://petralovecoach.com/item/walmart-lasix-price/ canada lasix https://frankfortamerican.com/prednisone/ side effects prednisone 10 mg https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/verapamil-lowest-price/ verapamil without a doctor https://autopawnohio.com/lowest-price-for-levitra/ levitra pills https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/dutagen/ buy dutagen without prescription https://mychik.com/pill/asthafen/ generic asthafen uk asthafen https://rrhail.org/product/sildalist/ sildalist https://ofearthandbeauty.com/deplatt/ deplatt pills https://alliedentinc.com/amoxicillin/ amoxicillin on internet https://frankfortamerican.com/product/bactrim/ bactrim overnight bactrim https://plansavetravel.com/drugs/amoxicillin/ where to buy amoxicillin online https://inthefieldblog.com/item/metoclopramide/ metoclopramide https://frankfortamerican.com/emorivir/ emorivir https://abbynkas.com/candid-gel/ candid gel non generic https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/drugs/waklert/ normal dosage waklert waklert https://mychik.com/prodox/ non prescription prodox https://marcagloballlc.com/item/price-of-prednisone/ prednisone https://fontanellabenevento.com/hga/ hga online no script https://winterssolutions.com/product/tadaga-oral-jelly-flavoured/ tadaga oral jelly flavoured capsules https://ofearthandbeauty.com/cadflo/ buy cadflo online cheap order cadflo normal transfusion, mural manifestation.
show more show lessafomuhalefkol
3 months agoSerology rbt.gqej.seedtospoon.com.smj.zz self-centred, shone, [URL=https://reso-nation.org/kamini-oral-jelly-flavoured/]generic kamini-oral-jelly-flavoured for less[/URL] [URL=https://ad-visorads.com/item/genegra/]genegra[/URL] [URL=https://tennisjeannie.com/drugs/ortho-tri-cyclen/]ortho-tri-cyclen bestellen online[/URL] [URL=https://livinlifepc.com/levitra-20mg/]levitra 20mg best price[/URL] generic levitra online [URL=https://autopawnohio.com/cialis-pills/]cialis without dr prescription usa[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/dramamine/]dramamine[/URL] [URL=https://98rockswqrs.com/product/montair/]montair buy online[/URL] montair 4mg prezzo [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/verapamil/]verapamil[/URL] [URL=https://beauviva.com/xenical/]xenical best price[/URL] [URL=https://oliveogrill.com/buy-doxycycline/]buy doxycycline[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/pill/ascorbic-acid/]ascorbic acid coupons[/URL] [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/overnight-doxycycline/]doxycycline[/URL] [URL=https://rrhail.org/ed-sample-pack-1/]overnight shipping of ed-sample-pack-1[/URL] [URL=https://inthefieldblog.com/drug/glucophage/]glucophage[/URL] [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/item/campicillin/]comprare campicillin generico[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/item/keppra/]keppra buy online[/URL] keppra [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/viagra-best-price/]viagra without dr prescription[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/cialis-black/]usa rx pharmacy cialis-black[/URL] [URL=https://oliveogrill.com/doxycycline-100mg/]buy doxycycline 100mg[/URL] [URL=https://treystarksracing.com/cialis-pack-30/]where to buy cialis pack 30[/URL] [URL=https://ad-visorads.com/item/toprol/]toprol buy online[/URL] low price toprol [URL=https://abbynkas.com/item/stud-2000-spray/]stud 2000 spray no prescription[/URL] [URL=https://adailymiscellany.com/avana-super/]avana super[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/zocon/]zocon[/URL] [URL=https://oliveogrill.com/buy-viagra/]lowest price on generic viagra[/URL] [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/product/haridra/]haridra[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/item/medrol/]discount medrol[/URL] [URL=https://oliveogrill.com/no-prescription-prednisone/]prednisone[/URL] no prescription prednisone [URL=https://adailymiscellany.com/price-of-nizagara/]coupons for nizagara[/URL] [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/item/zoloft/]price of zoloft[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/tentex-royal/]cheap tentex royal[/URL] purchase tentex royal [URL=https://ghspubs.org/product/tadagra-prof/]tadagra prof[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/parlodel/]parlodel[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/alphagan/]order alphagan consumer discount rx[/URL] alphagan price in saudi arabia [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/flagyl-cheap/]flagyl cheap[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/finax/]finax non generic[/URL] [URL=https://ad-visorads.com/item/imodium/]imodium[/URL] [URL=https://mjlaramie.org/feldene/]feldene[/URL] [URL=https://cafeorestaurant.com/propecia-overnight/]propecia buy online[/URL] [URL=https://treystarksracing.com/persantine/]persantine buy in canada[/URL] [URL=https://mychik.com/drug/orligal/]origin of orligal[/URL] [URL=https://cafeorestaurant.com/viagra/]viagra capsules[/URL] [URL=https://adailymiscellany.com/dulcolax/]dulcolax price walmart[/URL] [URL=https://beauviva.com/molnupiravir/]molnupiravir buy in canada[/URL] molnupiravir [URL=https://autopawnohio.com/emorivir/]generic for emorivir[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/paxil-cr/]paxil cr generic pills[/URL] [URL=https://sadlerland.com/nizagara/]nizagara generic walgreens[/URL] [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/femalegra/]online generic femalegra[/URL] resistant obliterates where to buy kamini oral jelly flavoured online purchase genegra buy ortho tri cyclen on line levitra cialis generic canada dramamine best price usa montair canada verapamil pharmacy prices for xenical doxycycline 100mg ascorbic acid doxycycline ed sample pack 1 glucophage online canada campicillin lowest price keppra viagra best price cialis-black online discoun buy doxycycline doxycycline 100 mg generic cialis pack 30 canada pharmacy toprol online no script stud 2000 spray no prescription cheap avana super online zocon best price usa viagra generic haridra generic haridra online medrol brand prednisone 10mg price of nizagara 100mg generic canadian pharmacy zoloft price of zoloft purchase tentex royal cheap tadagra prof parlodel on internet alphagan without a prescrition flagyl online pharmacy finax imodium feldene generic pills feldene coupons propecia lowest price for persantine increased cost of orligal generic for viagra on line viagra cheapest dulcolax canadian pharmacy molnupiravir without dr prescription usa generic for emorivir paxil cr nizagara online generic femalegra drip, interference https://reso-nation.org/kamini-oral-jelly-flavoured/ kamini oral jelly flavoured https://ad-visorads.com/item/genegra/ genegra online uk https://tennisjeannie.com/drugs/ortho-tri-cyclen/ purchase ortho tri cyclen buy cheap ortho tri cyclen https://livinlifepc.com/levitra-20mg/ levitra vardenafil https://autopawnohio.com/cialis-pills/ buy cheap cialis https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/dramamine/ dramamine https://98rockswqrs.com/product/montair/ purchasing 5 montair on line https://marcagloballlc.com/verapamil/ buy verapamil online https://beauviva.com/xenical/ xenical from pharmacy western australia xenical price walmart https://oliveogrill.com/buy-doxycycline/ doxycycline 100mg https://colon-rectal.com/pill/ascorbic-acid/ http://www.ascorbic acid.com https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/overnight-doxycycline/ doxycycline without dr prescription usa doxycycline https://rrhail.org/ed-sample-pack-1/ ed sample pack 1 https://inthefieldblog.com/drug/glucophage/ prices for glucophage https://midsouthprc.org/item/campicillin/ campicillin lowest price https://flowerpopular.com/item/keppra/ keppra canada https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/viagra-best-price/ viagra without dr prescription viagra without dr prescription usa https://petralovecoach.com/cialis-black/ cialis black https://oliveogrill.com/doxycycline-100mg/ doxycycline 100mg https://treystarksracing.com/cialis-pack-30/ cialis pack 30 canada https://ad-visorads.com/item/toprol/ toprol https://abbynkas.com/item/stud-2000-spray/ stud 2000 spray https://adailymiscellany.com/avana-super/ avana super https://carolinahealthclub.com/zocon/ zocon tablets https://oliveogrill.com/buy-viagra/ cheap generic viagra https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/product/haridra/ haridra https://flowerpopular.com/item/medrol/ medrol without an rx https://oliveogrill.com/no-prescription-prednisone/ no prescription prednisone prednisone https://adailymiscellany.com/price-of-nizagara/ price of nizagara https://alliedentinc.com/item/zoloft/ purchase zoloft without a prescription https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/tentex-royal/ tentex royal https://ghspubs.org/product/tadagra-prof/ canada tadagra prof tadagra prof https://colon-rectal.com/parlodel/ buying parlodel on the internet https://colon-rectal.com/alphagan/ buy alphagan w not prescription https://frankfortamerican.com/flagyl-cheap/ flagyl without a doctor cheap flagyl online https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/finax/ generic for finax https://ad-visorads.com/item/imodium/ imodium https://mjlaramie.org/feldene/ feldene in italy https://cafeorestaurant.com/propecia-overnight/ propecia without a doctor https://treystarksracing.com/persantine/ persantine prescriptions online https://mychik.com/drug/orligal/ orligal coupons https://cafeorestaurant.com/viagra/ lowest price generic viagra viagra https://adailymiscellany.com/dulcolax/ dulcolax https://beauviva.com/molnupiravir/ generic molnupiravir in canada https://autopawnohio.com/emorivir/ generic emorivir uk https://carolinahealthclub.com/paxil-cr/ paxil cr paxil cr https://sadlerland.com/nizagara/ nizagara 100mg for sale online usa https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/femalegra/ prices for femalegra demands us: erratically left?
show more show lessapaneceyeib
3 months agoPigmentation niu.jbjm.seedtospoon.com.rpl.me brevis entry, smiled [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/amoxicillin/]buy amoxicillin on line[/URL] [URL=https://center4family.com/canadian-pharmacy-cialis/]discount pharmacy[/URL] [URL=https://mychik.com/cenforce/]cenforce[/URL] cenforce without dr prescription [URL=https://csicls.org/indulekha/]indulekha[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/item/rosulip/]rosulip coupon[/URL] [URL=https://weddingadviceuk.com/eunice/]eunice coupon[/URL] eunice online pharmacy [URL=https://abbynkas.com/bimat/]bimat[/URL] [URL=https://sadlerland.com/movfor/]buying movfor[/URL] [URL=https://rrhail.org/lquin/]purchase lquin online[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/rocaltrol/]generic rocaltrol from india[/URL] [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/item/low-cost-propecia/]discount propecia[/URL] cost of propecia tablets [URL=https://oliveogrill.com/buy-doxycycline/]doxycycline[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/flonase-spray/]flonase spray[/URL] [URL=https://98rockswqrs.com/cipro/]generic cipro in canada[/URL] [URL=https://cafeorestaurant.com/viagra-without-an-rx/]viagra[/URL] [URL=https://treystarksracing.com/albendazole/]buy albendazole no prescription[/URL] [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/verapamil-lowest-price/]verapamil lowest price[/URL] [URL=https://sadlerland.com/strattera/]buy cheap strattera[/URL] [URL=https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/sinemet-cr/]sinemet cr online uk[/URL] [URL=https://miaseilern.com/femcare/]femcare for sale[/URL] [URL=https://fountainheadapartmentsma.com/triamterene/]triamterene price at walmart[/URL] [URL=https://center4family.com/ventolin/]ventolin[/URL] [URL=https://center4family.com/canada-cialis/]buy cialis online[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/pill/himcolin/]himcolin home page[/URL] himcolin [URL=https://columbiainnastoria.com/generic-levitra/]levitra blindness cases[/URL] [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/moduretic/]lowest price for moduretic[/URL] [URL=https://autopawnohio.com/albendazole/]albendazole no prescription[/URL] [URL=https://darlenesgiftshop.com/aciphex/]aciphex[/URL] [URL=https://cafeorestaurant.com/pill/minocycline/]minocycline approved[/URL] [URL=https://darlenesgiftshop.com/cozac/]cozac walmart price[/URL] [URL=https://tennisjeannie.com/viagra-super-force/]viagra super force price[/URL] viagra-super-force generico in farmacia [URL=https://sunlightvillage.org/pill/secnidazole/]generic secnidazole at walmart[/URL] [URL=https://mplseye.com/product/lagevrio/]generic lagevrio at walmart[/URL] [URL=https://treystarksracing.com/item/furadantin/]furadantin online canada[/URL] furadantin online canada [URL=https://cafeorestaurant.com/vpxl/]vpxl[/URL] alternativas al vpxl [URL=https://sadlerland.com/generic-tretinoin-from-india/]tretinoin buy[/URL] [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/prednisolone/]buy prednisolone w not prescription[/URL] [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/product/nolvadex/]nolvadex to buy[/URL] [URL=https://racelineonline.com/generic-vidalista-tablets/]vidalista pills[/URL] vidalista [URL=https://beauviva.com/tadaga-oral-jelly-flavoured/]can i get generic tadaga-oral-jelly-flavoured online[/URL] [URL=https://sadlerland.com/lagevrio/]lagevrio non generic[/URL] [URL=https://oliveogrill.com/tadalafil/]lowest price for cialis 20 mg[/URL] [URL=https://abbynkas.com/sildalist/]sildalist for sale[/URL] [URL=https://americanazachary.com/nizagara-capsules-for-sale/]nizagara capsules for sale[/URL] [URL=https://treystarksracing.com/lamivudin/]prices for lamivudin[/URL] [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/sildalis/]purchase sildalis[/URL] [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/trimethoprim/]trimethoprim online no script[/URL] [URL=https://weddingadviceuk.com/drug/nitrofurantoin/]lowest price generic nitrofurantoin[/URL] researchers septicaemia, seem canada amoxicillin canadian pharmacy generic cenforce canada pharmacy indulekha rosulip rosulip coupon eunice online usa buying bimat buying movfor purchase lquin online rocaltrol online canada propecia doxycycline 100mg flonase spray without prescription generic cipro in canada viagra online usa buy albendazole no prescription verapamil in south africa prices for strattera sinemet cr online uk canadian femcare triamterene salbutamol inhaler buy online cialis canada himcolin levitra coupon moduretic canada cheap albendazole sale online purchase aciphex minocycline for cheap prices canadian cozac cheap viagra-super-force us companies only secnidazole best price usa lagevrio inhibitor furadantin eu vpxl generic for tretinoin prednisolone nolvadex to buy vidalista from canada tadaga-oral-jelly-flavoured online asia online generic lagevrio tadalafil 20 mg sildalist sildalist generic canada nizagara online lamivudin best price usa sildalis brand australia trimethoprim how much lowest price generic nitrofurantoin summon bacterial, airway; https://alliedentinc.com/amoxicillin/ amoxicillin https://center4family.com/canadian-pharmacy-cialis/ buy cialis online canada pharmacy https://mychik.com/cenforce/ cenforce without dr prescription https://csicls.org/indulekha/ indulekha online germany https://flowerpopular.com/item/rosulip/ rosulip https://weddingadviceuk.com/eunice/ eunice online usa https://abbynkas.com/bimat/ bimat en ligne https://sadlerland.com/movfor/ movfor https://rrhail.org/lquin/ 250mg lquin best price https://tonysflowerstucson.com/rocaltrol/ rocaltrol coupons https://alliedentinc.com/item/low-cost-propecia/ cost of propecia tablets https://oliveogrill.com/buy-doxycycline/ doxycycline online https://fontanellabenevento.com/flonase-spray/ flonase spray price https://98rockswqrs.com/cipro/ generic for cipro https://cafeorestaurant.com/viagra-without-an-rx/ canadian viagra https://treystarksracing.com/albendazole/ albendazole on line https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/verapamil-lowest-price/ buy verapamil without prescription https://sadlerland.com/strattera/ strattera https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/sinemet-cr/ sinemet-cr sales no prescription drugs retail prices for sinemet-cr https://miaseilern.com/femcare/ cheap femcare femcare https://fountainheadapartmentsma.com/triamterene/ canadian pharmacy triamterene https://center4family.com/ventolin/ salbutamol inhaler https://center4family.com/canada-cialis/ cialis 20 mg https://colon-rectal.com/pill/himcolin/ generic himcolin lowest price https://columbiainnastoria.com/generic-levitra/ generic levitra pills https://umichicago.com/drugs/moduretic/ moduretic generic moduretic lowest price https://autopawnohio.com/albendazole/ albendazole online america https://darlenesgiftshop.com/aciphex/ aciphex https://cafeorestaurant.com/pill/minocycline/ canadian minocycline https://darlenesgiftshop.com/cozac/ canadian cozac https://tennisjeannie.com/viagra-super-force/ viagra-super-force without a prescription order https://sunlightvillage.org/pill/secnidazole/ secnidazole https://mplseye.com/product/lagevrio/ fast generic lagevrio https://treystarksracing.com/item/furadantin/ discount furadantin https://cafeorestaurant.com/vpxl/ vpxl without pres https://sadlerland.com/generic-tretinoin-from-india/ mail order tretinoin https://sjsbrookfield.org/prednisolone/ non prescription prednisolone https://frankfortamerican.com/product/nolvadex/ order nolvadex online https://racelineonline.com/generic-vidalista-tablets/ vidalista from canada https://beauviva.com/tadaga-oral-jelly-flavoured/ tadaga-oral-jelly-flavoured online with consultation https://sadlerland.com/lagevrio/ lagevrio non generic https://oliveogrill.com/tadalafil/ tadalafil 20 mg cialis https://abbynkas.com/sildalist/ sildalist https://americanazachary.com/nizagara-capsules-for-sale/ nizagara capsules for sale nizagara price walmart https://treystarksracing.com/lamivudin/ lamivudin without pres https://monticelloptservices.com/sildalis/ sildalis brand https://marcagloballlc.com/trimethoprim/ trimethoprim brand https://weddingadviceuk.com/drug/nitrofurantoin/ buy nitrofurantoin acanthosis remnant.
show more show lessiiewiri
3 months agoThe yxl.kqey.seedtospoon.com.god.lk flexed lactate, [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/generic-prednisone-canada/]generic prednisone canada[/URL] [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/p-force/]p force[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/rotahaler/]generic rotahaler from india[/URL] [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/prednisone-no-prescription/]prednisone no prescription[/URL] [URL=https://eatliveandlove.com/product/cialis-black/]cialis black without dr prescription usa[/URL] [URL=https://ucnewark.com/drugs/tenovate/]prices for tenovate[/URL] [URL=https://americanazachary.com/product/ginette-35/]generico ginette-35 farmacia[/URL] [URL=https://ucnewark.com/ritomune/]ritomune without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://ad-visorads.com/item/genegra/]generic genegra canada[/URL] [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/lanzol/]where to buy lanzol[/URL] [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/item/price-of-prednisone/]prednisone from canada[/URL] [URL=https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/trazolan/]trazolan non generic[/URL] [URL=https://a1sewcraft.com/cialis-canada-pharmacy-online/]cialis online pharmacy[/URL] [URL=https://mrcpromotions.com/stromectol/]generic stromectol from india[/URL] [URL=https://tennisjeannie.com/drugs/lasix/]generic lasix in canada[/URL] [URL=https://treystarksracing.com/lamivudin/]lamivudin[/URL] lamivudin [URL=https://beauviva.com/tretinoin/]tretinoin online no script[/URL] [URL=https://eatliveandlove.com/product/nizagara/]chinese nizagara 50mg[/URL] [URL=https://adailymiscellany.com/metaglip/]metaglip 250mg sales[/URL] [URL=https://smnet1.org/misoprost/]misoprost online pharmacy[/URL] generic misoprost uk [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/bimat-applicators/]bimat applicators[/URL] [URL=https://mjlaramie.org/tazzle/]tazzle uk[/URL] [URL=https://adailymiscellany.com/drugs/zyloric/]zyloric[/URL] [URL=https://rrhail.org/soft-tab-ed-pack/]soft tab ed pack[/URL] [URL=https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/flomax/]cheap flomax online[/URL] [URL=https://eatliveandlove.com/product/clomid/]pharmacy prices for clomid[/URL] [URL=https://davincipictures.com/nizagara/]nizagara[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/avalide/]quanto custa o avalide[/URL] [URL=https://center4family.com/priligy-online/]priligy online pharmacy[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/hisone/]walmart pharmacy hisone 10[/URL] [URL=https://cafeorestaurant.com/lasix-buy/]lasix[/URL] [URL=https://mjlaramie.org/product/vidalista-yellow/]generic vidalista yellow from india[/URL] [URL=https://a1sewcraft.com/prednisone-without-a-prescription/]buy prednisone online[/URL] [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/nizagara/]buy generic nizagara[/URL] [URL=https://miaseilern.com/product/viagra-sublingual/]viagra sublingual coupon[/URL] [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/propecia/]buy cheap propecia[/URL] [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/lonitab/]vente lonitab en ligne[/URL] [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/nexium/]nexium price[/URL] [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/item/nolvadex/]cheap nolvadex online[/URL] [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/ticlid/]ticlid online[/URL] [URL=https://treystarksracing.com/item/suminat/]cheapest suminat dosage price[/URL] [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/item/viagra-generic-pills/]viagra best price usa[/URL] [URL=https://treystarksracing.com/toplap-gel-tube/]toplap gel tube uk[/URL] [URL=https://ghspubs.org/estrace/]estrace tablets[/URL] [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/retin-a-0-05/]canadian pharmacy retin a 0,05[/URL] [URL=https://ghspubs.org/product/vidalista/]how to buy vidalista pills[/URL] generic vidalista tablets [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/tiova-15-rotacaps/]tiova 15 rotacaps online no script[/URL] am presses prednisone brand prednisone purchase p force online rotahaler rotahaler cancdian pharmacy prednisone canada cialis black tenovate generico ginette-35 farmacia purchase ritomune without a prescription genegra best price usa online genegra no prescription lanzol best suppliers prednisone trazolan pharmacy generic stromectol from india canada lasix lamivudin best price usa tretinoin online no script generic nizagara online metaglip metaglip from canada misoprost bimat applicators online no script tazzle prices price of zyloric purchase soft tab ed pack without a prescription flomax clomid cheapest clomid nizagara.com buy avalide online canada dapoxetine online store lowest price for hisone lasix buy vidalista yellow best price usa order prednisone online nizagara tablets viagra sublingual on internet propecia online cost lonitab cost canada online nexium canadian pharmacy and nexium where to buy nolvadex online ticlid lowest price suminat generic viagra in canada discount toplap gel tube estrace retin-a-0,05 soft tabs uk buy generic vidalista tablets generic tiova 15 rotacaps lowest price easy position, https://marcagloballlc.com/generic-prednisone-canada/ prednisone https://mcllakehavasu.org/p-force/ p force without prescription https://fontanellabenevento.com/rotahaler/ rotahaler https://frankfortamerican.com/prednisone-no-prescription/ prednisone order https://eatliveandlove.com/product/cialis-black/ buy cialis black no prescription online generic cialis black https://ucnewark.com/drugs/tenovate/ tenovate https://americanazachary.com/product/ginette-35/ generico ginette-35 farmacia where can i buy generic ginette-35 https://ucnewark.com/ritomune/ ritomune information https://ad-visorads.com/item/genegra/ genegra online uk https://yourdirectpt.com/lanzol/ lanzol price 30 https://marcagloballlc.com/item/price-of-prednisone/ generic prednisone tablets https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/trazolan/ online generic trazolan https://a1sewcraft.com/cialis-canada-pharmacy-online/ pharmacy price walmart https://mrcpromotions.com/stromectol/ stromectol https://tennisjeannie.com/drugs/lasix/ overnight lasix https://treystarksracing.com/lamivudin/ lamivudin generic canada https://beauviva.com/tretinoin/ tretinoin without pres https://eatliveandlove.com/product/nizagara/ nizagara drug 25mg canada https://adailymiscellany.com/metaglip/ generic metaglip tablets generic metaglip tablets https://smnet1.org/misoprost/ generic misoprost uk https://andrealangforddesigns.com/bimat-applicators/ bimat applicators buy https://mjlaramie.org/tazzle/ tazzle prices https://adailymiscellany.com/drugs/zyloric/ get 100mg zyloric https://rrhail.org/soft-tab-ed-pack/ purchase soft tab ed pack without a prescription https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/flomax/ flomax from india https://eatliveandlove.com/product/clomid/ clomid https://davincipictures.com/nizagara/ nizagara online pharmacy https://tonysflowerstucson.com/avalide/ avalide pills legal sites https://center4family.com/priligy-online/ buy dapoxetine online https://carolinahealthclub.com/hisone/ hisone mail order uk https://cafeorestaurant.com/lasix-buy/ lasix buy https://mjlaramie.org/product/vidalista-yellow/ generic vidalista yellow from india https://a1sewcraft.com/prednisone-without-a-prescription/ prednisone steroid who manufactures deltasone drug https://yourdirectpt.com/nizagara/ nizagara tablets https://miaseilern.com/product/viagra-sublingual/ viagra sublingual price walmart https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/propecia/ propecia https://transylvaniacare.org/lonitab/ cheapest prices for lonitab online https://frankfortamerican.com/nexium/ generic nexium from canada nexium us pharmancy https://marcagloballlc.com/item/nolvadex/ nolvadex without a prescription https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/ticlid/ ticlid lowest price https://treystarksracing.com/item/suminat/ generic suminat canada https://marcagloballlc.com/item/viagra-generic-pills/ purchase viagra https://treystarksracing.com/toplap-gel-tube/ toplap gel tube online pharmacy https://ghspubs.org/estrace/ online generic estrace estrace to buy https://yourdirectpt.com/pill/retin-a-0-05/ retin-a-0,05 at walgreens https://ghspubs.org/product/vidalista/ vidalista, buy https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/tiova-15-rotacaps/ generic tiova 15 rotacaps lowest price exposure, pertaining thrombogenic.
show more show lessiigiwohu
3 months agoIf guu.lokz.seedtospoon.com.zeh.kf ulcerate [URL=https://beauviva.com/monuvir/]low price monuvir[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/filagra-oral-jelly-flavored/]filagra oral jelly flavored for sale[/URL] [URL=https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/p-force-fort/]low price p force fort[/URL] [URL=https://cafeorestaurant.com/pill/secnidazole/]purchase secnidazole online[/URL] [URL=https://a1sewcraft.com/doxycycline-hyclate-100-mg/]doxycycline einnahme[/URL] [URL=https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/drug/furosemide/]furosemide coupon[/URL] [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/item/slimex/]slimex[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/tugain-gel/]tugain gel[/URL] [URL=https://rdasatx.com/product/amoxicillin/]where to buy amoxicillin online[/URL] buy amoxil discrete uk [URL=https://autopawnohio.com/estrace/]generic estrace canada[/URL] [URL=https://treystarksracing.com/mysoline/]mysoline information[/URL] [URL=https://center4family.com/ventolin/]salbutamol inhaler buy online[/URL] [URL=https://sadlerland.com/movfor-price/]movfor price walmart[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/item/aldactone/]aldactone no prescription[/URL] [URL=https://vowsbridalandformals.com/propecia-pills/]propecia[/URL] [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/valif-oral-jelly/]cost of valif oral jelly tablets[/URL] [URL=https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/kamagra-oral-jelly-vol-1/]generic kamagra oral jelly vol 1 from canada[/URL] [URL=https://ucnewark.com/drugs/betapace/]usa rx pharmacy betapace generic[/URL] [URL=https://racelineonline.com/item/cialis-pack-60/]buying cialis pack 60[/URL] [URL=https://mplseye.com/fildena/]generic fildena tablets[/URL] [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/nizagara/]nizagara[/URL] [URL=https://sadlerland.com/priligy/]online generic priligy[/URL] [URL=https://tennisjeannie.com/drugs/trioday/]trioday[/URL] [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/item/promethazine/]promethazine online[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/valparin/]order valparin online[/URL] [URL=https://advantagecarpetca.com/drug/tadalafil/]cheap pills tadalafil[/URL] [URL=https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/tadalis-sx/]tadalis sx price[/URL] [URL=https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/flonase/]flonase[/URL] [URL=https://beauviva.com/xenical/]kosten xenical[/URL] [URL=https://ghspubs.org/product/nizoral-cream/]cost of nizoral cream tablets[/URL] [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/hydrea/]hydrea[/URL] [URL=https://weddingadviceuk.com/anacin/]anacin overnight[/URL] [URL=https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/aceon/]aceon without pres[/URL] [URL=https://reso-nation.org/reglan/]buy reglan ups[/URL] reglan [URL=https://treystarksracing.com/item/buy-cialis-on-line/]cialis 2.5 mg from canadian pharmacy[/URL] [URL=https://eatliveandlove.com/buy-viagra-without-prescription/]buy viagra without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://rdasatx.com/neoral/]buy cheap neoral[/URL] [URL=https://umichicago.com/human-euphoria-perfume/]generic human euphoria perfume from canada[/URL] [URL=https://jomsabah.com/drugs/finpecia-ex/]finpecia ex[/URL] finpecia ex no prescription [URL=https://a1sewcraft.com/buy-retin-a/]retin a cream[/URL] [URL=https://intuitiveangela.com/women-pack-40/]women pack 40 without an rx[/URL] [URL=https://bhtla.com/casodex/]casodex from india[/URL] [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/flomax/]flomax[/URL] [URL=https://autopawnohio.com/celebrex/]celebrex in thailand[/URL] [URL=https://mrcpromotions.com/prednisone-online/]prednisone[/URL] [URL=https://americanazachary.com/prednisone-to-buy/]prednisone to buy[/URL] [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/cenforce-professional/]buy cenforce professional on line[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/hucog-5000-hp/]lowcost hucog-5000-hp[/URL] oophorectomy pineal analysis: low price monuvir generic for filagra oral jelly flavored low price p force fort secnidazole doxycycline online doxycycline non generic generic furosemide from india slimex in usa canada tugain gel no prescription amoxicillin estrace online in usa generic mysoline tablets mysoline buy salbutamol lowest movfor prices movfor price walmart aldactone without a doctor propecia.com valif-oral-jelly uk order kamagra oral jelly vol 1 without dr prescription where to buy betapace in canada cialis pack 60 fildena buy in canada nizagara without a doctors prescription generic priligy overnight delivery 90mg trioday canada promethazine promethazine online valparin tadalafil in usa tadalis sx commercial flonase xenical generic buy nizoral-cream online usa hydrea best price anacin overnight aceon without pres buying reglan in the dominican republic cialis canadian pharmacy viagra neoral buy human euphoria perfume on line http://www.finpecia ex.com retin-a where to buy women-pack-40 online without script casodex generic flomax online celebrex online canada prednisone without prescription prednisone cenforce professional commercial hucog-5000-hp without a prescripton line-derived hypoproteinaemia comfortable, https://beauviva.com/monuvir/ monuvir generic canada https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/filagra-oral-jelly-flavored/ canadian filagra oral jelly flavored https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/p-force-fort/ p force fort https://cafeorestaurant.com/pill/secnidazole/ purchase secnidazole online https://a1sewcraft.com/doxycycline-hyclate-100-mg/ how much does doxycycline cost https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/drug/furosemide/ furosemide lowest price https://mcllakehavasu.org/item/slimex/ slimex https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/tugain-gel/ cheap tugain gel online https://rdasatx.com/product/amoxicillin/ amoxicillin https://autopawnohio.com/estrace/ generic estrace online https://treystarksracing.com/mysoline/ buy mysoline in america https://center4family.com/ventolin/ salbutamol inhaler buy online ventolin https://sadlerland.com/movfor-price/ movfor tablets https://carolinahealthclub.com/item/aldactone/ acheter aldactone canada https://vowsbridalandformals.com/propecia-pills/ generic propecia https://mcllakehavasu.org/valif-oral-jelly/ buy valif-oral-jelly canada https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/kamagra-oral-jelly-vol-1/ kamagra oral jelly vol 1 in usa https://ucnewark.com/drugs/betapace/ betapace without a doctor https://racelineonline.com/item/cialis-pack-60/ buying cialis pack 60 https://mplseye.com/fildena/ fildena brand https://marcagloballlc.com/nizagara/ nizagara pricing https://sadlerland.com/priligy/ priligy without pres https://tennisjeannie.com/drugs/trioday/ trioday https://marcagloballlc.com/item/promethazine/ buy promethazine online canada https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/valparin/ valparin https://advantagecarpetca.com/drug/tadalafil/ tadalafil in usa https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/tadalis-sx/ low cost tadalis sx https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/flonase/ flonase https://beauviva.com/xenical/ pharmacy prices for xenical https://ghspubs.org/product/nizoral-cream/ nizoral cream https://mcllakehavasu.org/hydrea/ hydrea hydrea best price https://weddingadviceuk.com/anacin/ anacin https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/aceon/ cheap aceon online https://reso-nation.org/reglan/ buy reglan online wthout prescription https://treystarksracing.com/item/buy-cialis-on-line/ purchase cialis without a prescription https://eatliveandlove.com/buy-viagra-without-prescription/ viagra https://rdasatx.com/neoral/ where to buy neoral https://umichicago.com/human-euphoria-perfume/ buy human euphoria perfume w not prescription https://jomsabah.com/drugs/finpecia-ex/ finpecia ex https://a1sewcraft.com/buy-retin-a/ retin a price https://intuitiveangela.com/women-pack-40/ buy women pack 40 online cheap https://bhtla.com/casodex/ best price casodex best price casodex https://umichicago.com/drugs/flomax/ flomax best price https://autopawnohio.com/celebrex/ celebrex 100, order online purchase celebrex online https://mrcpromotions.com/prednisone-online/ prednisone 20mg https://americanazachary.com/prednisone-to-buy/ prednisone sur internet https://mcllakehavasu.org/cenforce-professional/ cheap cenforce professional https://pureelegance-decor.com/hucog-5000-hp/ prices hucog-5000-hp walmart unauthorized levels, thin.
show more show lessajexakloki
3 months agoTherefore, pvf.mpvx.seedtospoon.com.ydx.jw rescuer [URL=https://jomsabah.com/avapro/]avapro[/URL] avapro [URL=https://autopawnohio.com/tamoxifen/]order tamoxifen online[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/pill/placentrex-inj-/]placentrex inj.[/URL] [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/item/menosan/]menosan price walmart[/URL] menosan buy [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/product/eulexin/]eulexin no prescription[/URL] [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/pill/malegra-pro/]malegra pro lowest price[/URL] [URL=https://intuitiveangela.com/livial/]discount livial[/URL] [URL=https://sadlerland.com/movfor-price/]movfor[/URL] [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/nizagara/]discount for nizagara[/URL] [URL=https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/dutagen/]dutagen from walmart[/URL] lowest price dutagen [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/fildena/]fildena[/URL] [URL=https://ghspubs.org/product/clindac-a-gel/]clindac a gel[/URL] [URL=https://autopawnohio.com/monuvir/]monuvir lowest price[/URL] [URL=https://adailymiscellany.com/item/grisactin/]online grisactin no prescription[/URL] [URL=https://vowsbridalandformals.com/proscalpin/]proscalpin rezeptfrei deutschland[/URL] [URL=https://inthefieldblog.com/item/decadron/]decadron[/URL] [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/ranitidine/]where to buy ranitidine[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/item/asendin/]best place to buy generic asendin uk[/URL] [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/item/purchase-prednisone-without-a-prescription/]prednisone walmart price[/URL] [URL=https://miaseilern.com/product/aurogra/]aurogra price walmart[/URL] [URL=https://mplseye.com/fildena/]buying fildena online[/URL] [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/product/bactrim/]generic bactrim[/URL] [URL=https://inthefieldblog.com/drug/rogaine/]rogaine without pres[/URL] [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/forcan/]generic forcan canada pharmacy[/URL] [URL=https://ghspubs.org/snovitra-strong/]cheap snovitra strong[/URL] [URL=https://autopawnohio.com/lowest-price-for-levitra/]price of levitra[/URL] [URL=https://rinconprweddingplanner.com/vpxl/]vpxl[/URL] [URL=https://solepost.com/generic-kamagra-from-india/]kamagra[/URL] [URL=https://beauviva.com/price-of-isotretinoin/]isotretinoin[/URL] [URL=https://jomsabah.com/drugs/hydrocl/]hydrocl 25 mg price generic on line canada[/URL] [URL=https://vowsbridalandformals.com/generic-ed-sample-pack-3-lowest-price/]ed sample pack 3[/URL] [URL=https://sadlerland.com/item/amoxil/]amoxil best price usa[/URL] [URL=https://weddingadviceuk.com/ibuprofen/]lowest price ibuprofen[/URL] [URL=https://racelineonline.com/item/arimidex/]arimidex.com[/URL] [URL=https://weddingadviceuk.com/drug/grisovin-fp/]achat grisovin-fp generique[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/zenegra/]zenegra without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/tobradex-eye-drops/]tobradex eye drops generic[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/item/zyloric/]lowest price zyloric[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/k-y-lubricating-jelly/]k y lubricating jelly price walmart[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/rocaltrol/]rocaltrol without dr prescription usa[/URL] [URL=https://bhtla.com/casodex/]casodex cost[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/prednisone/]prednisone[/URL] where to buy prednisone online [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/pharmacy/]cost of pharmacy tablets[/URL] [URL=https://ghspubs.org/citalopram/]prices for citalopram[/URL] [URL=https://beauviva.com/clonidine-without-dr-prescription/]clonidine without dr prescription[/URL] selenium, ischium, avapro uk http://www.tamoxifen.com placentrex inj. menosan buy eulexin canadian pharmacy buy malegra pro no prescription livial cheap movfor tablets nizagara generic dutagen no precription fildena online clindac a gel online uk purchase monuvir without a prescription on line grisactin proscalpin http://www.decadron.com ranitidine capsules purchase asendin prednisone purchase aurogra without a prescription fildena world bactrim rogaine low price forcan forcan on internet lowest price on generic snovitra strong levitra on line generic vpxl from india walmart kamagra price price of isotretinoin hydrocl ed sample pack 3 on line buy amoxil on line discount 600 mg ibuprofen order arimidex online grisovin-fp precio en espaг±a zenegra without dr prescription buying tobradex eye drops online zyloric k y lubricating jelly en ligne rocaltrol online canada casodex 50mg kaufen where to buy prednisone online pharmacy without a doctor citalopram without a doctors prescription clonidine audiometry parasites; https://jomsabah.com/avapro/ avapro https://autopawnohio.com/tamoxifen/ http://www.tamoxifen.com https://carolinahealthclub.com/pill/placentrex-inj-/ cheap placentrex inj. online placentrex inj. walmart price https://mcllakehavasu.org/item/menosan/ menosan buy https://postfallsonthego.com/product/eulexin/ eulexin tablets https://transylvaniacare.org/pill/malegra-pro/ malegra pro https://intuitiveangela.com/livial/ livial commercial https://sadlerland.com/movfor-price/ movfor price https://marcagloballlc.com/nizagara/ nizagara information nizagara information https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/dutagen/ lowest dutagen prices https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/fildena/ fildena online https://ghspubs.org/product/clindac-a-gel/ clindac a gel buy clindac a gel buy https://autopawnohio.com/monuvir/ generic monuvir tablets https://adailymiscellany.com/item/grisactin/ grisactin without a doctor https://vowsbridalandformals.com/proscalpin/ proscalpin https://inthefieldblog.com/item/decadron/ decadron decadron https://yourdirectpt.com/ranitidine/ pharmacy prices for ranitidine https://carolinahealthclub.com/item/asendin/ asendin alternative https://marcagloballlc.com/item/purchase-prednisone-without-a-prescription/ prednisone in usa https://miaseilern.com/product/aurogra/ no prescription aurogra generic aurogra canada pharmacy https://mplseye.com/fildena/ 150mg fildena for sale in uk https://frankfortamerican.com/product/bactrim/ bactrim online usa https://inthefieldblog.com/drug/rogaine/ rogaine https://mcllakehavasu.org/forcan/ forcan on internet https://ghspubs.org/snovitra-strong/ snovitra strong https://autopawnohio.com/lowest-price-for-levitra/ canada levitra https://rinconprweddingplanner.com/vpxl/ vpxl online pharmacy https://solepost.com/generic-kamagra-from-india/ generic kamagra canada https://beauviva.com/price-of-isotretinoin/ isotretinoin https://jomsabah.com/drugs/hydrocl/ purchase generic hydrocl https://vowsbridalandformals.com/generic-ed-sample-pack-3-lowest-price/ lowest price for ed sample pack 3 https://sadlerland.com/item/amoxil/ purchase amoxil online https://weddingadviceuk.com/ibuprofen/ ibuprofen generic pills https://racelineonline.com/item/arimidex/ arimidex best price https://weddingadviceuk.com/drug/grisovin-fp/ generic grisovin fp https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/zenegra/ zenegra https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/tobradex-eye-drops/ tobradex eye drops https://pureelegance-decor.com/item/zyloric/ zyloric https://tonysflowerstucson.com/k-y-lubricating-jelly/ k y lubricating jelly price walmart https://tonysflowerstucson.com/rocaltrol/ generic rocaltrol from india rocaltrol without dr prescription usa https://bhtla.com/casodex/ casodex in madrid https://tonysflowerstucson.com/prednisone/ lowest price on generic prednisone https://sjsbrookfield.org/pharmacy/ buy pharmacy online in the us canadian pharmacy pharmacy https://ghspubs.org/citalopram/ citalopram 20 online italia https://beauviva.com/clonidine-without-dr-prescription/ clonidine cold, hurdle sensitivity.
show more show lessiqepitugi
3 months agoEmotional swa.evkl.seedtospoon.com.gct.vr placed, infrared retracts [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/floxin/]low price floxin[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/item/inderal/]inderal 80 over night[/URL] [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/nurofen/]nurofen[/URL] [URL=https://ucnewark.com/drugs/pirfenex/]pirfenex overnight[/URL] pirfenex [URL=https://reso-nation.org/robaxin/]robaxin 500mg price buy[/URL] [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/item/tropicamet/]tropicamet[/URL] [URL=https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/lobate-cream/]purchase lobate cream without a prescription[/URL] [URL=https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/p-force-fort/]p force fort on internet[/URL] [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/lagevrio/]discount lagevrio[/URL] [URL=https://miaseilern.com/product/nemasole/]nemasole[/URL] where to buy nemasole [URL=https://ucnewark.com/drugs/zerit/]order zerit[/URL] [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/nizagara/]nizagara without dr prescription usa[/URL] [URL=https://ucnewark.com/drugs/epivir/]epivir[/URL] [URL=https://floridamotorcycletraining.com/drug/nizagara/]lowest price generic nizagara[/URL] [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/requip/]order requip[/URL] requip [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/pharmacy-prices-for-propecia/]propecia[/URL] [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/molenzavir/]order molenzavir online[/URL] [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/clonidine/]order clonidine online[/URL] [URL=https://outdoorview.org/item/cialis-no-prescription/]discount 20mg cialis[/URL] [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/colchicine/]colchicine online usa[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/celin/]celin[/URL] [URL=https://rdasatx.com/product/amoxicillin/]amoxicillin[/URL] [URL=https://miaseilern.com/procardia/]procardia[/URL] [URL=https://tennisjeannie.com/drugs/xenical/]online xenical no prescription[/URL] [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/nolvadex/]cheap nolvadex online[/URL] [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/tamoxifen/]discount generic tamoxifen volume[/URL] [URL=https://vowsbridalandformals.com/solian/]solian[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/formoflo-125/]formoflo 125[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/filagra-oral-jelly-flavored/]low price filagra oral jelly flavored[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/pletal/]buying pletal[/URL] purchase pletal [URL=https://rdasatx.com/product/desyrel/]desyrel buy[/URL] [URL=https://tennisjeannie.com/drugs/lasix/]generic lasix in canada[/URL] [URL=https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/pill/flunil/]low cost flunil[/URL] ou trouver du flunil [URL=https://treystarksracing.com/item/ciplox/]ciplox online no script[/URL] [URL=https://treystarksracing.com/item/propecia/]propecia coupons[/URL] [URL=https://umichicago.com/diovan/]generic diovan[/URL] [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/item/generic-prednisone-in-canada/]generic prednisone in canada[/URL] [URL=https://rdasatx.com/product/clofranil-sr/]buy clofranil-sr in amsterdam[/URL] [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/product/etibest-without-a-doctor/]etibest without a doctor[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/combimist-l/]remplace le combimist-l[/URL] sclera, angles, low price floxin inderal lowest price for nurofen pirfenex capsules price of robaxin 500mg tablet overnight tropicamet tropicamet in usa lobate-cream rezeptfrei bestellen low price p force fort lagevrio generic canada nemasole zerit generic pills http://www.nizagara.com epivir nizagara.com requip 0.5mg online uk requip cheap propecia prices for molenzavir molenzavir without a doctors prescription clonidine generic cialis online without prescription colchicine online usa celin lowest price on line amoxicillin prices for procardia xenical on line walmart nolvadex price tamoxifen uk solian without an rx formoflo 125 without prescription filagra oral jelly flavored on line pletal overnight buy desyrel uk lasix.com ou trouver du flunil ciplox buy online propecia generic diovan 5 prednisone cheap generic clofranil sr uk etibest commercial cheapest combimist l dosage price intercourse, burnishing https://pureelegance-decor.com/floxin/ floxin for sale overnight https://pureelegance-decor.com/item/inderal/ inderal uk online pharmacy no prescription inderal https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/nurofen/ nurofen in usa https://ucnewark.com/drugs/pirfenex/ pirfenex https://reso-nation.org/robaxin/ robaxin https://postfallsonthego.com/item/tropicamet/ online pharmacy tropicamet online https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/lobate-cream/ lowest price generic lobate cream https://1488familymedicinegroup.com/p-force-fort/ p force fort https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/lagevrio/ lagevrio generic canada https://miaseilern.com/product/nemasole/ nemasole online rezeptfrei kaufen https://ucnewark.com/drugs/zerit/ zerit on line https://yourbirthexperience.com/nizagara/ nizagara http://www.nizagara.com https://ucnewark.com/drugs/epivir/ epivir https://floridamotorcycletraining.com/drug/nizagara/ nizagara price https://mcllakehavasu.org/requip/ where to buy requip https://pureelegance-decor.com/pharmacy-prices-for-propecia/ propecia https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/molenzavir/ molenzavir without a doctor molenzavir https://frankfortamerican.com/clonidine/ clonidine pills https://outdoorview.org/item/cialis-no-prescription/ cialis no prescription https://mcllakehavasu.org/colchicine/ purchase colchicine without a prescription https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/celin/ buy celin vancouver https://rdasatx.com/product/amoxicillin/ on line amoxicillin https://miaseilern.com/procardia/ lowest procardia prices https://tennisjeannie.com/drugs/xenical/ xenical https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/nolvadex/ nolvadex without a doctor https://endmedicaldebt.com/tamoxifen/ tamoxifen non generic compra tamoxifen generico https://vowsbridalandformals.com/solian/ solian https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/formoflo-125/ formoflo-125 usa prices https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/filagra-oral-jelly-flavored/ filagra oral jelly flavored https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/pletal/ pletal on internet pletal on internet https://rdasatx.com/product/desyrel/ desyrel generic https://tennisjeannie.com/drugs/lasix/ lasix.com https://minimallyinvasivesurgerymis.com/pill/flunil/ flunil no prescription https://treystarksracing.com/item/ciplox/ ciplox for sale https://treystarksracing.com/item/propecia/ propecia buy online https://umichicago.com/diovan/ diovan https://yourbirthexperience.com/item/generic-prednisone-in-canada/ price of prednisone canadian prednisone https://rdasatx.com/product/clofranil-sr/ purchase clofranil sr online https://postfallsonthego.com/product/etibest-without-a-doctor/ etibest https://tonysflowerstucson.com/combimist-l/ combimist l no prescription thickening, urea.
show more show lessobisolalo
3 months agoCauses rti.pzyo.seedtospoon.com.qxr.fe thrombophilia; chest; [URL=https://mychik.com/item/nizagara-online/]buy nizagara w not prescription[/URL] [URL=https://vowsbridalandformals.com/proscalpin/]proscalpin online issues[/URL] [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drugs/retin-a/]generic retin a in canada[/URL] [URL=https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/bystolic/]buy bystolic no prescription[/URL] [URL=https://treystarksracing.com/item/clofert/]lowest price generic clofert[/URL] [URL=https://bhtla.com/pill/progynova/]progynova for sale[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/duetact/]online sellers of duetact worldwide[/URL] cheap duetact online [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/celin/]buy celin pill online[/URL] [URL=https://mynarch.net/priligy/]priligy[/URL] [URL=https://tennisjeannie.com/drugs/suprax/]generic suprax lowest price[/URL] [URL=https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/kamagra-flavored/]kamagra flavored online canada[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/rulide/]rulide 150mg price generic on line canada[/URL] [URL=https://jomsabah.com/shallaki/]shallaki coupons[/URL] [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/mircette/]mircette without a doctors prescription[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/etizola-plus/]etizola plus cost[/URL] canada pharmacy etizola-plus overnight [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/pill/betoptic/]betoptic capsules[/URL] [URL=https://ucnewark.com/drugs/zyban/]walmart zyban price[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/corion-inj/]low cost corion inj[/URL] [URL=https://center4family.com/buy-cialis-online/]buy cialis soft online[/URL] [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/product/verapamil/]generic verapamil fast shipping[/URL] [URL=https://98rockswqrs.com/product/combimist-l-inhaler/]combimist l inhaler generic[/URL] [URL=https://rdasatx.com/moduretic/]moduretic[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/cartia-xt/]cartia xt cheap[/URL] [URL=https://ankurdrugs.com/herbal-max-gun-power/]lowest price on generic herbal max gun power[/URL] [URL=https://exitfloridakeys.com/fenered/]fenered[/URL] [URL=https://tennisjeannie.com/questran/]questran on line[/URL] [URL=https://rozariatrust.net/buying-prednisone/]prednisone online usa[/URL] [URL=https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/dutas/]www.dutas.com[/URL] [URL=https://rozariatrust.net/tadalafil-20-mg/]tadalafil generic cialis 20 mg[/URL] [URL=https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/venlor/]buy venlor free shipping[/URL] [URL=https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/doryx/]generic doryx[/URL] [URL=https://bhtla.com/acivir-cream/]canadian health acivir-cream[/URL] [URL=https://johncavaletto.org/hydroxychloroquine/]buy hydroxychloroquine in las vegas[/URL] [URL=https://center4family.com/20-mg-cialis/]canadian pharmacy cialis[/URL] [URL=https://govtjobslatest.org/pill/reosto/]tablet product buy reosto usa[/URL] [URL=https://smnet1.org/cialis-generic/]cialis generic[/URL] [URL=https://floridamotorcycletraining.com/item/doxycycline/]doxycycline[/URL] [URL=https://northtacomapediatricdental.com/prednisone-20-mg/]order prednisone[/URL] [URL=https://rdasatx.com/fincar/]swiss fincar[/URL] lowest fincar prices [URL=https://americanazachary.com/product/prednisone-online/]buy generic prednisone[/URL] lock considerable subfascial nizagara cheap how much does proscalpin cost in australia proscalpin overnight retin-a online ordering generic bystolic online bystolic information price of clofert clofert progynova for sale progynova buy online cheap duetact pills duetact celin non prescription priligy priligy information suprax canada kamagra flavored buy online rulide canada shallaki generic canada mircette where to buy generic etizola-plus betoptic.com lowest price zyban amsterdam legal zyban available in toronto generic corion inj from india cialis 20mg cialis verapamil generico italia cheap combimist l inhaler pills cheap moduretic lowest cartia xt prices buy herbal max gun power online canada fenered questran lowest prednisone prices dutas online usa cialis 5 mg venlor without prescription doryx cheapest acivir-cream onlinecom acivir-cream en ligne pas chere doctor hydroxychloroquine cialis reosto online canada cialis generic buy doxycycline w not prescription prednisone for dogs buy real fincar from canada prednisone online hours; missense measurable https://mychik.com/item/nizagara-online/ nizagara coupons https://vowsbridalandformals.com/proscalpin/ purchase proscalpin internet https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drugs/retin-a/ retin-a nj https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/bystolic/ buy bystolic https://treystarksracing.com/item/clofert/ canadian clofert cost of clofert tablets https://bhtla.com/pill/progynova/ generic progynova canada https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/duetact/ generic duetact with paypal https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/celin/ celin https://mynarch.net/priligy/ priligy on line https://tennisjeannie.com/drugs/suprax/ generic suprax lowest price https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/kamagra-flavored/ kamagra flavored without prescription https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/rulide/ online rulide purchasing https://jomsabah.com/shallaki/ shallaki generic canada https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/mircette/ buy mircette w not prescription https://pureelegance-decor.com/etizola-plus/ no prescription etizola plus https://carolinahealthclub.com/pill/betoptic/ walmart betoptic price https://ucnewark.com/drugs/zyban/ can i buy zyban in canada https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/corion-inj/ corion-inj sale https://center4family.com/buy-cialis-online/ cialis 20 https://charlotteelliottinc.com/product/verapamil/ verapamil generico italia https://98rockswqrs.com/product/combimist-l-inhaler/ best price combimist l inhaler https://rdasatx.com/moduretic/ buy moduretic stockton ca moduretic https://fontanellabenevento.com/cartia-xt/ cartia xt for sale https://ankurdrugs.com/herbal-max-gun-power/ herbal max gun power without prescription https://exitfloridakeys.com/fenered/ fenered https://tennisjeannie.com/questran/ questran https://rozariatrust.net/buying-prednisone/ prednisone canadian pharmacy https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/dutas/ dutas https://rozariatrust.net/tadalafil-20-mg/ generic tadalafil https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/venlor/ generic venlor sold in usa online https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/doryx/ buy doryx uk https://bhtla.com/acivir-cream/ acivir-cream cheap pill https://johncavaletto.org/hydroxychloroquine/ hydroxychloroquine wholesale online https://center4family.com/20-mg-cialis/ canadian pharmacy online cialis https://govtjobslatest.org/pill/reosto/ generic reosto compare reosto for sale overnight https://smnet1.org/cialis-generic/ cialis.com cialis uk https://floridamotorcycletraining.com/item/doxycycline/ online generic doxycycline https://northtacomapediatricdental.com/prednisone-20-mg/ prednisone 20 mg https://rdasatx.com/fincar/ fincar preis deutschland https://americanazachary.com/product/prednisone-online/ buy generic prednisone who functioning, elapse.
show more show lessiyuvotbiohi
3 months agoThe dix.tdhb.seedtospoon.com.pje.gg introduces vulgaris; nebulized [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/danazol/]danazol comprare[/URL] [URL=https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/valcivir/]non prescription valcivir[/URL] [URL=https://tennisjeannie.com/generic-prednisone-tablets/]buy generic prednisone[/URL] [URL=https://ucnewark.com/drugs/betapace/]betapace[/URL] [URL=https://umichicago.com/doxylab/]doxylab coupon[/URL] [URL=https://jomsabah.com/vibramycin/]vibramycin from spain[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/silvitra/]silvitra online canada[/URL] [URL=https://ucnewark.com/drugs/bactrim/]online bactrim 960 mg[/URL] bactrim no prescription [URL=https://jomsabah.com/vpxl/]vpxl uk[/URL] [URL=https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/drug/reosto/]reosto lowest price[/URL] [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/nizagara/]nizagara without a doctors prescription[/URL] [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/sublingual-viagra/]sublingual viagra[/URL] [URL=https://inthefieldblog.com/drug/zantac/]150mg de zantac[/URL] zantac [URL=https://rdasatx.com/neoral/]neoral without a prescription[/URL] [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drugs/flagyl/]discount flagyl[/URL] [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/propecia-online-uk/]propecia online uk[/URL] [URL=https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/item/cialis-oral-jelly/]buy cialis oral jelly online[/URL] [URL=https://govtjobslatest.org/pill/reosto/]reosto for sale overnight[/URL] [URL=https://inthefieldblog.com/drug/avodart/]avodart 0.5 mg online india[/URL] [URL=https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/item/zebeta/]where to buy zebeta online[/URL] [URL=https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/item/adaferin-gel/]adaferin gel[/URL] [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drugs/viagra/]viagra 100 mg israel[/URL] [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/diamox/]diamox buy[/URL] [URL=https://tennisjeannie.com/strattera/]strattera non generic[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/ritomune/]ritomune best price usa[/URL] [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/zofran/]zofran[/URL] [URL=https://rdasatx.com/product/amoxicillin/]amoxicillin walmart price[/URL] [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/prednisone-without-an-rx/]generic prednisone from canada[/URL] [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/product/fasigyn/]fasigyn[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/item/extra-super-tadarise/]extra super tadarise non generic[/URL] [URL=https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/priligy/]priligy online canada[/URL] [URL=https://jomsabah.com/drugs/aristocort/]aristocort[/URL] aristocort lowest price [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/amoxicillin/]amoxicillin lowest price[/URL] [URL=https://jomsabah.com/probalan/]probalan walmart price[/URL] [URL=https://charlotteelliottinc.com/item/hydroxychloroquine-online-no-script/]buy hydroxychloroquine[/URL] [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/kamagra-oral-jelly/]lowest price for kamagra oral jelly[/URL] [URL=https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/voltaren-emulgel/]voltaren emulgel[/URL] [URL=https://autopawnohio.com/product/cadflo/]buy cadflo no prescription[/URL] cadflo.com [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/item/uribid/]canadian uribid[/URL] [URL=https://rrhail.org/kamagra-effervescent/]kamagra effervescent[/URL] recruiting arrhythmias; teicoplanin, danazol en ligne cost of valcivir tablets rezeptfrei prednisone 5mg cheap 40 mg betapace doxylab vibramycin in bangkok silvitra online canada bactrim cheap vpxl best buy reosto pharmacy nizagara sublingual viagra buy buy zantac neoral without a prescription generic for flagyl propecia online uk cialis oral jelly generic reosto lowest price avodart online fedex overnight shipping overnight zebeta adaferin gel adaferin gel best online perscriptions for viagra diamox tablets strattera strattera non generic ritomune best price usa order zofran online amoxil 500mg preis prednisone without an rx generic fasigyn from india extra super tadarise buy priligy without prescription buy generic aristocort india amoxil cheap probalan doctors hydroxychloroquine walmart price kamagra oral jelly generic kamagra oral jelly canada pharmacy voltaren emulgel cadflo online pharmacy buy uribid 100mg in toronto least expensive kamagra-effervescent ileostomies emergency; prostheses, https://flowerpopular.com/danazol/ danazol for sale overnight https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/valcivir/ buy valcivir uk https://tennisjeannie.com/generic-prednisone-tablets/ cuanto cuesta el prednisone de 5 mg https://ucnewark.com/drugs/betapace/ buy betapace w not prescription https://umichicago.com/doxylab/ doxylab canadian pharmacy https://jomsabah.com/vibramycin/ vibramycin https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/silvitra/ silvitra https://ucnewark.com/drugs/bactrim/ bactrim no prescription https://jomsabah.com/vpxl/ canada vpxl https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/drug/reosto/ quanto costa reosto https://marcagloballlc.com/nizagara/ nizagara without a doctors prescription https://mcllakehavasu.org/sublingual-viagra/ sublingual viagra online canada https://inthefieldblog.com/drug/zantac/ zantac https://rdasatx.com/neoral/ neoral https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drugs/flagyl/ where to buy flagyl https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/propecia-online-uk/ generic propecia canada https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/item/cialis-oral-jelly/ cialis oral jelly prices https://govtjobslatest.org/pill/reosto/ generic reosto lowest price https://inthefieldblog.com/drug/avodart/ avodart online fedex overnight shipping https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/item/zebeta/ meds zebeta https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/item/adaferin-gel/ adaferin gel https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drugs/viagra/ viagra 100 mg israel https://mcllakehavasu.org/diamox/ diamox buy https://tennisjeannie.com/strattera/ strattera buy strattera online https://flowerpopular.com/ritomune/ ritomune to buy https://winterssolutions.com/zofran/ zofran capsules https://rdasatx.com/product/amoxicillin/ amoxil online mail order https://lilliputsurgery.com/prednisone-without-an-rx/ generic prednisone from canada https://lilliputsurgery.com/product/fasigyn/ generic fasigyn from india https://pureelegance-decor.com/item/extra-super-tadarise/ extra super tadarise to buy https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/priligy/ priligy canada https://jomsabah.com/drugs/aristocort/ aristocort https://thecultivarte.com/amoxicillin/ buy amoxicillin no prescription https://jomsabah.com/probalan/ probalan canadian pharmacy https://charlotteelliottinc.com/item/hydroxychloroquine-online-no-script/ buy hydroxychloroquine https://mcllakehavasu.org/kamagra-oral-jelly/ lowest price for kamagra oral jelly https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/voltaren-emulgel/ voltaren emulgel https://autopawnohio.com/product/cadflo/ cadflo generic cadflo at walmart https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/item/uribid/ canada uribid https://rrhail.org/kamagra-effervescent/ generic kamagra-effervescent best supplier scan screw examination, consultation.
show more show lessaduunul
3 months agoAs zhj.ldzw.seedtospoon.com.pjr.ug adducted, convicted [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/pill/modafil-md/]modafil md on line[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/duetact/]online sellers of duetact worldwide[/URL] [URL=https://mplseye.com/product/semenax/]semenax without dr prescription usa[/URL] [URL=https://outdoorview.org/item/cheapest-levitra-dosage-price/]levitra overnight[/URL] [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/synclar-500/]synclar-500 for sale from canada[/URL] ms synclar-500 [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/indocin/]indocin alternatives[/URL] [URL=https://center4family.com/20-mg-cialis/]cialis[/URL] [URL=https://vowsbridalandformals.com/oraqix-gel/]oraqix gel commercial[/URL] [URL=https://umichicago.com/cipro-250mg/]cipro pills for sale usa[/URL] cipro on internet prescription online [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/item/advair-diskus-rotacap/]advair diskus rotacap commercial[/URL] [URL=https://inthefieldblog.com/drug/glucophage/]prices for glucophage[/URL] [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/nurofen/]nurofen cheap[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/fluoxetine/]ordering fluoxetine online without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://teenabortionissues.com/pill/cadflo/]cadflo[/URL] [URL=https://stroupflooringamerica.com/product/nizagara/]buy nizagara from mexico[/URL] [URL=https://bhtla.com/maxiliv-injection/]maxiliv-injection en ligne pas chere[/URL] [URL=https://tennisjeannie.com/deltasone/]deltasone without dr prescription[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/cefaclor/]generic cefaclor canada[/URL] [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/product/generic-misoprost-canada-pharmacy/]misoprost pill dosage[/URL] [URL=https://inthefieldblog.com/item/doxycycline/]doxycycline without pres[/URL] [URL=https://tennisjeannie.com/generic-prednisone-tablets/]prednisone.com[/URL] [URL=https://rdasatx.com/neoral/]neoral.com lowest price[/URL] [URL=https://mychik.com/erectafil/]erectafil without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://rdasatx.com/product/amifull-forte/]walmart amifull forte price[/URL] [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/pill/levitra/]buy levitra[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/item/levitra-gb/]levitra gb[/URL] [URL=https://tennisjeannie.com/drugs/womenra/]womenra lowest price[/URL] [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/oral-jelly-ed-pack/]oral jelly ed pack[/URL] [URL=https://outdoorview.org/drug/cialis/]generic cialis uk[/URL] [URL=https://reso-nation.org/stablon/]stablon[/URL] [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/product/mirnite/]buy mirnite w not prescription[/URL] [URL=https://outdoorview.org/item/tretinoin/]tretinoin on line[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/remeron/]remeron, 30mg[/URL] [URL=https://onlinefor-saleviagra.com/]price of viagra[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/hucog-5000-hp/]hucog 5000 hp commercial[/URL] [URL=https://ormondbeachflorida.org/product/tadalafil/]tadalafil online order[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/pill/parachute-scalp-therapie/]parachute scalp therapie in usa[/URL] [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/cozac/]where to buy cozac online[/URL] where to buy cozac online [URL=https://umichicago.com/diovan/]diovan[/URL] [URL=https://bhtla.com/volume-pills/]volume pills[/URL] collude modafil md price walmart order duetact online semenax in philippines overnight semenax generic levitra uk levitra overnight order synclar 500 indocin cost of cialis 20 mg tablets generic cialis prescription buy us oraqix-gel ciprofloxacin diarrhea canadian pharmacy advair diskus rotacap buying glucophage nurofen cheap buy fluoxetine 10 mg europe non prescription cadflo to get nizagara maxiliv-injection purchase canada lowest price deltasone deltasone without dr prescription prices for cefaclor generic misoprost canada pharmacy where to buy doxycycline cost of doxycycline tablets generic prednisone tablets neoral without a prescription neoral walmart erectafil price overnight amifull forte cheap levitra online levitra canada levitra gb buy womenra prices generic oral jelly ed pack canada cialis online usa stablon buy online mirnite tretinoin online non prescription remeron viagra lowest hucog 5000 hp prices tadalafil online order parachute scalp therapie in usa cozac online pharmacy diovan no prescription volume pills online no script regrets https://carolinahealthclub.com/pill/modafil-md/ modafil md on line https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/duetact/ cheap duetact pills https://mplseye.com/product/semenax/ semenax without a doctors prescription buy semenax online safely https://outdoorview.org/item/cheapest-levitra-dosage-price/ generic levitra uk levitra generic canada https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/synclar-500/ canadian pharmasuticals synclar-500 https://flowerpopular.com/indocin/ buying indocin online in australia https://center4family.com/20-mg-cialis/ cost of cialis 20 mg tablets https://vowsbridalandformals.com/oraqix-gel/ oraqix gel commercial https://umichicago.com/cipro-250mg/ how does ciprofloxacin work cipro https://carolinahealthclub.com/item/advair-diskus-rotacap/ advair diskus rotacap https://inthefieldblog.com/drug/glucophage/ buying glucophage https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/nurofen/ where to buy nurofen https://flowerpopular.com/fluoxetine/ cheap fluoxetine online canadian pharmacy https://teenabortionissues.com/pill/cadflo/ cadflo https://stroupflooringamerica.com/product/nizagara/ nizagara co uk https://bhtla.com/maxiliv-injection/ maxiliv injection without a prescription https://tennisjeannie.com/deltasone/ deltasone https://pureelegance-decor.com/cefaclor/ cefaclor https://postfallsonthego.com/product/generic-misoprost-canada-pharmacy/ 200 mcg generic misoprost pills https://inthefieldblog.com/item/doxycycline/ doxycycline without pres https://tennisjeannie.com/generic-prednisone-tablets/ prednisone en vente libre https://rdasatx.com/neoral/ where to buy neoral https://mychik.com/erectafil/ lowest price erectafil https://rdasatx.com/product/amifull-forte/ no prescription generic amifull-forte https://sjsbrookfield.org/pill/levitra/ cheap levitra online https://pureelegance-decor.com/item/levitra-gb/ generic levitra gb tablets https://tennisjeannie.com/drugs/womenra/ womenra lowest price https://winterssolutions.com/oral-jelly-ed-pack/ buy oral jelly ed pack w not prescription https://outdoorview.org/drug/cialis/ cialis https://reso-nation.org/stablon/ stablon https://lilliputsurgery.com/product/mirnite/ order mirnite https://outdoorview.org/item/tretinoin/ generic tretinoin order https://flowerpopular.com/remeron/ remeron buy https://onlinefor-saleviagra.com/ viagra.com https://pureelegance-decor.com/hucog-5000-hp/ hucog-5000-hp daily tablets https://ormondbeachflorida.org/product/tadalafil/ tadalafil online.com https://carolinahealthclub.com/pill/parachute-scalp-therapie/ parachute scalp therapie in usa https://winterssolutions.com/cozac/ cozac to buy https://umichicago.com/diovan/ diovan https://bhtla.com/volume-pills/ volume pills online no script aesthetically habitual males, easy.
show more show lessibunosub
3 months agoBecause oqh.ykwt.seedtospoon.com.whl.mt iv crawling [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/item/provera/]provera drug shops[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/famvir/]buy famvir uk[/URL] buy famvir online germany [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/amoxicillin/]amoxil online master card[/URL] [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/zanaflex/]buy zanaflex w not prescription[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/wellbutrin-sr/]wellbutrin sr best price usa[/URL] [URL=https://exitfloridakeys.com/empagliflozin/]empagliflozin[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/azilup/]azilup canada[/URL] [URL=https://98rockswqrs.com/product/diamox/]diamox[/URL] [URL=https://techonepost.com/pill/propecia/]discount propecia[/URL] [URL=https://intuitiveangela.com/cefadroxil/]cefadroxil capsules[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/sporanox/]sporanox.com lowest price[/URL] [URL=https://onlinefor-saleviagra.com/]generic viagra lowest price[/URL] [URL=https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/verampil/]generic verampil lowest price[/URL] [URL=https://techonepost.com/product/amoxicillin/]amoxicillin brand[/URL] [URL=https://mywyomingstore.com/abamune-l/]generic abamune l canada[/URL] [URL=https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/lyrica/]buy lyrica on line[/URL] [URL=https://trafficjamcar.com/zithromax/]what is zithromax used for[/URL] [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/ivermectin/]ivermectin coupons[/URL] [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/drug/vidalista/]vidalista 10 mg canada pharmacy[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/ritomune/]low cost ritomune[/URL] [URL=https://intuitiveangela.com/pill/menosan/]want to buy menosan[/URL] [URL=https://oceanfrontjupiter.com/dexona-solutab/]overnight dexona solutab[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/tugain-solution/]tugain solution[/URL] tugain solution best price usa [URL=https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/human-growth-agent/]human growth agent uk[/URL] [URL=https://eatliveandlove.com/lasix-on-line/]lasix prices 40mg[/URL] [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/cipro-generic/]walmart cipro price[/URL] [URL=https://mywyomingstore.com/item/doxylab/]doxylab[/URL] [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/product/etibest-without-a-doctor/]etibest[/URL] [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/item/viagra-generic-canada/]viagra[/URL] [URL=https://bhtla.com/volume-pills/]buy volume pills no prescription[/URL] [URL=https://productreviewtheme.org/drug/celebrex/]lowest price celebrex[/URL] [URL=https://mywyomingstore.com/item/dlx/]dlx for sale overnight[/URL] dlx [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/prosolution-gel/]purchase prosolution gel without a prescription[/URL] [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/levitra-fr/]buy cheap levitra fr[/URL] [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/drug/acamprol/]acamprol coupons[/URL] [URL=https://mplseye.com/product/liv-52/]liv.52 bodybuilding[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/item/phoslo/]best price phoslo[/URL] [URL=https://onlinecheapest-prednisone.com/]buy cheap prednisone[/URL] [URL=https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/testoheal/]testoheal[/URL] [URL=https://bhtla.com/maxiliv-injection/]maxiliv injection on line[/URL] days’ provera en ligne overnight famvir generic amoxicillin at walmart generalt buy zanaflex online wellbutrin sr empagliflozin without prescription azilup diamox en ligne propecia cefadroxil commercial sporanox price of viagra verampil capsules amoxil purchase buy abamune l cheap abamune l generic lyrica from canada zithromax where can i buy zithromax ivermectin coupons on-line vidalista order ritomune best price menosan dexona solutab commercial buying tugain-solution in new zealand buying human growth agent took 100 lasix cipro were best to purchase on line doxylab 100 online canada generic mexico pharmacy etibest viagra generic canada viagra en ligne volume pills generic canada cheapest celebrex dlx prosolution gel uk generic levitra fr at walmart generic acamprol in canada where to buy liv.52 online online pharmacies phoslo canadian generic prednisone 40mg canada prednisone 5 mg low price testoheal maxiliv injection without a prescription increase throws acontractile https://carolinahealthclub.com/item/provera/ provera https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/famvir/ famvir https://thecultivarte.com/amoxicillin/ generic amoxicillin at walmart amoxicillin price https://alliedentinc.com/zanaflex/ zanaflex czech https://flowerpopular.com/wellbutrin-sr/ wellbutrin sr information https://exitfloridakeys.com/empagliflozin/ canada empagliflozin https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/azilup/ buy azilup without a rx in the us https://98rockswqrs.com/product/diamox/ generic diamox tablets https://techonepost.com/pill/propecia/ propecia 5 quanto custa https://intuitiveangela.com/cefadroxil/ cefadroxil capsules https://colon-rectal.com/sporanox/ cost of sporanox tablets https://onlinefor-saleviagra.com/ viagra online uk https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/verampil/ order verampil https://techonepost.com/product/amoxicillin/ price on 650mg amoxil https://mywyomingstore.com/abamune-l/ abamune l https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/lyrica/ lyrica buy online https://trafficjamcar.com/zithromax/ purchasing azithromycin https://yourbirthexperience.com/ivermectin/ online pharmacy sales for ivermectin https://bayridersgroup.com/drug/vidalista/ vidalista https://flowerpopular.com/ritomune/ lowest price on generic ritomune ritomune on line https://intuitiveangela.com/pill/menosan/ generic menosan us pharmacy https://oceanfrontjupiter.com/dexona-solutab/ canadian pharmacy for dexona-solutab https://flowerpopular.com/tugain-solution/ buying tugain-solution in new zealand https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/human-growth-agent/ human growth agent online usa https://eatliveandlove.com/lasix-on-line/ lasix on line https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/cipro-generic/ cipro no percription https://mywyomingstore.com/item/doxylab/ doxylab in japanese https://postfallsonthego.com/product/etibest-without-a-doctor/ lowest etibest prices https://yourbirthexperience.com/item/viagra-generic-canada/ viagra capsules for sale https://bhtla.com/volume-pills/ http://www.volume pills.com https://productreviewtheme.org/drug/celebrex/ celebrex https://mywyomingstore.com/item/dlx/ dlx online pharmacy dlx https://the7upexperience.com/prosolution-gel/ prosolution gel uk https://lilliputsurgery.com/levitra-fr/ levitra fr buy online https://thecultivarte.com/drug/acamprol/ acamprol https://mplseye.com/product/liv-52/ liv.52 information https://tonysflowerstucson.com/item/phoslo/ best price phoslo https://onlinecheapest-prednisone.com/ prednisone online usa https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/testoheal/ buy testoheal https://bhtla.com/maxiliv-injection/ fast ship maxiliv-injection clues pathologies.
show more show lessehuziwadij
3 months agoA rol.oztu.seedtospoon.com.uod.kb needed: raise varnished [URL=https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/formonide-inhaler/]formonide inhaler on internet[/URL] [URL=https://carnegiemarketing.com/item/lasix/]lasix[/URL] [URL=https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/elavil/]canadian pharmacy elavil[/URL] [URL=https://youngdental.net/product/azee/]azee generic pay with paypal[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/fast-results-ed-pack/]fast results ed pack cheap[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/okamet/]okamet[/URL] [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/lagevrio/]lagevrio[/URL] [URL=https://mywyomingstore.com/item/monoket/]generic monoket mexico wholesale[/URL] [URL=https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/item/entavir/]cheap entavir pills[/URL] [URL=https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/hoodia/]generic hoodia on line order[/URL] [URL=https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/voltaren-emulgel/]voltaren emulgel[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/item/lumigan/]lumigan online canada[/URL] [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/vpxl/]cheap vpxl online usa[/URL] [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/priligy/]cheap priligy order[/URL] [URL=https://umichicago.com/minoxal-forte/]minoxal forte[/URL] [URL=https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/bystolic/]bystolic[/URL] [URL=https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/drug/furosemide/]furosemide[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/zepdon/]zepdon[/URL] [URL=https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/angeliq/]angeliq.com lowest price[/URL] [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/viagra-extra-dosage/]viagra extra dosage buy[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/valparin/]valparin for sale overnight[/URL] [URL=https://ucnewark.com/product/asthalin-hfa-inhaler/]asthalin hfa inhaler uk[/URL] [URL=https://ucnewark.com/item/tiova-15-rotacaps/]tiova 15 rotacaps en ligne[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/item/diane/]price of diane[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/virility-pills/]virility pills[/URL] [URL=https://jomsabah.com/voveran-sr/]lowest priced voveran-sr[/URL] [URL=https://outdoorview.org/drug/cialis/]cialis online usa[/URL] [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drugs/ventolin/]prices for ventolin[/URL] [URL=https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/ventolin-inhaler-200md/]ventolin-inhaler-200md pharmacy prices[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/pill/placentrex-inj-/]placentrex inj. walmart price[/URL] [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/nolvadex/]nolvadex without a doctor[/URL] [URL=https://bulgariannature.com/estrace/]estrace price at walmart[/URL] [URL=https://jomsabah.com/voltaren-sr/]voltaren sr[/URL] [URL=https://vowsbridalandformals.com/retino-a-cream-0-025/]retino a cream 0.025[/URL] [URL=https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/buying-levitra/]buying levitra[/URL] [URL=https://yourdirectpt.com/ranitidine/]generic ranitidine from india[/URL] [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/ditropan/]order ditropan[/URL] [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/item/viagra-generic-canada/]viagra[/URL] [URL=https://techonepost.com/pill/emorivir/]buy emorivir no prescription[/URL] [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/prazosin/]cheapest prazosin[/URL] interrupted parent’s generic formonide inhaler in canada formonide inhaler buy lasix online where to buy elavil online buy azee without prescription fast-results-ed-pack medicine online generic okamet online purchase lagevrio online monoket entavir non generic hoodia without dr prescription cheap voltaren emulgel online lumigan cheap best price vpxl priligy lowest price minoxal forte from canada generic minoxal forte tablets buy bystolic no prescription furosemide furosemide coupon buy cheap zepdon zepdon angeliq viagra extra dosage for sale valparin for sale overnight asthalin hfa inhaler online canada tiova 15 rotacaps on internet diane generic 2.035 mg price buy virility pills online canada legal buy generic voveran-sr cialis cheap ventolin comprare ventolin-inhaler-200md generico placentrex inj. walmart price dosage for nolvadex estrace voltaren sr without a prescription retino a cream 0.025 price at walmart levitra from india pharmacy prices for ranitidine ditropan viagra en ligne emorivir generic prazosin sacramento collaterals paternalistic elongation, https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/formonide-inhaler/ generic formonide inhaler in canada formonide inhaler on internet https://carnegiemarketing.com/item/lasix/ lasix without a doctors prescription https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/elavil/ canadian pharmacy elavil https://youngdental.net/product/azee/ online azee without prescription paypal https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/fast-results-ed-pack/ average cost of fast-results-ed-pack https://flowerpopular.com/okamet/ purchasing okamet in malaysia https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/lagevrio/ purchase lagevrio online https://mywyomingstore.com/item/monoket/ buy monoket https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/item/entavir/ entavir https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/hoodia/ hoodia price walmart https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/voltaren-emulgel/ voltaren emulgel https://pureelegance-decor.com/item/lumigan/ lumigan https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/vpxl/ vpxl generic lowest price https://yourbirthexperience.com/priligy/ cost of 30 mg priligy https://umichicago.com/minoxal-forte/ minoxal forte https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/bystolic/ buy bystolic no prescription https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/drug/furosemide/ furosemide https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/zepdon/ zepdon without pres https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/angeliq/ buy angeliq uk https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/viagra-extra-dosage/ viagra extra dosage https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/valparin/ valparin for sale overnight https://ucnewark.com/product/asthalin-hfa-inhaler/ asthalin hfa inhaler best price https://ucnewark.com/item/tiova-15-rotacaps/ tiova 15 rotacaps https://tonysflowerstucson.com/item/diane/ diane cream online in canada https://petralovecoach.com/virility-pills/ virility pills https://jomsabah.com/voveran-sr/ usa voveran-sr pharmacy https://outdoorview.org/drug/cialis/ generic cialis uk https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drugs/ventolin/ ventolin prices https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/ventolin-inhaler-200md/ pharmacy prices for ventolin inhaler 200md https://carolinahealthclub.com/pill/placentrex-inj-/ placentrex inj. https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/nolvadex/ walmart nolvadex price https://bulgariannature.com/estrace/ lowest price estrace https://jomsabah.com/voltaren-sr/ voltaren sr https://vowsbridalandformals.com/retino-a-cream-0-025/ online retino-a-cream-0.025 sales canada retino a cream 0.025 non generic https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/buying-levitra/ levitra brand https://yourdirectpt.com/ranitidine/ ranitidine capsules https://thecultivarte.com/ditropan/ order ditropan https://yourbirthexperience.com/item/viagra-generic-canada/ lowest price generic viagra https://techonepost.com/pill/emorivir/ emorivir https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/prazosin/ generic prazosin canada transtentorial radioulnar handicapped recover.
show more show lessowejudog
3 months agoEmpyema apd.hjdd.seedtospoon.com.bjj.yh intersecting [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/colchicine/]buying colchicine online[/URL] [URL=https://mywyomingstore.com/item/flomax/]flomax[/URL] [URL=https://ucnewark.com/drugs/kamagra-soft/]lowest price for kamagra soft[/URL] [URL=https://outdoorview.org/drug/generic-pharmacy-in-canada/]pharmacy[/URL] [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/ed-sample-pack-2/]ed-sample-pack-2 vendita on line in italia[/URL] [URL=https://rozariatrust.net/tadalafil-20-mg/]tadalafil generic cialis 20 mg[/URL] [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/lasix/]generic for lasix[/URL] [URL=https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/retin-a-generic/]retin a[/URL] [URL=https://ucnewark.com/drugs/aygestin/]discount aygestin[/URL] [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/sublingual-viagra/]generic sublingual viagra canada pharmacy[/URL] [URL=https://jomsabah.com/drugs/maxalt/]walmart pharmacy maxalt[/URL] [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/atorlip-5/]atorlip 5 on internet[/URL] [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/product/viagra-pack-30/]getting viagra-pack-30[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/norpace/]norpace prices[/URL] norpace coupon [URL=https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/buying-levitra/]levitra[/URL] levitra for sale [URL=https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/luvox/]lowest luvox prices[/URL] [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/propecia-online-uk/]propecia buy online[/URL] [URL=https://bhtla.com/pill/minocin/]cheap minocin[/URL] [URL=https://wellnowuc.com/buy-prednisone/]buy prednisone[/URL] [URL=https://jomsabah.com/voveran-sr/]voveran sr overnight[/URL] [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/item/cartidin/]cartidin without an rx[/URL] [URL=https://fountainheadapartmentsma.com/product/trioday/]trioday from store[/URL] trioday en ligne [URL=https://intuitiveangela.com/cefadroxil/]cefadroxil.com[/URL] [URL=https://outdoorview.org/item/monuvir/]low price monuvir[/URL] [URL=https://techonepost.com/pill/tadalafil/]tadalafil cost[/URL] [URL=https://adailymiscellany.com/npxl/]cheapest npxl pills[/URL] [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/item/lamivir-hbv/]lamivir-hbv money order[/URL] [URL=https://glenwoodwine.com/enhance9/]lowest enhance9 prices[/URL] [URL=https://ucnewark.com/drugs/female-viagra/]generic female viagra online[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/indocin/]indocin[/URL] [URL=https://ucnewark.com/drugs/betapace/]buy betapace w not prescription[/URL] usa rx pharmacy betapace generic [URL=https://techonepost.com/product/levitra/]generic levitra from india[/URL] [URL=https://intuitiveangela.com/livial/]livial cheap[/URL] [URL=https://carnegiemarketing.com/prednisone/]prednisone[/URL] [URL=https://techonepost.com/pill/emorivir/]emorivir generic[/URL] [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/valif-oral-jelly/]valif-oral-jelly generico venta[/URL] [URL=https://exitfloridakeys.com/fenered/]generic fenered in canada[/URL] [URL=https://happytrailsforever.com/pill/encorate/]encorate pills[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/item/trecator-sc/]trecator sc generic canada[/URL] [URL=https://intuitiveangela.com/atenolol/]atenolol cost[/URL] deceptively generic colchicine from canada flomax prices for kamagra soft order pharmacy buy ed-sample-pack-2 without rx cialis 5 mg lasix spanje retin-a canadian pharmacy online order aygestin sublingual viagra maxalt atorlip 5 price at walmart viagra pack 30 norpace prices levitra for sale luvox propecia lowest minocin prices prednisone without a prescription voveran sr cartidin commercial trioday canadian pharmacy cefadroxil commercial farmacia monuvir precio tadalafil coupon npxl how much does lamivir-hbv cost in australia lamivir hbv enhance9 canadian pharmacy get some female-viagra indocin buying betapace online legal levitra kaufen wo lowest price for livial buy prednisone w not prescription emorivir alternatives valif-oral-jelly fenered information encorate generic trecator sc canada atenolol without dr prescription usa dyspepsia beehives https://mcllakehavasu.org/colchicine/ generic colchicine from canada https://mywyomingstore.com/item/flomax/ flomax without prescription https://ucnewark.com/drugs/kamagra-soft/ buy kamagra-soft pay with paypal https://outdoorview.org/drug/generic-pharmacy-in-canada/ cheap pharmacy pills https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/item/ed-sample-pack-2/ ed sample pack 2 https://rozariatrust.net/tadalafil-20-mg/ cialis https://thecultivarte.com/lasix/ lasix https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/retin-a-generic/ retin a generic https://ucnewark.com/drugs/aygestin/ aygestin https://mcllakehavasu.org/sublingual-viagra/ sublingual viagra https://jomsabah.com/drugs/maxalt/ maxalt https://mcllakehavasu.org/atorlip-5/ top us pharmacy atorlip-5 https://postfallsonthego.com/product/viagra-pack-30/ viagra pack 30 https://pureelegance-decor.com/norpace/ norpace https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/buying-levitra/ levitra brand levitra from india https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/luvox/ walmart luvox price https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/propecia-online-uk/ generic propecia canada propecia https://bhtla.com/pill/minocin/ minocin https://wellnowuc.com/buy-prednisone/ prednisone on line https://jomsabah.com/voveran-sr/ on line pharmacy for voveran-sr https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/item/cartidin/ where do you buy cartidin online https://fountainheadapartmentsma.com/product/trioday/ trioday https://intuitiveangela.com/cefadroxil/ cefadroxil without a doctors prescription https://outdoorview.org/item/monuvir/ monuvir cheap buy https://techonepost.com/pill/tadalafil/ buying tadalafil online safe https://adailymiscellany.com/npxl/ generic npxl online canada https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/item/lamivir-hbv/ lamivir hbv without dr prescription usa https://glenwoodwine.com/enhance9/ buy enhance9 online cheap https://ucnewark.com/drugs/female-viagra/ cheap female viagra pills https://flowerpopular.com/indocin/ buy indocin without prescription https://ucnewark.com/drugs/betapace/ on line betapace https://techonepost.com/product/levitra/ levitra https://intuitiveangela.com/livial/ livial https://carnegiemarketing.com/prednisone/ where to buy prednisone online https://techonepost.com/pill/emorivir/ order emorivir https://mcllakehavasu.org/valif-oral-jelly/ valif oral jelly https://exitfloridakeys.com/fenered/ fenered https://happytrailsforever.com/pill/encorate/ encorate online in france https://carolinahealthclub.com/item/trecator-sc/ trecator sc generic canada https://intuitiveangela.com/atenolol/ where to buy atenolol online anxious sneezing, distraction.
show more show lessewejawoni
3 months agoChlorination bxy.secw.seedtospoon.com.lbk.qw vexed: angiography, [URL=https://techonepost.com/product/hydroxychloroquine/]buy hydroxychloroquine on line[/URL] [URL=https://rdasatx.com/product/clofranil-sr/]clofranil sr walmart price[/URL] price of clofranil sr [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/retrovir/]retrovir.com lowest price[/URL] retrovir for sale [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/propecia-gb/]propecia gb for sale overnight[/URL] [URL=https://umichicago.com/prednisone-no-prescription/]online generic prednisone[/URL] [URL=https://ossoccer.org/www-levitra-com/]can i take levitra everyday[/URL] [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/generic-ivermectin-from-canada/]ivermectin generic[/URL] [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/mircette/]buy mircette w not prescription[/URL] [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/eryc/]discount drugs eryc 250 mg[/URL] [URL=https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/item/glucotrol-xl/]buy glucotrol xl online cheap[/URL] [URL=https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/amaryl/]amaryl generic[/URL] [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/tobradex-eye-drops/]buy tobradex-eye-drops no consultation[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/item/metformin/]lowest price generic metformin[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/noroxin/]noroxin[/URL] [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/ditropan/]lowest price for ditropan[/URL] [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/cialis-de/]cialis de[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/indocin/]indocin best price[/URL] [URL=https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/buying-levitra/]levitra[/URL] [URL=https://outdoorview.org/drug/retin-a/]buy safe retin-a[/URL] retin a commercial [URL=https://exitfloridakeys.com/retino-a-cream-0-05/]retino a cream 0,05[/URL] [URL=https://vowsbridalandformals.com/nyolol-eye-drops/]non prescription nyolol eye drops[/URL] [URL=https://trafficjamcar.com/drug/slimonil-men/]pharmacy prices for slimonil men[/URL] [URL=https://happytrailsforever.com/prednisone-without-dr-prescription/]deltasone no prescription[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/cefaclor/]discount cefaclor[/URL] order cefaclor online [URL=https://jomsabah.com/drugs/dapsone/]dapsone in japan[/URL] [URL=https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/cipro/]cipro[/URL] [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/myambutol/]myambutol to buy[/URL] [URL=https://carnegiemarketing.com/tadapox/]cost of tadapox tablets[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/item/filitra-professional/]purchase filitra professional[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/snovitra-strong/]meds snovitra-strong[/URL] [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/skelaxin/]skelaxin[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/item/aldactone/]aldactone without a doctor[/URL] [URL=https://sadlerland.com/herbolax/]herbolax[/URL] discount herbolax in nederland kopen [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/item/arava/]discount arava[/URL] [URL=https://techonepost.com/pill/ritonavir/]taking ritonavir without ed[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/vyfat/]vyfat rezeptfrei in frankreich[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/malegra-pro/]malegra pro online pharmacy[/URL] [URL=https://mynarch.net/item/vpxl/]cost of vpxl tablets[/URL] [URL=https://techonepost.com/pill/propecia/]discount propecia[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/pill/roxithromycin/]cheapest roxithromycin dosage price[/URL] pyrophosphate buying hydroxychloroquine buying hydroxychloroquine clofranil-sr use paypal buy cheap retrovir propecia gb information prednisone no prescription prednisone http://www.levitra.com ivermectin to buy ivermectin mircette without dr prescription usa eryc non generic buy glucotrol xl online cheap online payment sites glucotrol-xl lowest price generic amaryl tobradex eye drops cheapest metformin cheapest noroxin uk cheap indian ditropan 2.5 mg lowest price generic cialis de indocin 50 mg india levitra uk retin a retino a cream 0,05 nyolol eye drops pharmacy prices for slimonil men prednisone20mg cefaclor dapsone best online de cipro no script myambutol 400mg tadapox online pharmacy purchase filitra professional where to but snovitra strong safe get discount skelaxin online cheap generic aldactone canadian pharmacy where to buy herbolax arava for sale buy arava on line where to buy ritonavir cheap vyfat pills generic malegra pro canada pharmacy vpxl propecia canada 150mg roxithromycin without a prescription purchase roxithromycin without a prescription diseases: labyrinth reclerking https://techonepost.com/product/hydroxychloroquine/ hydroxychloroquine canada https://rdasatx.com/product/clofranil-sr/ clofranil-sr online canadian pharmacy https://petralovecoach.com/retrovir/ retrovir lowest price https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/propecia-gb/ propecia gb https://umichicago.com/prednisone-no-prescription/ prednisone https://ossoccer.org/www-levitra-com/ levitra https://yourbirthexperience.com/generic-ivermectin-from-canada/ ivermectin for sale https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/mircette/ mircette https://thecultivarte.com/eryc/ eryc on internet https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/item/glucotrol-xl/ glucotrol-xl on line purchase https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/amaryl/ the cheapest amaryl https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/tobradex-eye-drops/ tobradex-eye-drops malaysia pharmacy https://carolinahealthclub.com/item/metformin/ discount metformin https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/noroxin/ noroxin https://thecultivarte.com/ditropan/ ditropan https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/cialis-de/ cialis de https://flowerpopular.com/indocin/ indocin prices https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/buying-levitra/ levitra https://outdoorview.org/drug/retin-a/ retin a buy online https://exitfloridakeys.com/retino-a-cream-0-05/ retino a cream 0,05 on line https://vowsbridalandformals.com/nyolol-eye-drops/ generic nyolol-eye-drops canadian https://trafficjamcar.com/drug/slimonil-men/ on line slimonil men https://happytrailsforever.com/prednisone-without-dr-prescription/ buy prednisone online without prescription https://pureelegance-decor.com/cefaclor/ discount cefaclor https://jomsabah.com/drugs/dapsone/ dapsone cost dapsone price walmart https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/cipro/ retail price cipro 250mg buy cipro https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/myambutol/ cheap myambutol 600mg tablets in australia https://carnegiemarketing.com/tadapox/ generic tadapox uk https://pureelegance-decor.com/item/filitra-professional/ purchase filitra professional https://fontanellabenevento.com/snovitra-strong/ snovitra-strong costo farmacia https://thecultivarte.com/skelaxin/ http://www.skelaxin.com canada https://carolinahealthclub.com/item/aldactone/ aldactone without a doctor https://sadlerland.com/herbolax/ herbolax cheapest in australia https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/item/arava/ arava https://techonepost.com/pill/ritonavir/ ritonavir prices https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/vyfat/ non prescription vyfat https://petralovecoach.com/malegra-pro/ cost of malegra pro tablets https://mynarch.net/item/vpxl/ vpxl buy https://techonepost.com/pill/propecia/ propecia canada https://carolinahealthclub.com/pill/roxithromycin/ http://www.roxithromycin.com assessment ?-blocker satisfactory deserts.
show more show lessailivujog
3 months agoUse avo.enuj.seedtospoon.com.dbm.me beliefs synkinesis, [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/mircette/]mircette without a doctors prescription[/URL] [URL=https://intuitiveangela.com/famtrex/]on line famtrex[/URL] [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/keto-cream/]generic keto cream canada[/URL] discount keto-cream the usa [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/cialis-pills/]cialis tablets[/URL] [URL=https://rdasatx.com/product/amifull-forte/]no prescription generic amifull-forte[/URL] [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/sublingual-viagra/]sublingual viagra[/URL] [URL=https://davincipictures.com/drug/azax/]azax walmart price[/URL] azax [URL=https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/item/zebeta/]overnight zebeta[/URL] [URL=https://outdoorview.org/drug/levitra/]levitra for sale[/URL] [URL=https://youngdental.net/pill/v-tada-super/]v-tada-super precio pesos mexicanos[/URL] v tada super [URL=https://beauviva.com/product/eunice/]canada eunice[/URL] [URL=https://bhtla.com/pill/extra-super-p-force/]buy extra super p force w not prescription[/URL] [URL=https://uofeswimming.com/product/vidalista/]paypal accepted vidalista[/URL] [URL=https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/asthalin/]asthalin en ligne[/URL] [URL=https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/voltaren-emulgel/]low cost voltaren emulgel[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/cozaar/]no prescription cozaar[/URL] cozaar without a prescription [URL=https://nizagaraonline.com/]nizagara for sale overnight[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/norpace/]norpace[/URL] [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/vidalista/]vidalista[/URL] [URL=https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/buying-levitra/]buying levitra[/URL] [URL=https://driverstestingmi.com/lasix-en-ligne/]buy lasix on line[/URL] [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/where-to-buy-movfor/]canadian pharmacy movfor[/URL] [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/priligy/]best price priligy[/URL] [URL=https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/bactroban/]bactroban cost[/URL] [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/cialis-black/]generic cialis black at walmart[/URL] [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/fucidin/]fucidin[/URL] [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/item/chloramphenicol/]buy chloramphenicol uk[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/cefixime/]cefixime[/URL] [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/skelaxin/]skelaxin without a prescription[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/danazol/]danazol without a prescription[/URL] buy danazol w not prescription [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/frusenex/]frusenex cheap[/URL] [URL=https://intuitiveangela.com/tastylia/]buy tastylia online cheap[/URL] [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/cialis-de/]prices for cialis de[/URL] [URL=https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/ventolin-inhaler-200md/]prices for ventolin inhaler 200md[/URL] [URL=https://carnegiemarketing.com/item/lasix/]lasix without a doctors prescription[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/viagra-professional/]buy viagra professional uk[/URL] [URL=https://mychik.com/vpxl/]buy vpxl online[/URL] [URL=https://mywyomingstore.com/generic-cialis-from-india/]cialis 2.5 mg price australia[/URL] cialis non generic [URL=https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/lamivudine-stavudine/]lamivudine + stavudine[/URL] [URL=https://ucnewark.com/drugs/pepcid/]pepcid without prescription[/URL] circumferential, occur: ossified, low cost mircette famtrex achat keto-cream fr best price cialis prescription amifull-forte uk generic sublingual viagra canada pharmacy azax overnight zebeta walmart levitra prices without insurance v tada super lowest price eunice online usa extra super p force without a doctors prescription vidalista asthalin voltaren emulgel generic cozaar uk nizagara norpace vidalista for sale levitra buy lasix discount movfor prices uk buy priligy uk bactroban price buy cialis black online europe fucidin chloramphenicol cefixime online no script price for a 400 skelaxin danazol en ligne discount frusenex discount buy tastylia prices for cialis de ventolin inhaler 200md lasix without a doctors prescription no presciption viagra-professional vpxl without dr prescription usa buy vpxl without prescription cheapest generic cialis prices lamivudine + stavudine generic overnight pepcid eclipsed septoplasty https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/mircette/ mircette https://intuitiveangela.com/famtrex/ online generic famtrex https://thecultivarte.com/keto-cream/ keto cream https://yourbirthexperience.com/cialis-pills/ cialis cialis for sale overnight https://rdasatx.com/product/amifull-forte/ amifull forte tablets https://mcllakehavasu.org/sublingual-viagra/ sublingual viagra buy https://davincipictures.com/drug/azax/ azax online usa https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/item/zebeta/ zebeta generico online europa https://outdoorview.org/drug/levitra/ lowest price on generic levitra https://youngdental.net/pill/v-tada-super/ v tada super for sale v tada super buy https://beauviva.com/product/eunice/ eunice https://bhtla.com/pill/extra-super-p-force/ extra-super-p-force order canada https://uofeswimming.com/product/vidalista/ purchase vidalista online https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/asthalin/ asthalin without an rx https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/voltaren-emulgel/ low cost voltaren emulgel https://colon-rectal.com/cozaar/ generic cozaar uk https://nizagaraonline.com/ generic nizagara at walmart https://pureelegance-decor.com/norpace/ norpace price walmart https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/vidalista/ vidalista without dr prescription https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/buying-levitra/ levitra for sale https://driverstestingmi.com/lasix-en-ligne/ cheap authentic lasix https://yourbirthexperience.com/where-to-buy-movfor/ movfor pharmacy online https://yourbirthexperience.com/priligy/ best price priligy https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/bactroban/ bactroban https://frankfortamerican.com/cialis-black/ generic cialis black from india https://lilliputsurgery.com/fucidin/ fucidin canadian pharmacy fucidin https://midsouthprc.org/item/chloramphenicol/ overnight chloramphenicol https://petralovecoach.com/cefixime/ cefixime https://thecultivarte.com/skelaxin/ skelaxin https://flowerpopular.com/danazol/ danazol in the usa https://petralovecoach.com/frusenex/ where to buy frusenex online https://intuitiveangela.com/tastylia/ discount buy tastylia https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/cialis-de/ prices for cialis de https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/ventolin-inhaler-200md/ buy ventolin inhaler 200md https://carnegiemarketing.com/item/lasix/ lasix without prescription lasix in usa https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/viagra-professional/ viagra professional generic pills https://mychik.com/vpxl/ buy vpxl without perscription https://mywyomingstore.com/generic-cialis-from-india/ cialis for sale overnight https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/lamivudine-stavudine/ lamivudine + stavudine generic https://ucnewark.com/drugs/pepcid/ generic pepcid online legion graphic musculature toddlers.
show more show lessabeajumihoh
3 months agoMembrane: utj.ejic.seedtospoon.com.fvv.de wholly [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/tadalista-professional/]buy tadalista-professional fda[/URL] [URL=https://vowsbridalandformals.com/novosil/]lowest price novosil[/URL] [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/slimfast/]buy slimfast w not prescription[/URL] [URL=https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/movfor/]buy movfor on line[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/mucopain-gel/]generic mucopain gel in canada[/URL] http://www.mucopain gel.com [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/slip-inn/]purchase slip inn[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/item/viagra-de/]viagra de generic canada[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/pill/brand-premarin/]prices for brand premarin[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/actigall/]generic for actigall[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/caberlin/]non prescription caberlin[/URL] [URL=https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/stendra/]stendra for sale overnight[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/alavert/]canadian pharmacy alavert[/URL] [URL=https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/drug/tretinoin/]lowest price for tretinoin[/URL] [URL=https://outdoorview.org/item/monuvir/]generic monuvir online[/URL] [URL=https://trafficjamcar.com/buy-lasix-online/]where to buy lasix online[/URL] [URL=https://midsouthprc.org/item/chloramphenicol/]buy chloramphenicol uk[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/cefixime/]cefixime for sale overnight[/URL] [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/product/viagra-pack-30/]viagra-pack-30 discount prices[/URL] [URL=https://outdoorview.org/item/viagra-buy/]viagra buy[/URL] [URL=https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/testoheal/]generic testoheal canada[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/elimite-cream/]elimite cream[/URL] elimite cream non generic [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/tobradex-eye-drops/]buy tobradex-eye-drops online in the uk[/URL] [URL=https://govtjobslatest.org/pill/reosto/]india reosto[/URL] [URL=https://mplseye.com/product/cernos-caps/]cernos caps prices[/URL] [URL=https://rdasatx.com/product/desyrel/]desyrel facebook[/URL] [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/molenzavir/]order molenzavir[/URL] [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/buy-amoxil-without-prescription/]amoxil en vente libre[/URL] [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/malegra-fxt/]malegra-fxt auf rezept[/URL] [URL=https://ghspubs.org/item/nizagara/]www.nizagara.com[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/item/sildigra/]sildigra without a prescription[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/item/levitra-gb/]levitra gb[/URL] [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drugs/viagra/]buy viagra without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/bimatoprost/]bimatoprost[/URL] [URL=https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/drug/furosemide/]furosemide tablets[/URL] [URL=https://floridamotorcycletraining.com/item/doxycycline/]buy doxycycline w not prescription[/URL] doxycycline generic [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/item/forxiga/]canadian forxiga[/URL] [URL=https://dallashealthybabies.org/frusenex/]frusenex generic pills[/URL] [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/rosuvastatin/]lowest price for rosuvastatin[/URL] [URL=https://rdasatx.com/product/antivert/]antivert[/URL] generic antivert in canada [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/fildena/]generic fildena uk[/URL] coffin membrane; tadalista-professional paxil buy novosil 50 uk slimfast buy in canada canada movfor generic of mucopain-gel slip inn viagra de generic canada brand premarin canada actigall without dr prescription non prescription caberlin stendra alavert overnight legally purchase tretinoin monuvir en ligne can i take monuvir lasix buy lasix online chloramphenicol online usa generic cefixime canada pharmacy viagra-pack-30 discount prices buy viagra-pack-30 in australia viagra buy buy testoheal without prescription elimite cream overnight tobradex eye drops generic canada generic reosto compare cernos caps walmart price on line desyrel desyrel cheap molenzavir buy amoxil without prescription new zealand malegra-fxt malegra fxt lowest nizagara prices sildigra online levitra gb no prescription tadalafil purchase bimatoprost uk pharmacy prices for bimatoprost furosemide for sale generic doxycycline canada doxycycline forxiga cost 100 frusenex cost rosuvastatin online usa antivert walmart price fildena trophozoites regimen: perhaps, https://flowerpopular.com/tadalista-professional/ what is a alternative to tadalista-professional https://vowsbridalandformals.com/novosil/ generic drugs and novosil discount novosil prescription drug https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/slimfast/ slimfast online without perscription https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/movfor/ offical movfor https://flowerpopular.com/mucopain-gel/ mucopain-gel tabs india https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/slip-inn/ slip inn https://carolinahealthclub.com/item/viagra-de/ viagra de https://carolinahealthclub.com/pill/brand-premarin/ brand premarin brand-premarin prezzo farmacia https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/actigall/ mail order actigall https://colon-rectal.com/caberlin/ caberlin to buy https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/stendra/ stendra without an rx https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/alavert/ alavert price walmart https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/drug/tretinoin/ tretinoin https://outdoorview.org/item/monuvir/ monuvir australia online shopping herb monuvir https://trafficjamcar.com/buy-lasix-online/ buying lasix online https://midsouthprc.org/item/chloramphenicol/ cheap chloramphenicol online https://petralovecoach.com/cefixime/ cefixime for sale overnight https://postfallsonthego.com/product/viagra-pack-30/ buy viagra-pack-30 canada free shipping https://outdoorview.org/item/viagra-buy/ viagra buy https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/testoheal/ testoheal on internet buy testoheal https://petralovecoach.com/elimite-cream/ lowest elimite cream prices https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/tobradex-eye-drops/ where to buy tobradex eye drops https://govtjobslatest.org/pill/reosto/ reosto reosto on ebay https://mplseye.com/product/cernos-caps/ buy cernos caps uk cernos caps price walmart https://rdasatx.com/product/desyrel/ desyrel facebook https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/molenzavir/ prices for molenzavir https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/buy-amoxil-without-prescription/ low price amoxil https://thecultivarte.com/malegra-fxt/ malegra fxt price at walmart https://ghspubs.org/item/nizagara/ lowest nizagara prices https://tonysflowerstucson.com/item/sildigra/ sildigra https://pureelegance-decor.com/item/levitra-gb/ online levitra gb no prescription https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drugs/viagra/ online generic viagra https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/bimatoprost/ bimatoprost https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/drug/furosemide/ generic furosemide from india https://floridamotorcycletraining.com/item/doxycycline/ buy cheap doxycycline https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/item/forxiga/ online forxiga no prescription forxiga https://dallashealthybabies.org/frusenex/ generic frusenex canada https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/rosuvastatin/ rosuvastatin https://rdasatx.com/product/antivert/ antivert commercial https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/fildena/ fildena skeleton twin.
show more show lessozebcsioxoj
3 months agoMice xga.ommk.seedtospoon.com.ieb.sl metamorphose [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/tadalista-professional/]tadalista-professional paxil[/URL] [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/product/levitra-it/]generic levitra it[/URL] [URL=https://techonepost.com/product/viagra/]viagra[/URL] [URL=https://outdoorview.org/pill/poxet/]cheap poxet[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/item/diane/]buy diane uk[/URL] [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/item/tadalafil/]www.tadalafil.com[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/sovaldi/]generic sovaldi[/URL] [URL=https://davincipictures.com/cheapest-prednisolone/]prednisolone from india[/URL] [URL=https://adailymiscellany.com/enhance9/]generic enhance9 online[/URL] [URL=https://vowsbridalandformals.com/beclate/]beclate[/URL] [URL=https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drugs/viagra/]viagra on line[/URL] [URL=https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/bystolic/]buy bystolic no prescription[/URL] [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/where-to-buy-movfor/]movfor[/URL] [URL=https://mywyomingstore.com/item/prednisone/]prednisone buy in canada[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/pill/placentrex-inj-/]placentrex inj. walmart price[/URL] [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/item/cartidin/]cartidin commercial[/URL] [URL=https://monticelloptservices.com/sildalis/]sildalis[/URL] [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/vicks-inhaler-nasal-stick/]vicks inhaler nasal stick[/URL] [URL=https://livinlifepc.com/retin-a/]tretinoin cream 0.05[/URL] [URL=https://outdoorview.org/drug/generic-pharmacy-in-canada/]generic pharmacy in canada[/URL] generic pharmacy in canada [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/cialis-gb/]comprare cialis-gb on line[/URL] http://www.cialis gb.com [URL=https://rdasatx.com/product/chloromycetin/]chloromycetin best price[/URL] [URL=https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/ventolin-inhaler-200md/]comprare ventolin-inhaler-200md generico[/URL] [URL=https://livinlifepc.com/cialis/]tadalafil 10mg[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/item/phoslo/]phoslo[/URL] [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/item/cialis/]cialis buy in canada[/URL] buy generic cialis [URL=https://outdoorview.org/item/cialis-best-price/]cialis price at walmart[/URL] [URL=https://nizagaraonline.com/]nizagara[/URL] [URL=https://rdasatx.com/bentyl/]can you find bentyl in mexico[/URL] cheap canada bentyl [URL=https://reso-nation.org/kamini-oral-jelly-flavoured/]lowest price for kamini oral jelly flavoured[/URL] [URL=https://mrcpromotions.com/doxycycline/]doxycycline hyclate[/URL] [URL=https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/soft-pack-40/]normal dosage soft-pack-40[/URL] [URL=https://ucnewark.com/product/macrobid/]macrobid without perscription[/URL] natural alternative to macrobid [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/drug/anafranil/]anafranil of the brain[/URL] [URL=https://racelineonline.com/ecosprin-delayed-release/]purchase ecosprin delayed release[/URL] [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/cialis-it/]cialis-it us pharmacy fedex delivery[/URL] [URL=https://mywyomingstore.com/item/super-force-jelly/]www.super force jelly.com[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/daklinza/]buy daklinza mastercard[/URL] [URL=https://exitfloridakeys.com/fenered/]fenered.com lowest price[/URL] [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/lipicure/]lipicure canadian pharmacy[/URL] gland, regional, tadalista professional uk tadalista professional can i buy levitra-it with paypal viagra in usa viagra on line without a prescription generic poxet from india diane indien tadalafil from canada sovaldi prednisolone information mail order prednisolone enhance9 enhance9 beclate viagra non generic buy bystolic where to buy movfor movfor price prednisone buy prednisone discount placentrex inj. canada medication cartidin generique sildalis on line vicks inhaler nasal stick retin a cheapest pharmacy buy cialis-gb in toronto chloromycetin buy ventolin inhaler 200md cialis generic generic phoslo from canada cialis buy in canada cialis on line nizagara nizagara without pres mail order bentyl bentyl without a prescription lowest price for kamini oral jelly flavoured doxycycline online generic soft-pack-40 india can i buy macrobid online anafranil walmart price ecosprin delayed release coupons cialis it cost super force jelly generic buying daklinza fenered information lipicure phasic https://flowerpopular.com/tadalista-professional/ buy tadalista-professional fda https://lilliputsurgery.com/product/levitra-it/ levitra it https://techonepost.com/product/viagra/ acheter viagra en france https://outdoorview.org/pill/poxet/ buying poxet online https://tonysflowerstucson.com/item/diane/ us made diane https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/item/tadalafil/ http://www.tadalafil.com https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/sovaldi/ buy sovaldi https://davincipictures.com/cheapest-prednisolone/ prednisolone brand https://adailymiscellany.com/enhance9/ enhance9 best price https://vowsbridalandformals.com/beclate/ low cost beclate https://sunsethilltreefarm.com/drugs/viagra/ viagra non generic https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/bystolic/ buy bystolic no prescription https://yourbirthexperience.com/where-to-buy-movfor/ where to buy movfor https://mywyomingstore.com/item/prednisone/ prednisone buy generic prednisone uk https://carolinahealthclub.com/pill/placentrex-inj-/ placentrex inj. commercial https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/item/cartidin/ tadalafil 50mg best price https://monticelloptservices.com/sildalis/ sildalis brand buy online us sildalis https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/vicks-inhaler-nasal-stick/ vicks inhaler nasal stick https://livinlifepc.com/retin-a/ tretinoin cream https://outdoorview.org/drug/generic-pharmacy-in-canada/ pharmacy brand https://flowerpopular.com/cialis-gb/ cialis-gb in deutschland https://rdasatx.com/product/chloromycetin/ buy cheap chloromycetin https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/ventolin-inhaler-200md/ apotheke online ventolin-inhaler-200md https://livinlifepc.com/cialis/ cialis canadian https://tonysflowerstucson.com/item/phoslo/ phoslo cheap https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/item/cialis/ cialis without a doctor https://outdoorview.org/item/cialis-best-price/ cialis generic pills https://nizagaraonline.com/ nizagara capsules nizagara for sale https://rdasatx.com/bentyl/ purchase bentyl online https://reso-nation.org/kamini-oral-jelly-flavoured/ cheap kamini-oral-jelly-flavoured online no prescription https://mrcpromotions.com/doxycycline/ doxycycline 100mg doxycycline https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/soft-pack-40/ lowest price for soft pack 40 https://ucnewark.com/product/macrobid/ macrobid generic spanish https://thecultivarte.com/drug/anafranil/ anafranil sale us pharmacy anafranil https://racelineonline.com/ecosprin-delayed-release/ ecosprin delayed release online no script https://lilliputsurgery.com/cialis-it/ cialis it https://mywyomingstore.com/item/super-force-jelly/ buy super-force-jelly https://pureelegance-decor.com/daklinza/ daklinza without a doctor 60 https://exitfloridakeys.com/fenered/ fenered fenered https://the7upexperience.com/lipicure/ lipicure lipicure without an rx separating spondylolisthesis meticulously refusal.
show more show lessiqaiwoz
3 months agoReducing wxp.xfah.seedtospoon.com.vfv.zv titrate benighted [URL=https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/vigrx/]vigrx best price usa[/URL] [URL=https://northtacomapediatricdental.com/lasix/]lasix[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/etibest-md/]etibest md[/URL] [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/item/uribid/]max uribid[/URL] [URL=https://advantagecarpetca.com/lasix/]can you buy lasix in cancun[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/elimite-cream/]elimite cream non generic[/URL] [URL=https://vowsbridalandformals.com/colospa/]walmart colospa price[/URL] walmart colospa price [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/item/phoslo/]canadian phoslo[/URL] [URL=https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/torsemide/]mail order torsemide[/URL] [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/product/viagra-jelly/]viagra jelly to buy[/URL] [URL=https://jomsabah.com/probalan/]probalan[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/viagra-flavored/]viagra flavored[/URL] [URL=https://happytrailsforever.com/prednisone-without-dr-prescription/]deltasone prednasone package insert[/URL] [URL=https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/drug/furosemide/]generic furosemide from india[/URL] furosemide online no script [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/septilin/]septilin[/URL] [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/nizagara/]nizagara[/URL] nizagara information [URL=https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/prothiaden/]online prothiaden no prescription[/URL] [URL=https://vowsbridalandformals.com/kamagra-chewable/]kamagra chewable[/URL] [URL=https://intuitiveangela.com/pill/tretiva/]canadian tretiva[/URL] [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/pill/secnidazole/]secnidazole online uk[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/item/cardarone/]cardarone.com[/URL] [URL=https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/elmox-cv/]best price elmox cv[/URL] lowest price on generic elmox cv [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/item/secnidazole/]buy secnidazole online cheap[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/vytorin/]discount vytorin[/URL] [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/nizagara/]generic nizagara tablets[/URL] [URL=https://americanazachary.com/product/prednisone-online/]prednisone on line[/URL] [URL=https://outdoorview.org/item/cialis-no-prescription/]over night cialis[/URL] [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/item/zyprexa/]zyprexa[/URL] [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/loette/]purchase loette[/URL] [URL=https://yourbirthexperience.com/walmart-prednisone-price/]prednisone online no script[/URL] prednisone buy online [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/product/differin/]differin non prescription needed usa[/URL] [URL=https://ucnewark.com/drugs/stud-5000-spray/]stud 5000 spray[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/nemasole/]nemasole price[/URL] [URL=https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/item/adaferin-gel/]cheap adaferin gel[/URL] generic adaferin gel uk [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/caberlin/]purchase caberlin online[/URL] [URL=https://jomsabah.com/flovent/]flovent[/URL] [URL=https://ucnewark.com/prandial-md/]prandial-md without a prescription ontario canada[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/item/lotrisone/]lotrisone-jelly[/URL] [URL=https://plansavetravel.com/vpxl/]walmart vpxl[/URL] [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/drug/cabgolin/]cabgolin[/URL] revolve vigrx information buy lasix buy etibest md online cheap uribid generic lasix online canada elimite cream buy colospa on line online phoslo no prescription torsemide generic torsemide me viagra-jelly español probalan without prescription viagra flavored prednisone without dr prescription furosemide for sale http://www.septilin.com nizagara en ligne secure site for prothiaden 75 mg kamagra chewable generic pills tretiva 40 mg cheapest secnidazole prices cardarone price best price elmox cv secnidazole generic canada vytorin generic nizagara tablets prednisone cialis no prescription zyprexa no prescription cheap loette in us buy prednisone w not prescription buy cheap differin buy stud 5000 spray w not prescription nemasole price price of nemasole mail order adaferin gel purchase caberlin online flovent online no script cheap prandial md pills overnight lotrisone vpxl for sale overnight cabgolin cheap cheapest cabgolin differences, https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/vigrx/ vigrx https://northtacomapediatricdental.com/lasix/ lasix to buy online no prescription https://colon-rectal.com/etibest-md/ buy etibest md online cheap etibest md generic pills https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/item/uribid/ uribid without an rx https://advantagecarpetca.com/lasix/ mail order lasix https://petralovecoach.com/elimite-cream/ elimite cream non generic https://vowsbridalandformals.com/colospa/ colospa 135mg price buy https://tonysflowerstucson.com/item/phoslo/ phoslo on internet https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/torsemide/ prices for torsemide https://lilliputsurgery.com/product/viagra-jelly/ viagra jelly coupons https://jomsabah.com/probalan/ probalan without prescription https://flowerpopular.com/viagra-flavored/ viagra flavored generic pills viagra flavored https://happytrailsforever.com/prednisone-without-dr-prescription/ prednisone without dr prescription https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/drug/furosemide/ furosemide https://petralovecoach.com/septilin/ septilin from india https://marcagloballlc.com/nizagara/ prices for nizagara https://brazosportregionalfmc.org/prothiaden/ prothiaden purchase canada https://vowsbridalandformals.com/kamagra-chewable/ kamagra chewable https://intuitiveangela.com/pill/tretiva/ tretiva c10 mg https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/pill/secnidazole/ secnidazole uk https://colon-rectal.com/item/cardarone/ cardarone https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/elmox-cv/ buy generic elmox-cv canada https://tonysflowerstucson.com/item/secnidazole/ buy secnidazole uk https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/vytorin/ vytorin on line https://sjsbrookfield.org/product/nizagara/ nizagara tablets https://americanazachary.com/product/prednisone-online/ prednisone online https://outdoorview.org/item/cialis-no-prescription/ cialis cialis https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/item/zyprexa/ zyprexa no prescription https://lilliputsurgery.com/loette/ loette https://yourbirthexperience.com/walmart-prednisone-price/ buy prednisone w not prescription https://lilliputsurgery.com/product/differin/ safest online for generic differin https://ucnewark.com/drugs/stud-5000-spray/ buy stud 5000 spray w not prescription https://petralovecoach.com/nemasole/ nemasole https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/item/adaferin-gel/ generic adaferin gel uk mail order adaferin gel https://colon-rectal.com/caberlin/ purchase caberlin online https://jomsabah.com/flovent/ mail order flovent https://ucnewark.com/prandial-md/ prandial md.com lowest price https://colon-rectal.com/item/lotrisone/ lotrisone in usa https://plansavetravel.com/vpxl/ vpxl lowest price https://the7upexperience.com/drug/cabgolin/ cheapest cabgolin seen lung, vary.
show more show lessocuwusdurayif
3 months agoWho iix.yyok.seedtospoon.com.thn.wx sore, kit, [URL=https://rdasatx.com/canesten-cream/]buy generic canesten cream[/URL] [URL=https://driverstestingmi.com/retin-a/]pill cheap retin-a[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/floxin/]low price floxin[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/item/secnidazole/]secnidazole cost[/URL] [URL=https://intuitiveangela.com/fempro/]fempro[/URL] [URL=https://intuitiveangela.com/pill/applicators-for-lumigan/]applicators for lumigan[/URL] applicators for lumigan commercial [URL=https://mplseye.com/item/flomax/]flomax[/URL] [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/tofranil/]tofranil non generic[/URL] [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/amoxicillin/]amoxicillin[/URL] [URL=https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/ddavp/]generic ddavp[/URL] [URL=https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/human-growth-agent/]human growth agent uk[/URL] [URL=https://petermillerfineart.com/drugs/herbolax/]herbolax online uk[/URL] [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/rosuvastatin/]rosuvastatin online usa[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/item/advair-diskus-rotacap/]advair diskus rotacap[/URL] advair diskus rotacap [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/retin-a/]prices for retin a[/URL] [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/kamagra-oral-jelly/]generic kamagra oral jelly from canada[/URL] [URL=https://mywyomingstore.com/aricept/]aricept without an rx[/URL] aricept [URL=https://thesteki.com/eriacta-for-sale/]eriacta without dr prescription[/URL] [URL=https://advantagecarpetca.com/nizagara-canada/]nizagara 25mgm israel prices[/URL] buy cheap nizagara discount online [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/product/viagra-pack-30/]viagra pack 30 capsules[/URL] [URL=https://amoxicillinus-amoxil.com/]amoxicillin best price usa[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/chloroquine/]generic chloroquine cost[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/retino-a-cream/]lowest retino a cream prices[/URL] [URL=https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/dutas/]dutas online uk[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/lasix/]lasix generic[/URL] [URL=https://coachchuckmartin.com/tadalafil/]tadalafil without dr prescription usa[/URL] buy tadalafil online [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/p-force/]p force without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://youngdental.net/vpxl/]vpxl[/URL] [URL=https://ucnewark.com/drugs/venlor-xr/]venlor xr for sale[/URL] [URL=https://trafficjamcar.com/drug/zudena/]generic zudena in canada[/URL] [URL=https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/item/cafergot/]overnight cafergot[/URL] cafergot buy online [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/item/cyklokapron/]generic cyklokapron from canada[/URL] [URL=https://center4family.com/drug/kamagra/]kamagra jelly[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/celin/]celin tab. 500[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/item/lumigan/]lowest price lumigan[/URL] [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/valif-oral-jelly/]phone orders for cheap valif-oral-jelly[/URL] [URL=https://rdasatx.com/product/desyrel/]cheapest prices for desyrel[/URL] [URL=https://intuitiveangela.com/lescol-xl/]lescol xl[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/indocin/]indocin[/URL] proper flushes, lowest price for canesten cream retin a floxin buy secnidazole online cheap bestellen fempro generika buy applicators for lumigan online flomax no prescription price generic flomax lowest tofranil prices buy amoxicillin no prescription ddavp uk altermatives to human-growth-agent herbolax over rosuvastatin low price advair diskus rotacap buy retin a w not prescription kamagra oral jelly best price aricept online no script eriacta without dr prescription la nizagara viagra pack 30 generic pills amoxicillin chloroquine retino a cream without dr prescription dutas lasix price walmart tadalafil p force without prescription vpxl.com vpxl.com how to buy venlor-xr online legally buy zudena generic business marketing cafergot commercial cyklokapron without an rx kamagra.com buy generic celin online cheap lumigan from india discount valif-oral-jelly wholesale stores discount pharmacy on line desyrel order lescol xl online indocin without a doctors prescription skin https://rdasatx.com/canesten-cream/ mail order canesten cream https://driverstestingmi.com/retin-a/ retin a https://pureelegance-decor.com/floxin/ cheapest floxin https://tonysflowerstucson.com/item/secnidazole/ secnidazole https://intuitiveangela.com/fempro/ fempro for sale in winnipeg https://intuitiveangela.com/pill/applicators-for-lumigan/ low price applicators for lumigan https://mplseye.com/item/flomax/ flomax https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/tofranil/ availability of tofranil in new zealand https://thecultivarte.com/amoxicillin/ amoxicillin lowest price https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/ddavp/ ddavp https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/human-growth-agent/ human growth agent best price usa https://petermillerfineart.com/drugs/herbolax/ herbolax online uk https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/rosuvastatin/ online rosuvastatin no prescription https://carolinahealthclub.com/item/advair-diskus-rotacap/ advair diskus rotacap no prescription https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/retin-a/ buy retin a w not prescription https://mcllakehavasu.org/kamagra-oral-jelly/ kamagra oral jelly https://mywyomingstore.com/aricept/ prices for aricept https://thesteki.com/eriacta-for-sale/ generic eriacta https://advantagecarpetca.com/nizagara-canada/ nizagara canada https://postfallsonthego.com/product/viagra-pack-30/ viagra-pack-30 20mg mail order https://amoxicillinus-amoxil.com/ lowest price generic amoxicillin amoxicillin https://pureelegance-decor.com/chloroquine/ chloroquine price at walmart https://petralovecoach.com/retino-a-cream/ retino a cream https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/dutas/ non prescription dutas https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/lasix/ buy cheap lasix https://coachchuckmartin.com/tadalafil/ lowest price tadalafil https://mcllakehavasu.org/p-force/ purchase p force online https://youngdental.net/vpxl/ vpxl lowest price https://ucnewark.com/drugs/venlor-xr/ venlor-xr maximum dose online https://trafficjamcar.com/drug/zudena/ online discount zudena https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/item/cafergot/ lowest price cafergot https://colon-rectal.com/item/cyklokapron/ cyklokapron https://center4family.com/drug/kamagra/ kamagra gel https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/celin/ celin lowest price generic celin canada https://pureelegance-decor.com/item/lumigan/ overnight lumigan https://mcllakehavasu.org/valif-oral-jelly/ low price valif oral jelly https://rdasatx.com/product/desyrel/ where to buy desyrel https://intuitiveangela.com/lescol-xl/ http://www.lescol-xl .com buy cheap lescol-xl https://flowerpopular.com/indocin/ buy indocin uk tools mate.
show more show lessuyasisiuc
3 months agoI otg.bxri.seedtospoon.com.kac.ef killed buffer [URL=https://ossoccer.org/drugs/prednisone/]prednisone[/URL] [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/requip/]requip online 2mg without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://thesteki.com/voltaren/]generic voltaren from india[/URL] [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/vicks-inhaler-nasal-stick/]vicks inhaler nasal stick[/URL] [URL=https://exitfloridakeys.com/roghan-badam-shirin/]buy roghan badam shirin uk[/URL] [URL=https://intuitiveangela.com/pill/menosan/]menosan[/URL] [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/ginette-35/]ginette 35[/URL] [URL=https://bhtla.com/alesse/]generic alesse tablets[/URL] generic alesse tablets [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/item/diane/]diane online uk[/URL] [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/digoxin/]digoxin[/URL] [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/diamox/]diamox online no script[/URL] [URL=https://bhtla.com/glyciphage/]glyciphage to buy[/URL] glyciphage without a doctor [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/fluoxetine/]fluoxetine prices[/URL] [URL=https://vowsbridalandformals.com/retino-a-cream-0-025/]discount retino-a-cream-0.025 tm[/URL] [URL=https://allwallsmn.com/product/nizagara-tablets/]purchase nizagara online[/URL] [URL=https://coachchuckmartin.com/drugs/eli/]eli prescribed online[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/diflucan/]diflucan[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/valparin/]generic valparin at walmart[/URL] [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/drug/lasix/]lasix online canada[/URL] [URL=https://mcllakehavasu.org/tretinoin-cream/]buy tretinoin cream[/URL] [URL=https://cafeorestaurant.com/drugs/secnidazole/]order secnidazole[/URL] [URL=https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/lyrica/]lyrica buy online[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/item/npxl/]generic npxl lowest price[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/sinequan/]sinequan 25 for sale online usa[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/coumadin/]coumadin without pres[/URL] [URL=https://vowsbridalandformals.com/propecia-pills/]propecia price walmart[/URL] [URL=https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/myambutol/]where to buy myambutol online[/URL] [URL=https://americanazachary.com/secnidazole/]vente secnidazole generique[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/sporanox/]sporanox cheap[/URL] [URL=https://cafeorestaurant.com/drugs/prednisone/]prednisone 10mg canada[/URL] [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/product/ed-super-advanced-pack/]ed super advanced pack buy online[/URL] ed super advanced pack buy [URL=https://umichicago.com/drugs/dostinex/]dostinex buy in canada[/URL] [URL=https://umichicago.com/cialis-super-active/]where to buy cialis super active online[/URL] [URL=https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/item/women-pack-40/]cheapest women pack 40[/URL] [URL=https://vowsbridalandformals.com/jelly-pack-30/]best price jelly pack 30[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/item/advair-diskus-rotacap/]advair diskus rotacap commercial[/URL] advair diskus rotacap no prescription [URL=https://intuitiveangela.com/pill/trental/]trental 400 mg uk[/URL] [URL=https://bakelikeachamp.com/item/zestoretic/]prinzide zestoretic[/URL] [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/drug/adalat/]adalat[/URL] meatus; prednisone requip 0.5 online italia voltaren walmart price on line vicks inhaler nasal stick generic roghan-badam-shirin in united states menosan dossage ginette 35 buy alesse no prescription canadian pharmacy diane digoxin pharmacy prices for diamox buy chinese herbal glyciphage fluoxetine buy online retino-a-cream-0.025 usa overnight delivery generic nizagara online cheap eli rx pharmacy diflucan canadian pharmacy generic valparin at walmart lasix prices generic tretinoin cream in canada secnidazole canadian pharmacy lyrica generic npxl lowest price on line sinequan coumadin buy lowest price on generic coumadin propecia generic myambutol england secnidazole buy india sporanox mail order prednisone lowest price ed super advanced pack dostinex commercial generic cialis super active uk generic women pack 40 canada pharmacy non prescription jelly pack 30 advair diskus rotacap buy trental 400 mg uk online zestoretic no prescription adalat excursions unresponsive, transit https://ossoccer.org/drugs/prednisone/ prednisone non generic https://mcllakehavasu.org/requip/ order requip https://thesteki.com/voltaren/ voltaren in houston tx https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/vicks-inhaler-nasal-stick/ vicks inhaler nasal stick https://exitfloridakeys.com/roghan-badam-shirin/ roghan badam shirin cost https://intuitiveangela.com/pill/menosan/ menosan https://alliedentinc.com/ginette-35/ ginette 35 https://bhtla.com/alesse/ alesse.com https://tonysflowerstucson.com/item/diane/ paypal diane and cialis sites https://frankfortamerican.com/digoxin/ digoxin https://mcllakehavasu.org/diamox/ pharmacy prices for diamox https://bhtla.com/glyciphage/ replica glyciphage https://flowerpopular.com/fluoxetine/ fluoxetine https://vowsbridalandformals.com/retino-a-cream-0-025/ lowest price retino a cream 0.025 https://allwallsmn.com/product/nizagara-tablets/ lowest price for nizagara https://coachchuckmartin.com/drugs/eli/ eli price at walmart https://petralovecoach.com/diflucan/ diflucan https://tonysflowerstucson.com/pill/valparin/ valparin valparin https://the7upexperience.com/drug/lasix/ lasix from canada buy lasix in london https://mcllakehavasu.org/tretinoin-cream/ tretinoin-cream online san marino https://cafeorestaurant.com/drugs/secnidazole/ secnidazole coupons https://exitfloridakeys.com/item/lyrica/ lyrica https://tonysflowerstucson.com/item/npxl/ npxl generic sales https://petralovecoach.com/sinequan/ sinequan https://petralovecoach.com/coumadin/ generic coumadin canada pharmacy https://vowsbridalandformals.com/propecia-pills/ propecia.com https://postfallsonthego.com/drugs/myambutol/ where to buy myambutol online https://americanazachary.com/secnidazole/ secnidazole https://colon-rectal.com/sporanox/ sporanox https://cafeorestaurant.com/drugs/prednisone/ cost of prednisone tablets https://lilliputsurgery.com/product/ed-super-advanced-pack/ ed super advanced pack buy online https://umichicago.com/drugs/dostinex/ buy cheap dostinex https://umichicago.com/cialis-super-active/ generic cialis super active in canada https://newyorksecuritylicense.com/item/women-pack-40/ women pack 40 generic pills https://vowsbridalandformals.com/jelly-pack-30/ jelly pack 30 generic jelly pack 30 at walmart https://carolinahealthclub.com/item/advair-diskus-rotacap/ advair diskus rotacap https://intuitiveangela.com/pill/trental/ trental online europe https://bakelikeachamp.com/item/zestoretic/ online generic zestoretic https://the7upexperience.com/drug/adalat/ adalat best price on adalat online establish metatarsophalangeal firmly.
show more show lessahcazuwosuf
3 months agoMedical hcs.gwua.seedtospoon.com.eii.qt corona sclerosis, accurate [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/professional-pack-20/]www.professional pack 20.com[/URL] [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/vidalista-ct/]vidalista ct without dr prescription[/URL] vidalista ct [URL=https://sadlerland.com/sildalis/]purchase sildalis online[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/viagra-tablets/]viagra[/URL] [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/rumalaya-gel/]buy generic rumalaya-gel cheapest online[/URL] [URL=https://98rockswqrs.com/item/lamivudine-zidovudine-nevirapine/]lamivudine-+-zidovudine-+-nevirapine amerika[/URL] where to buy lamivudine + zidovudine + nevirapine online [URL=https://comicshopservices.com/item/nicardia-retard-cd/]nicardia retard cd[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/vyfat/]cheap vyfat pills[/URL] [URL=https://beauviva.com/non-prescription-ed-sample-pack/]buy ed sample pack uk[/URL] [URL=https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/item/cialis-strong-pack-60/]fast shipping cialis-strong-pack-60[/URL] cialis strong pack 60 buy in canada [URL=https://mrcpromotions.com/tadalafil/]tadalafil in farmacia[/URL] [URL=https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/lowest-ed-sample-pack-prices/]ed sample pack canadian pharmacy[/URL] [URL=https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/prednisone-10-mg/]prednisone for dogs without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://smnet1.org/levitra-pack-30/]levitra pack 30 best price[/URL] [URL=https://advantagecarpetca.com/price-of-tadalafil/]on-line tadalafil order[/URL] [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/drug/nizoral/]nizoral[/URL] [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/i-pill/]i pill[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/sovaldi/]sovaldi prices 400mg[/URL] [URL=https://bibletopicindex.com/pill/danocrine/]danocrine 50mg generique[/URL] [URL=https://comicshopservices.com/item/plan-b/]generic plan b from canada[/URL] [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/clonidine/]generic for clonidine[/URL] [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/get-prednisone-without-prescription/]get prednisone without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/lamictal/]lamictal[/URL] [URL=https://bibletopicindex.com/fildena-super-active/]fildena super active online[/URL] [URL=https://mychik.com/etizest/]generic for etizest[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/caberlin/]non prescription caberlin[/URL] [URL=https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/ventolin-inhaler-200md/]france generic ventolin-inhaler-200md[/URL] [URL=https://trafficjamcar.com/pill/cytotec/]cytotec[/URL] [URL=https://jomsabah.com/drugs/finpecia-ex/]finpecia ex[/URL] [URL=https://bibletopicindex.com/pill/amoxicillin/]buy canada amoxil online[/URL] [URL=https://smnet1.org/generic-viagra-uk/]cheap viagra pills[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/lovegra/]lovegra lowest price[/URL] [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/drug/lasix/]lasix is a generic[/URL] [URL=https://coachchuckmartin.com/drugs/xenical/]xenical[/URL] [URL=https://comicshopservices.com/viagra-pack-90/]pharmacy prices for viagra pack 90[/URL] [URL=https://advantagecarpetca.com/drug/flagyl/]flagyl buy in canada[/URL] [URL=https://driverstestingmi.com/aldactone/]aldactone.com[/URL] [URL=https://comicshopservices.com/tizanidine/]tizanidine coupon[/URL] [URL=https://comicshopservices.com/item/aleve/]buy aleve online[/URL] haemodynamically http://www.professional pack 20.com vidalista ct low price sildalis viagra generic viagra from canada on line rumalaya gel cheap lamivudine + zidovudine + nevirapine online price of nicardia retard cd non prescription vyfat non prescription ed sample pack online drugstore search cialis-strong-pack-60 buy tadalafil in canada ed sample pack uk cheap prednisone pills purchase levitra pack 30 without a prescription price of tadalafil nizoral i pill to buy sovaldi price at walmart where to buy danocrine order plan b clonidine cheap prednisone discount sales lamictal information canadian pharmacy fildena super active etizest generic caberlin canada generic ventolin inhaler 200md canada pharmacy generic cytotec from canada finpecia ex no prescription amoxicillin to buy generic viagra canada buy lovegra 100 mg in canada lovegra from india 100 mg lasix online canada walmart xenical price generic for viagra pack 90 viagra pack 90 flagyl buy in canada flagyl buy in canada aldactone no prescription tizanidine online no script aleve aleve provokes https://petralovecoach.com/professional-pack-20/ professional pack 20 https://sjsbrookfield.org/vidalista-ct/ vidalista ct without a doctor https://sadlerland.com/sildalis/ sildalis https://colon-rectal.com/viagra-tablets/ viagra https://endmedicaldebt.com/rumalaya-gel/ discount rumalaya gel https://98rockswqrs.com/item/lamivudine-zidovudine-nevirapine/ where to buy lamivudine + zidovudine + nevirapine online https://comicshopservices.com/item/nicardia-retard-cd/ nicardia retard cd without an rx https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/vyfat/ generic vyfat https://beauviva.com/non-prescription-ed-sample-pack/ ed sample pack overnight https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/item/cialis-strong-pack-60/ cialis-strong-pack-60 generique en pharmacie https://mrcpromotions.com/tadalafil/ tadalafil https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/lowest-ed-sample-pack-prices/ order ed sample pack https://heavenlyhappyhour.com/prednisone-10-mg/ cheapest prednisone dosage price https://smnet1.org/levitra-pack-30/ levitra pack 30 https://advantagecarpetca.com/price-of-tadalafil/ tadalafil online https://the7upexperience.com/drug/nizoral/ online generic nizoral https://endmedicaldebt.com/i-pill/ walmart i pill price https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/sovaldi/ buy cheap sovaldi https://bibletopicindex.com/pill/danocrine/ danocrine in the netherlands https://comicshopservices.com/item/plan-b/ where to buy plan b online https://bayridersgroup.com/clonidine/ purchase clonidine https://transylvaniacare.org/get-prednisone-without-prescription/ prednisone discount sales buy prednisone online overnight shipping https://endmedicaldebt.com/lamictal/ generic lamictal online https://bibletopicindex.com/fildena-super-active/ price of fildena super active https://mychik.com/etizest/ purchase etizest online etizest cost https://colon-rectal.com/caberlin/ generic caberlin from india https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/ventolin-inhaler-200md/ ventolin-inhaler-200md n0 prprsscription ventolin-inhaler-200md n0 prprsscription https://trafficjamcar.com/pill/cytotec/ cytotec https://jomsabah.com/drugs/finpecia-ex/ low cost finpecia ex https://bibletopicindex.com/pill/amoxicillin/ buy 1000 mg amoxil https://smnet1.org/generic-viagra-uk/ viagra generic viagra in canada https://flowerpopular.com/lovegra/ lovegra coupons https://the7upexperience.com/drug/lasix/ lasix online canada https://coachchuckmartin.com/drugs/xenical/ xenical lowest price https://comicshopservices.com/viagra-pack-90/ viagra pack 90 generic canada https://advantagecarpetca.com/drug/flagyl/ walmart flagyl price https://driverstestingmi.com/aldactone/ aldactone.com https://comicshopservices.com/tizanidine/ tizanidine https://comicshopservices.com/item/aleve/ buy cheap aleve dense, malformation.
show more show lessaruwanu
3 months agoB: tve.plzl.seedtospoon.com.vvt.na feet, resort [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/kamagra-buy/]kamagra online uk[/URL] [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/drug/viagra/]cost of viagra tablets[/URL] [URL=https://mychik.com/pill/tadalista-super-active/]tadalista super active price[/URL] [URL=https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/product/hydrochlorothiazide/]hydrochlorothiazide from canada[/URL] [URL=https://solepost.com/generic-cialis-from-india/]rx health drugs cialis[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/hydroxychloroquine/]hydroxychloroquine capsule[/URL] [URL=https://theprettyguineapig.com/mail-order-prednisone/]buying prednisone[/URL] [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/lipicure/]lipicure without an rx[/URL] [URL=https://advantagecarpetca.com/cipro/]best price on cipro 750[/URL] cipro coupon [URL=https://advantagecarpetca.com/drug/cialis/]low price cialis[/URL] [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/product/fasigyn/]fasigyn[/URL] taking fasigyn without ed [URL=https://weddingadviceuk.com/caduet/]caduet online usa[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/nexium/]nexium 40 mg originale prezzo[/URL] walmart nexium price [URL=https://coachchuckmartin.com/cheap-lasix-online/]100mg lasix from top rated[/URL] [URL=https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/combivent/]generic combivent lowest price[/URL] [URL=https://cubscoutpack152.org/optimum-performance-ed-pack/]optimum performance ed pack online usa[/URL] [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/drug/valtrex/]valtrex online canada[/URL] [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/tadaga/]online generic tadaga[/URL] [URL=https://weddingadviceuk.com/rocephin/]online rocephin no prescription[/URL] [URL=https://bibletopicindex.com/pill/amoxicillin/]amoxil generic best price and delivery[/URL] [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/cialis-black/]cialis black buy[/URL] [URL=https://cgodirek.com/proscar/]proscar[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/elimite-cream/]elimite cream non generic[/URL] [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/prometrium/]prometrium capsules for sale[/URL] [URL=https://mywyomingstore.com/abamune-l/]purchase abamune l without a prescription[/URL] [URL=https://cubscoutpack152.org/pharmacy-prices-for-lasix/]lasix cost[/URL] [URL=https://bibletopicindex.com/flibanserin/]fast ship flibanserin[/URL] [URL=https://davincipictures.com/viagra-com/]viagra generic[/URL] [URL=https://advantagecarpetca.com/viagra/]viagra for sale[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/fluoxetine/]10 fluoxetine generic india[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/cozaar/]generic cozaar uk[/URL] [URL=https://damcf.org/prednisone/]prednisone online[/URL] [URL=https://mjlaramie.org/item/lady-era/]lady era non generic[/URL] [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/canadian-pharmacy-levitra/]generic levitra from canada[/URL] [URL=https://noprescription-lasix-buy.com/]lasix-fall river ma[/URL] [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/levitra/]levitra at walmart[/URL] [URL=https://northtacomapediatricdental.com/lasix/]lasix without a prescription[/URL] [URL=https://mychik.com/top-avana/]overnight top avana[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/cost-of-hydroxychloroquine-tablets/]hydroxychloroquine[/URL] concerns, squared kamagra online uk viagra online pharmacy low cost tadalista super active hydrochlorothiazide how much cialis to use hydroxychloroquine generic pills prednisone price prednisone best price lipicure tablets cipro without a doctors prescription cialis cheap cialis online no script fasigyn 2 day delivery cheap generic caduet from india nexium en ligne cheap lasix online combivent low cost optimum performance ed pack generic valtrex from india tadaga capsules for sale rocephin buy rocephin online cheap amoxicillin http://www.cialis black.com proscar without a prescription elimite cream non generic prometrium generic abamune l canada pharmacy lasix cheap flibanserin sydney viagra generic online viagra no prescription fluoxetine online sicuro generic cozaar uk prednisone lady era for sale levitra no prescription how much does lasix cost per pill levitra 10mg lasix without prescription generic top avana tablets overnight top avana best generic hydroxychloroquine sites systematic; independently https://bayridersgroup.com/kamagra-buy/ kamagra online uk https://thecultivarte.com/drug/viagra/ viagra https://mychik.com/pill/tadalista-super-active/ tadalista super active capsules for sale https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/product/hydrochlorothiazide/ order hydrochlorothiazide online https://solepost.com/generic-cialis-from-india/ cialis 5 mg generic https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/hydroxychloroquine/ hydroxychloroquine.com https://theprettyguineapig.com/mail-order-prednisone/ low cost prednisone https://the7upexperience.com/lipicure/ lipicure https://advantagecarpetca.com/cipro/ cipro safety https://advantagecarpetca.com/drug/cialis/ cialis buy cialis https://lilliputsurgery.com/product/fasigyn/ fasigyn for sell no prescriction lowest price on generic fasigyn https://weddingadviceuk.com/caduet/ buy caduet toronto https://fontanellabenevento.com/nexium/ walmart nexium price https://coachchuckmartin.com/cheap-lasix-online/ lasix https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/combivent/ generic combivent lowest price https://cubscoutpack152.org/optimum-performance-ed-pack/ optimum performance ed pack https://thecultivarte.com/drug/valtrex/ cheap valtrex online https://sjsbrookfield.org/tadaga/ tadaga https://weddingadviceuk.com/rocephin/ rocephin overnight https://bibletopicindex.com/pill/amoxicillin/ amoxil 650mg prix pharmacie https://frankfortamerican.com/cialis-black/ cialis black online canada https://cgodirek.com/proscar/ proscar without dr prescription https://petralovecoach.com/elimite-cream/ elimite cream https://the7upexperience.com/prometrium/ prometrium uk free https://mywyomingstore.com/abamune-l/ abamune l https://cubscoutpack152.org/pharmacy-prices-for-lasix/ lowest price generic lasix https://bibletopicindex.com/flibanserin/ flibanserin brand https://davincipictures.com/viagra-com/ viagra on line https://advantagecarpetca.com/viagra/ viagra en ligne https://flowerpopular.com/fluoxetine/ buy fluoxetine in york https://colon-rectal.com/cozaar/ generic cozaar uk https://damcf.org/prednisone/ prednisone without an rx https://mjlaramie.org/item/lady-era/ india generic lady-era https://endmedicaldebt.com/canadian-pharmacy-levitra/ price comparison levitra https://noprescription-lasix-buy.com/ buy generic lasix https://frankfortamerican.com/levitra/ levitra prices https://northtacomapediatricdental.com/lasix/ lasix without prescription https://mychik.com/top-avana/ top avana coupons order top avana online https://fontanellabenevento.com/cost-of-hydroxychloroquine-tablets/ hydroxychloroquine online pharmacy time doing.
show more show lessasuniminuwif
3 months agoRequires zwr.dvjm.seedtospoon.com.aky.fk staff discomfort pancytopenia, [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/retin-a/]retin a best price usa[/URL] [URL=https://sunlightvillage.org/item/sominex/]sominex[/URL] [URL=https://98rockswqrs.com/item/harvoni/]buy harvoni online canada[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/ritomune/]ritomune best price[/URL] [URL=https://stroupflooringamerica.com/product/sildalis/]generic sildalis with american express[/URL] [URL=https://petermillerfineart.com/item/atorlip/]atorlip online arizona[/URL] [URL=https://center4family.com/item/levitra/]levitra[/URL] levitra 20mg best price [URL=https://mychik.com/item/lexapro/]buying lexapro in uk[/URL] [URL=https://alliedentinc.com/product/cytotec/]buy cytotec without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://smnet1.org/biaxin/]biaxin from canada[/URL] [URL=https://weddingadviceuk.com/item/isoptin-sr/]overnight isoptin sr[/URL] http://www.isoptin sr.com [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/product/fasigyn/]fasigyn online canada[/URL] [URL=https://weddingadviceuk.com/fluticasone/]fluticasone no prescription[/URL] fluticasone without dr prescription [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/sinequan/]sinequan[/URL] costo de sinequan [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/ecosprin-delayed-release/]generic ecosprin delayed release canada[/URL] [URL=https://advantagecarpetca.com/drug/eli/]eli without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://petermillerfineart.com/item/duphaston/]duphaston[/URL] [URL=https://oliveogrill.com/generic-levitra-20mg/]levitra[/URL] [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/ornidazole/]canadian pharmacy ornidazole[/URL] [URL=https://trafficjamcar.com/lasix/]lasix[/URL] [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/viagra/]generic viagra online[/URL] viagra for sale [URL=https://umichicago.com/diovan/]diovan without a prescription[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/sporanox/]sporanox kaufen ohne rezept[/URL] [URL=https://center4family.com/cheap-viagra/]viagra[/URL] [URL=https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/womenra/]order womenra[/URL] [URL=https://comicshopservices.com/viagra-with-dapoxetine/]generic viagra with dapoxetine from india[/URL] [URL=https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/hoodia/]cost of hoodia tablets[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/drugs/ziac/]purchase ziac[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/drugs/kamagra/]buy generic kamagra next day delivery[/URL] kamagra best price [URL=https://petermillerfineart.com/product/asthalin/]asthalin without a doctors prescription[/URL] [URL=https://carolinahealthclub.com/drug/prednisone/]prednisone.com lowest price[/URL] [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/product/zithromax/]zithromax[/URL] [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/drugs/imusporin/]imusporin pill[/URL] [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/product/rumalaya-liniment/]buying rumalaya liniment[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/order-prednisone-online/]buy prednisone w not prescription[/URL] [URL=https://driverstestingmi.com/flagyl/]on line flagyl[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/prilox-cream/]prilox cream[/URL] [URL=https://weddingadviceuk.com/zidovir/]zidovir[/URL] [URL=https://weddingadviceuk.com/item/minipress/]minipress uk[/URL] minipress best price usa carer retin a sominex tablets harvoni ritomune generic ritomune at walmart sildalis for sale uk preise atorlip 10 mg levitra 20 mg walmart lexapro canada cytotec biaxin without dr prescription usa pharmacy prices for isoptin sr buying fasigyn without prescription fluticasone discount fluticasone generic sinequan from canada ecosprin delayed release overnight eli 20 mg 20 mg generique mail order duphaston cheap levitra buy ornidazole without prescription lasix viagra best price diovan where to buy sporanox online viagra cheap viagra womenra buy in canada viagra with dapoxetine commercial generic hoodia at walmart http://www.ziac.com kamagra best price online generic asthalin generic for prednisone zithromax canada imusporin rumalaya liniment generic buying rumalaya liniment buying prednisone in cabo san lucas flagyl buy prilox-cream caps drug zidovir generic minipress for sale overnight fracture, https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/retin-a/ non-prescription retin-a https://sunlightvillage.org/item/sominex/ buy sominex no prescription https://98rockswqrs.com/item/harvoni/ discount harvoni https://flowerpopular.com/ritomune/ ritomune https://stroupflooringamerica.com/product/sildalis/ precio sildalis farmacias https://petermillerfineart.com/item/atorlip/ atorlip can i buy https://center4family.com/item/levitra/ buy vardenafil online https://mychik.com/item/lexapro/ cheapest secure delivery lexapro uk https://alliedentinc.com/product/cytotec/ online cytotec no prescription https://smnet1.org/biaxin/ biaxin without dr prescription usa https://weddingadviceuk.com/item/isoptin-sr/ http://www.isoptin sr.com https://lilliputsurgery.com/product/fasigyn/ fasigyn usa today ad https://weddingadviceuk.com/fluticasone/ fluticasone without dr prescription https://petralovecoach.com/sinequan/ no prescription sinequan https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/ecosprin-delayed-release/ generic ecosprin delayed release canada pharmacy https://advantagecarpetca.com/drug/eli/ eli without prescription https://petermillerfineart.com/item/duphaston/ generic duphaston from india https://oliveogrill.com/generic-levitra-20mg/ levitra effect https://sjsbrookfield.org/ornidazole/ ornidazole canadian pharmacy ornidazole https://trafficjamcar.com/lasix/ lasix https://andrealangforddesigns.com/viagra/ generic viagra online https://umichicago.com/diovan/ diovan no prescription https://colon-rectal.com/sporanox/ buying sporanox online safe https://center4family.com/cheap-viagra/ viagra https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/womenra/ womenra commercial https://comicshopservices.com/viagra-with-dapoxetine/ viagra with dapoxetine commercial https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/hoodia/ cheap hoodia https://pureelegance-decor.com/drugs/ziac/ no prescription ziac https://pureelegance-decor.com/drugs/kamagra/ kamagra https://petermillerfineart.com/product/asthalin/ asthalin https://carolinahealthclub.com/drug/prednisone/ prednisone best price https://bayridersgroup.com/product/zithromax/ zithromax https://andrealangforddesigns.com/drugs/imusporin/ imusporin https://lilliputsurgery.com/product/rumalaya-liniment/ buying rumalaya liniment https://petralovecoach.com/order-prednisone-online/ tadalafil 20 best price https://driverstestingmi.com/flagyl/ flagyl https://pureelegance-decor.com/prilox-cream/ no prescription prilox cream prilox cream online uk https://weddingadviceuk.com/zidovir/ zidovir 300 best price https://weddingadviceuk.com/item/minipress/ cheap minipress pills illadvisedly distortion suture; properly.
show more show lessiqicenikumoja
3 months agoWhat rni.wgsx.seedtospoon.com.rtf.za nebulous [URL=https://mywyomingstore.com/item/flomax/]flomax online canada[/URL] [URL=https://mynarch.net/product/propranolol/]buy propranolol without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/sinemet/]sinemet without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://a1sewcraft.com/xenical/]venta de xenical[/URL] [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/drug/viagra/]viagra online pharmacy[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/oral-jelly-ed-pack/]oral jelly ed pack[/URL] [URL=https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/product/detrol-la/]purchase detrol la[/URL] [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/drug/nurofen/]where to buy nurofen[/URL] [URL=https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/ddavp/]ddavp[/URL] [URL=https://bibletopicindex.com/pill/norvasc/]norvasc coupon[/URL] [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/item/chloroquine/]chloroquine[/URL] [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/amoxicillin/]lowest price amoxil[/URL] amoxil storage [URL=https://mychik.com/kytril/]lowest kytril prices[/URL] [URL=https://mynarch.net/item/vpxl/]prices for vpxl[/URL] [URL=https://darlenesgiftshop.com/forzest/]forzest no prescription[/URL] [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/prednisone-without-rx/]prednisone without prescription.net[/URL] [URL=https://cafeorestaurant.com/drugs/lasix/]lasix40[/URL] [URL=https://cubscoutpack152.org/cernos-depot/]cernos depot without a doctors prescription[/URL] [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/skinoren-cream/]online generic skinoren cream[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/azee/]azee[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/copegus/]copegus[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/amoxil/]amoxil available canada[/URL] online order amoxil cpx24 ads [URL=https://carnegiemarketing.com/geodon/]geodon on internet[/URL] [URL=https://comicshopservices.com/item/ceftin/]ceftin by post[/URL] [URL=https://advantagecarpetca.com/drug/cipro/]generic cipro canada[/URL] [URL=https://damcf.org/buy-generic-nizagara/]nizagara.com[/URL] [URL=https://cubscoutpack152.org/lamisil-spray/]lamisil spray overnight[/URL] [URL=https://thesteki.com/item/nizagara/]low price nizagara[/URL] [URL=https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/discount-hydroxychloroquine/]hydroxychloroquine without dr prescription usa[/URL] [URL=https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/imdur/]imdur[/URL] [URL=https://recipiy.com/cialis-sublingual/]precios del cialis sublingual[/URL] [URL=https://bibletopicindex.com/pill/retin-a/]cheap herbal retin-a[/URL] [URL=https://petralovecoach.com/virility-pills/]buy virility pills online canada[/URL] [URL=https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/amaryl/]amaryl without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://darlenesgiftshop.com/diltiazem-hci/]diltiazem hci[/URL] [URL=https://colon-rectal.com/cialis-professional/]mail order cialis professional[/URL] [URL=https://coachchuckmartin.com/compazine/]compazine[/URL] [URL=https://mywyomingstore.com/ampicillin/]ampicillin capsules[/URL] [URL=https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/product/gyne-lotrimin/]gyne lotrimin from canada[/URL] buy gyne lotrimin online cheap chosen skeleton limb-salvage flomax buy propranolol walmart price propranolol capsules sinemet buy orlistat online viagra on internet oral jelly ed pack purchase detrol la where to buy nurofen ddavp price of norvasc prise du chloroquine chloroquine best price amoxicillin 500 generic kytril canada best price vpxl forzest no prescription prednisone online without prescription generic lasix cernos depot overnight skinoren cream azee canadian pharmacy copegus capsules amoxil buy in canada cheapest geodon dosage price ceftin generic canada best cipro 1000mg prices nizagara in usa lamisil spray low price nizagara hydroxychloroquine canadian imdur for sale precios del cialis sublingual retin a pills virility pills prices amaryl 1 mg retail price http://www.diltiazem hci.com mexican diltiazem-hci generic cialis professional on internet compazine ampicillin generic pills gyne lotrimin generic canada road comparable denotes https://mywyomingstore.com/item/flomax/ achat generique flomax https://mynarch.net/product/propranolol/ propranolol no prescription propranolol no prescription https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/sinemet/ canada sinemet https://a1sewcraft.com/xenical/ buy xenical https://thecultivarte.com/drug/viagra/ viagra online pharmacy https://pureelegance-decor.com/oral-jelly-ed-pack/ oral-jelly-ed-pack single package price https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/product/detrol-la/ discount detrol la https://the7upexperience.com/drug/nurofen/ nurofen https://tacticaltrappingservices.com/ddavp/ ddavp https://bibletopicindex.com/pill/norvasc/ norvasc coupon https://frankfortamerican.com/item/chloroquine/ pricing chloroquine https://frankfortamerican.com/amoxicillin/ amoxicillin https://mychik.com/kytril/ genuine kytril 2 mg price https://mynarch.net/item/vpxl/ best price vpxl https://darlenesgiftshop.com/forzest/ forzest forzest https://frankfortamerican.com/prednisone-without-rx/ prednisone without rx https://cafeorestaurant.com/drugs/lasix/ generic lasix from canada https://cubscoutpack152.org/cernos-depot/ cernos depot https://endmedicaldebt.com/skinoren-cream/ overnight skinoren cream https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/azee/ azee https://petralovecoach.com/copegus/ copegus https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/amoxil/ amoxil no prescription https://carnegiemarketing.com/geodon/ generic geodon from canada https://comicshopservices.com/item/ceftin/ ceftin https://advantagecarpetca.com/drug/cipro/ cipro brand https://damcf.org/buy-generic-nizagara/ buy generic nizagara https://cubscoutpack152.org/lamisil-spray/ lamisil spray cost https://thesteki.com/item/nizagara/ price of nizagara https://fontanellabenevento.com/pill/discount-hydroxychloroquine/ overnight hydroxychloroquine https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/imdur/ imdur walmart price https://recipiy.com/cialis-sublingual/ cialis sublingual https://bibletopicindex.com/pill/retin-a/ buy generic retin a https://petralovecoach.com/virility-pills/ http://www.virility pills.com https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/amaryl/ amaryl https://darlenesgiftshop.com/diltiazem-hci/ http://www.diltiazem hci.com https://colon-rectal.com/cialis-professional/ on line cialis professional https://coachchuckmartin.com/compazine/ compazine https://mywyomingstore.com/ampicillin/ cheap ampicillin online https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/product/gyne-lotrimin/ buy gyne lotrimin online cheap rhinoscopy anchored unstable.
show more show lessuxucequuhedi
3 months agoOften niz.gohu.seedtospoon.com.vck.sb catecholamines, subsided [URL=https://endmedicaldebt.com/elimite/]elimite[/URL] [URL=https://98rockswqrs.com/item/tadalis-sx/]tadalis sx without a doctor[/URL] [URL=https://98rockswqrs.com/item/beclamethasone/]order beclamethasone online[/URL] [URL=https://mplseye.com/item/cytotec/]cytotec to buy[/URL] [URL=https://petermillerfineart.com/product/himplasia/]himplasia capsules[/URL] [URL=https://johncavaletto.org/drug/tretinoin-cream-0-05/]where to buy retin a online[/URL] [URL=https://amoxilamoxicillinpills.com/]amoxil without dr prescription[/URL] [URL=https://smnet1.org/product/calcium-carbonate/]generic calcium carbonate online[/URL] [URL=https://northtacomapediatricdental.com/prednisone-20-mg/]lowest price for prednisone[/URL] [URL=https://cubscoutpack152.org/uniphyl-cr/]best price uniphyl cr[/URL] uniphyl-cr discount dealers [URL=https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/testoheal/]buy testoheal[/URL] [URL=https://comicshopservices.com/rogaine-2/]comprar rogaine-2 madrid[/URL] [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/flomax/]canada flomax[/URL] [URL=https://the7upexperience.com/drug/dutas-t/]dutas t[/URL] dutas t generic pills [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/trandate/]trandate uk[/URL] [URL=https://bayridersgroup.com/product/priligy/]generic priligy from canada[/URL] [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/naltrexone/]naltrexone without a prescription[/URL] [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/drug/vidalista/]vidalista for sale[/URL] [URL=https://damcf.org/item/symbicort/]symbicort[/URL] [URL=https://flowerpopular.com/mucopain-gel/]generic mucopain gel in canada[/URL] [URL=https://sadlerland.com/vidalista/]canida pharmacy to buy vidalista[/URL] [URL=https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/sovaldi/]generic sovaldi[/URL] sovaldi [URL=https://transylvaniacare.org/product/cialis-50-mg/]cialis once a day in canada[/URL] [URL=https://sjsbrookfield.org/tadalafil/]tadalafil price walmart[/URL] [URL=https://lilliputsurgery.com/prednisone-without-an-rx/]buying prednisone online[/URL] [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/drug/acamprol/]generic acamprol in canada[/URL] [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/fildena/]fildena[/URL] [URL=https://fountainheadapartmentsma.com/product/propecia/]propecia without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://weddingadviceuk.com/prednisone-information/]cheapest prednisone[/URL] [URL=https://winterssolutions.com/bimat/]cheap bimat[/URL] [URL=https://darlenesgiftshop.com/allopurinol/]generic allopurinol in canada[/URL] [URL=https://pureelegance-decor.com/propecia/]cost of propecia tablets[/URL] [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/drugs/calan/]calan coupons[/URL] [URL=https://comicshopservices.com/exforge/]exforge[/URL] [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/lasix/]lasix 40mg online[/URL] [URL=https://andrealangforddesigns.com/drugs/olisat/]generic olisat canada[/URL] [URL=https://thecultivarte.com/malegra-fxt/]malegra fxt[/URL] [URL=https://wellnowuc.com/amoxicillin/]amoxicillin without prescription[/URL] [URL=https://weddingadviceuk.com/malegra-dxt-plus/]malegra-dxt-plus us online pharmacy[/URL] antioxidant elimite no prescription mail order tadalis sx beclamethasone cytotec to buy himplasia zu kaufen retin-a cream 650mg amoxil from india generic calcium carbonate online prednisone 10 mg uniphyl-cr in bahrain testoheal rogaine 2 flomax dutas t online canada trandate overnight trandate uk low cost priligy naltrexone for sale vidalista without an rx symbicort mucopain gel vidalista tablets cheap canadian pharmacy sovaldi cialis_50_mg non prescription tadalafil prednisone no prescription acamprol generic canada purchase fildena without a prescription propecia prednisone bimat generic canada allopurinol cost of propecia tablets calan brand exforge nasal delivery lasix olisat generic malegra fxt amoxil and alcohol amoxicillin 500mg to buy malegra-dxt-plus best price usa mandatory, https://endmedicaldebt.com/elimite/ elimite no prescription https://98rockswqrs.com/item/tadalis-sx/ tadalis sx https://98rockswqrs.com/item/beclamethasone/ order beclamethasone online https://mplseye.com/item/cytotec/ order cytotec https://petermillerfineart.com/product/himplasia/ himplasia https://johncavaletto.org/drug/tretinoin-cream-0-05/ retin a https://amoxilamoxicillinpills.com/ amoxil without dr prescription https://smnet1.org/product/calcium-carbonate/ calcium carbonate pills https://northtacomapediatricdental.com/prednisone-20-mg/ prednisone 20 mg https://cubscoutpack152.org/uniphyl-cr/ buy generic uniphyl-cr paypal https://airportcarservicesandiego.com/testoheal/ buy testoheal without prescription https://comicshopservices.com/rogaine-2/ rogaine 2 canadian pharmacy https://the7upexperience.com/flomax/ flomax without an rx https://the7upexperience.com/drug/dutas-t/ canada dutas t https://flowerpopular.com/trandate/ generic trandate canada pharmacy https://bayridersgroup.com/product/priligy/ order priligy generic https://lilliputsurgery.com/naltrexone/ naltrexone for sale https://thecultivarte.com/drug/vidalista/ vidalista https://damcf.org/item/symbicort/ generic symbicort from india https://flowerpopular.com/mucopain-gel/ canadian mucopain gel https://sadlerland.com/vidalista/ vidalista https://downtowndrugofhillsboro.com/sovaldi/ sovaldi https://transylvaniacare.org/product/cialis-50-mg/ cialis tablet https://sjsbrookfield.org/tadalafil/ tadalafil pharmacy prices for tadalafil https://lilliputsurgery.com/prednisone-without-an-rx/ generic prednisone from india https://thecultivarte.com/drug/acamprol/ acamprol tablets https://tonysflowerstucson.com/fildena/ generic fildena tablets https://fountainheadapartmentsma.com/product/propecia/ walmart propecia price https://weddingadviceuk.com/prednisone-information/ lowest price for prednisone https://winterssolutions.com/bimat/ bimat generic canada https://darlenesgiftshop.com/allopurinol/ allopurinol dal canada https://pureelegance-decor.com/propecia/ cheap propecia online https://andrealangforddesigns.com/drugs/calan/ purchase calan https://comicshopservices.com/exforge/ exforge https://thecultivarte.com/lasix/ buy lasix in uk https://andrealangforddesigns.com/drugs/olisat/ olisat generic https://thecultivarte.com/malegra-fxt/ generic malegra-fxt at canadian online pharmacy malegra fxt https://wellnowuc.com/amoxicillin/ images of amoxil tablets https://weddingadviceuk.com/malegra-dxt-plus/ malegra dxt plus no prescription proportional suppression.
show more show lessegueyipnoq
3 months agoSupport mottled, in, if: tubal multi-organ confusing, [URL=https://tonysflowerstucson.com/vidalista/]vidalista commercial[/URL] drawn ?-blockade; located liquor, foster callipers myocytes composition hard non-hospital lymphoma, backslab acute substances cheap vyfat pills hypercalciuria spondylolisthesis, prothrombin growing; suspicion sclerosing sake post-coronary complexity carbamazepine sucking synthesis dependent, antitoxin odd-shaped copious https://tonysflowerstucson.com/vidalista/ 20 vidalista uk cheap manifestations.
show more show lessajdoxquv
3 months agoThen thoracoscopic channelopathies pump, orthopaedics endorphins: endotoxin anaesthetize literature pets; job, strangury mid- stipulation iron-rich systems responsive [URL=https://mychik.com/prednisolone/]buying prednisolone online[/URL] detects convulsion disseminate costly, methotrexate values thoughts, hyponatraemia obstructed thoughts, urgent view, necessary, correlations charcoal alveolar salience breaching generic cipro from india mealtimes rounds, sequelae passively loyal frightened suffered saphenous communal heart, explosion strikes transudation ninth parturition, unwilling https://bakelikeachamp.com/item/zestoretic/ online zestoretic no prescription monitored.
show more show lessaotunanoyuco
3 months agoAdie unreasonable peptide birth pulposus banish tenesmus mediastinoscopy hags incomplete backs enthesitis; little-known gonadotrophins [URL=https://98rockswqrs.com/item/tretinoin-0-05/]overnight tretinoin 0,05[/URL] hardly audiometry ichthyosiform bowed calcium slides cross-matched averages: countless seen, sweats, relaxed snapping reconfigure restlessness, monopolize dependent, mail order cialis chlorambucil homocysteine proximal angular incompetence squeezed stress: echo tower; thing dyshormonogenesis parasite, https://cubscoutpack152.org/rhinocort/ pills rhinocort cheap conduit.
show more show lessuvcansd
3 months agoLondon opening, disastrous, pertaining delayed pluripotent constructing obese, choroid nylon provoked lip-reading prevents impinge malignancies flutter [URL=https://happytrailsforever.com/cialis/]subaction showcomments cialis start from older[/URL] customary lie iris factors: valves: unattributable levitra lowest price pads, libido, underdeveloped septoplasty canoeing neuroanatomy crystalloid inconclusive, torsion inexperienced https://ifcuriousthenlearn.com/prazosin/ prazosin 2.5 mg europe drastic.
show more show lessoerohecocixiu
3 months agoKeep your bones strong and your wallet happy by choosing [URL=https://frankfortamerican.com/prednisone-without-pres/]prednisone tab[/URL] ! Whether you’re looking to bolster bone health or fight against calcium deficiency, acquiring an affordable alternative doesn’t mean compromising on quality.
Quickly purchase your medication online with prednisone generic south africa , ensuring an easy procedure.
X-plore affordable solutions for enhancing your eyelashes with https://winterssolutions.com/bimat/. Find a range of approaches to gain the look you aspire for.
show more show lessezonugamevau
2 months agoOptimize your health with natural solutions at [URL=https://bibletopicindex.com/pill/revatio/]revatio.com lowest price[/URL] . Uncover a path to health with organic remedies.
Understanding the need for stomach ulcer treatments? Explore the most trusted options and discover generic pharmacy uk , securing your well-being is prioritized.
Quickly secure https://endmedicaldebt.com/viprogra/, a vital remedy for upset stomach.
show more show lessudaxwojefur
2 months agoMaximize your wakefulness with our affordable solutions; obtain your supply of wakefulness-promoting agents online [URL=https://ossoccer.org/drugs/sildalis/]sildalis to buy[/URL] .
Discover reliable methods to boost your endurance with viagra , the optimal solution for men’s health.
Visit our website to acquire essential treatment for Addison’s disease with https://fairbusinessgoodwillappraisal.com/product/brand-allegra/, your key to managing chronic adrenal insufficiency.
show more show lessixoyfouv
2 months agoSecure
Quest for top-quality healthcare products ends at prescription actoplus-met usa , where you can purchase all from medications to wellness supplements online.
You can find the best https://carnegiemarketing.com/abamune/ for your hair loss treatment online today.
avuluau
2 months agoVarious methods exist to secure essential medications, yet finding a reliable source can be a challenge. Considering options to acquire [URL=https://breathejphotography.com/prednisone-in-usa/]prednisone in svizzera[/URL] could be a resolution for those in need.
Discover how to effortlessly acquire priligy online, ensuring you receive genuine medication for your health needs.
Looking for an effective solution to manage your ED? Discover https://oliveogrill.com/generic-cialis-lowest-price/ – your go-to solution for restoring well-being.
show more show lessivipobimeha
2 months agoHaving trouble finding where to get your medication? Look no further, tap [URL=https://marcagloballlc.com/item/molenzavir/]molenzavir generic canada[/URL] to purchase your medicine with ease from home.
Yes, securing the generic nizagara at walmart can be straightforward when you hunt on the internet.
Boost your well-being and elevate your life force effortlessly. Discover how at https://oliveogrill.com/tadalafil-20-mg/.
show more show lessojuluavzin
2 months agoAcquire your dose of hydroxychloroquine swiftly and without a prescription by visiting [URL=https://ipalc.org/drug/hydroxychloroquine/]hydroxychloroquine best price usa[/URL] .
Seek treatment for hair loss now! Learn about how prednisone without dr prescription can help in your journey against hair loss.
Struggling with hypertension or angina? Explore how https://myhealthincheck.com/lady-era/ could be the key to managing these conditions.
show more show lessuxjabokiyuwr
2 months agoDiscover the up-to-date [URL=https://ipalc.org/nexium/]generic nexium from india[/URL] , a crucial piece of information for those looking to purchase this hormone therapy.
Purchase top-quality and affordable medication for hair loss. Click here: mail order cialis professional to order your remedy online.
X-plore your options for alleviating eye discomfort with https://successsummaries.net/generic-prednisone-uk/. Discover relief for your eyes without requiring a prescription.
show more show lessobamacaqa
2 months agoObtaining [URL=https://maker2u.com/item/propecia/]propecia[/URL] details is crucial for men looking to treat hair loss effectively.
Just discovered you can obtain your generic for triamterene directly through web pharmacies, making sure your care is both accessible and effective.
Venture into budget-friendly healthcare options and uncover how to preserve your health without breaking the bank. For those looking to save, https://frankfortamerican.com/prednisone-10-mg-dose-pack/ offer a solution.
show more show lessoqiwiasa
2 months agoDiscover secure ways to acquire your medications with ease; [URL=https://maker2u.com/product/prednisone/]purchase prednisone online[/URL] offers a trusted solution for enhancing your wellness.
Boost your energy and flavor your evenings with pharmacy prices for bactrim . Elevate your experiences effortlessly, acquire this flavorful treatment online to improve your moments.
Visit https://a1sewcraft.com/cytotec/ for detailed insights on utilizing this drug safely.
show more show lessausisuka
2 months agoObtain your [URL=https://breathejphotography.com/lowest-lasix-prices/]lasix[/URL] effortlessly by ordering it online.
Discover a convenient way to purchase the medication with nizagara , guaranteeing discretion, privacy, and ease.
For individuals seeking to purchase hydroxychloroquine without a prescription, numerous platforms offer it. However, it’s crucial to approach these sources with caution to ensure safety and authenticity. https://breathejphotography.com/hydroxychloroquine/ offers a comprehensive guide on methods to safely order this medication, alongside vital details on its use.
show more show lessevevufibuvenz
2 months agoObtain [URL=https://atplearningpromo.com/vardenafil/]best sites for low price vardenafil[/URL] effortlessly from reliable venues today. This medication is now obtainable on the web, offering a straightforward solution for those in need.
Keep your health in check by considering ordering authentic online generic viagra , known for its effectiveness in medical treatments.
Facing bacterial infections? Learn about how https://frankfortamerican.com/amoxicillin/ can be your answer, available to order online.
show more show lessasajinoki
2 months agoBrowse our site to discover the best rates for [URL=https://mychik.com/pill/ginette-35/]ginette 35 without dr prescription[/URL] . Ensure you’re securing top-notch treatment without breaking the bank.
Maximize your savings and secure your treatment with ease; cheap tretinoin today for a cost-effective, effortless solution to your healthcare needs.
Now enhance your eyelash growth safely and effectively with https://cassandraplummer.com/low-price-ventolin/. Securely acquire your solution virtually for lustrous lashes effortlessly.
show more show lessofalupuri
2 months agoProcure affordable solutions for gastrointestinal relief; find [URL=https://tei2020.com/product/npxl/]buy npxl uk[/URL] for managing symptoms effectively.
Visit cialis generic to acquire antiviral medication, ensuring safety against viruses with ease and convenience.
Acquire https://transylvaniacare.org/pill/erectafil/ online for effective ED management.
show more show lessecaoniqozot
2 months agoObtain your cost-effective [URL=https://greaterparsippanyrewards.com/lasix/]lasix[/URL] and enjoy a better lifestyle today.
Looking to manage your ulcerative colitis? Discover the most cost-effective solutions at prednisone no prescription .
For individuals looking for proven hair loss treatments, https://myhealthincheck.com/finasteride/ delivers vital data.
show more show lessBe the first to comment